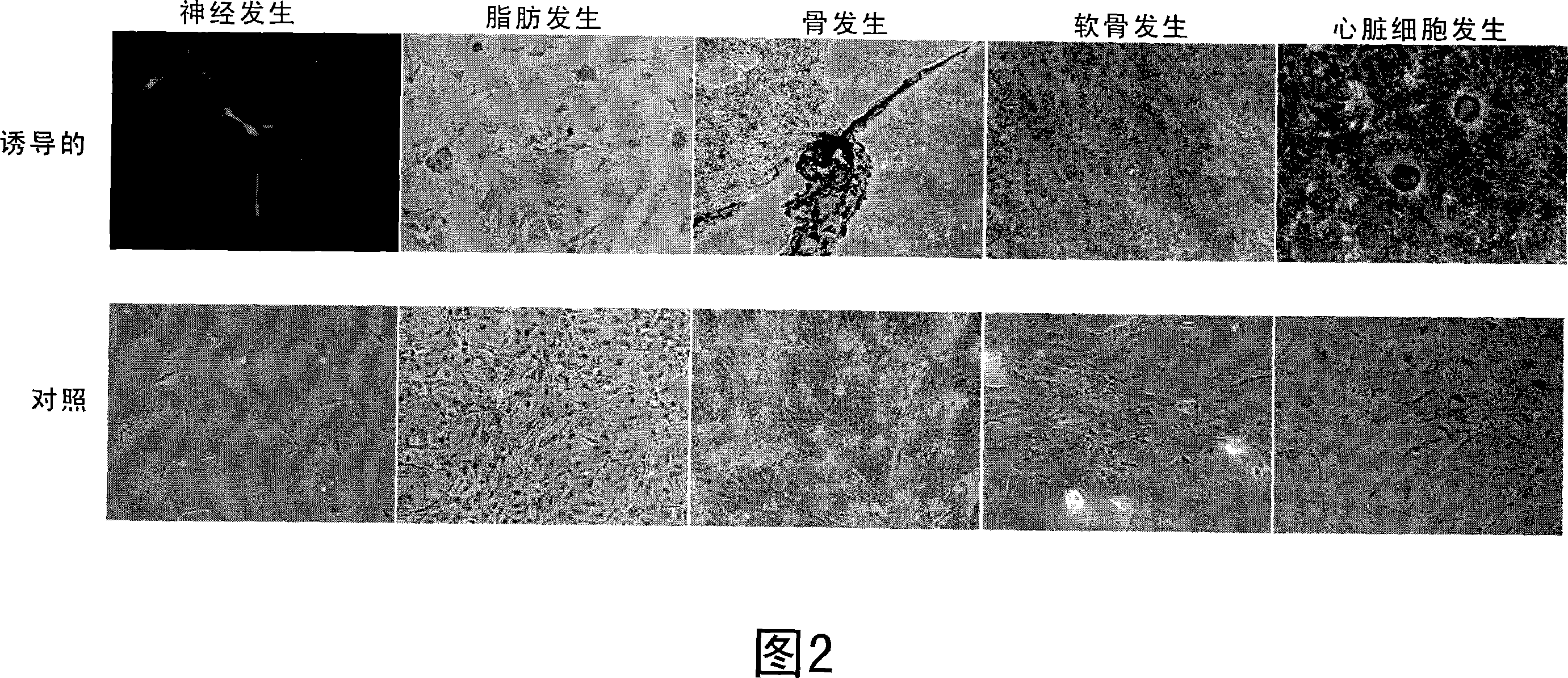
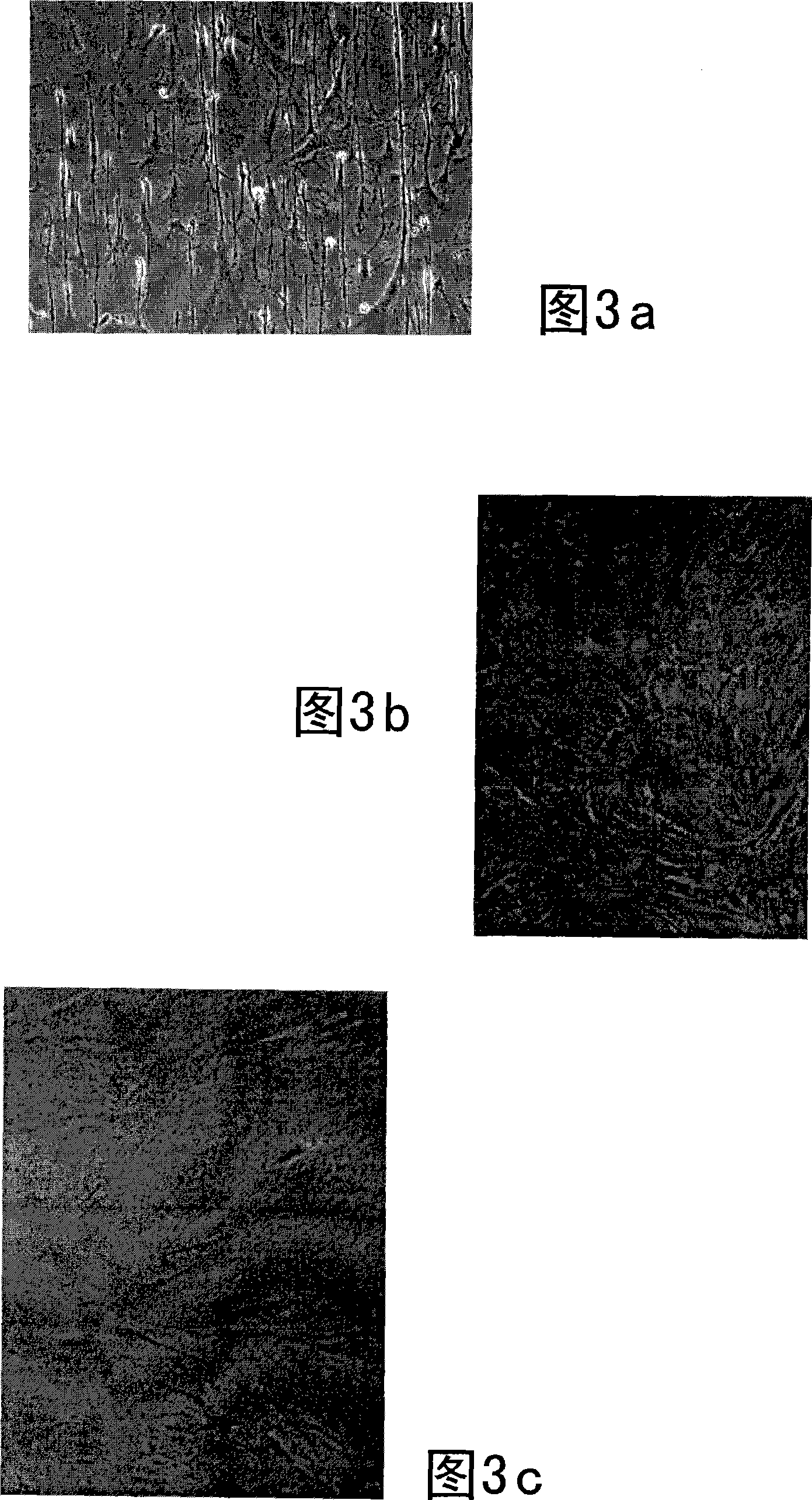
Therapeutic reprogramming, hybrid stem cells and maturation
A technology of stem cells and embryonic stem cells, applied in the direction of non-embryonic pluripotent stem cells, fusion cells, animal cells, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0121] Maturity-pre-embryo, embryo transfer
[0122] Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) obtained from 129 / SvJ strain mice were injected into C57BL / 6J blastocysts at 3.5 days post gestation. In the blastocyst is the inner cell mass niche that contains the epiblast for the establishment of the germ layers and ultimately all cells in the embryo. ESC cells recognize this niche and respond by being properly oriented to become embryonic bodies. After a brief culture period, blastocysts are transferred back to pseudopregnant female mice and allowed to develop to term. Maturation of ESC cells directed by the inner cell mass and cellular environment into distinct stem and support cells required at specific stages in embryogenesis and organogenesis. Chimeric mice were born with varying levels of chimerism depending on the ability of the ESC cells to respond to maturation factors present during embryogenesis and organogenesis. Some of the mice had very high ESC cell contributions and some ...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Maturation of embryonic stem cells in the developing embryo
[0125] In this example, embryonic stem cells mature in the developing bone marrow niche. Blood cell development, known as hematopoiesis, proceeds through discrete stages in specific tissues in the developing embryo, before converging in the bone marrow, where it continues throughout adulthood. In the developing embryo, hematopoietic stem cell precursors first develop in the yolk sac and a region known as the aorta-gonad-mesonephros (AGM). During embryogenesis and organogenesis, hematopoietic stem cell precursors migrate to the liver, then to the spleen, and finally colonize the bone marrow before birth. In this specific example, hematopoietic, mesenchymal stem cells and multipotent adult progenitor cells (MAPCs) are generated, which can be isolated from postnatal organisms.
[0126] Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) were obtained from 129 / SvJ strain mice and transfected with a fluorescent reporter gene (ie, GFP...
Embodiment 3
[0129] Therapeutic cloning and maturation
[0130] This example describes the preparation of human primordial sex cells (donor cells) that respond to maturation signals for therapeutic cloning. In some cases, donor cells require additional steps to prepare for maturation. The methods involved in making primordial sex cells (PSCs) from other mammals, including humans, are similar to those described herein, with some possible exceptions for modifications of media or chemicals specific to that particular species.
[0131] Oogonia were harvested after ovarian stimulation and matured in vitro in G1.2 medium (Vitro Life, Goteborg, Sweden). Oogonia with first polar bodies were selected for enucleation. Ca-free buffered in HEPES 2+ Enucleation was performed in amino acid-containing CR2 medium (hCR2aa supplemented with 10% FBS and 5 μg / mL cytochalasin B (Sigma)). The oogonia are held in place with a holding pipette and a fine needle is used to create small slits in the zona pellu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com