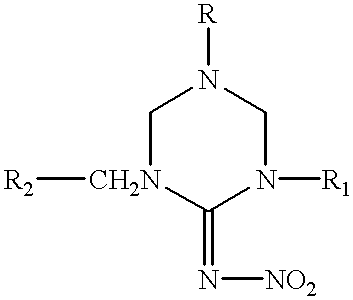
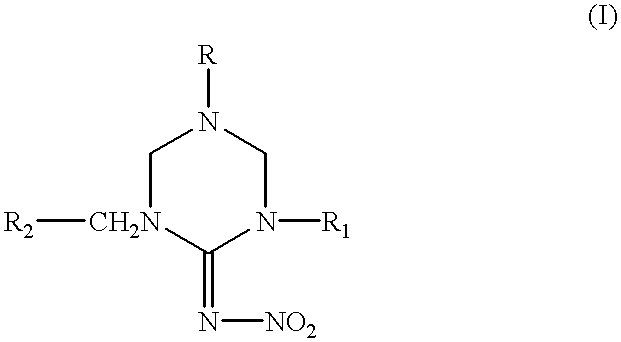
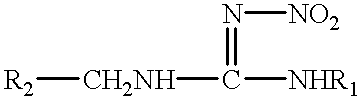Hexahydrotriazine compounds and insecticides
a technology of hexahydrotriazine and compounds, applied in the field of hexahydrotriazine compounds and insecticides, can solve the problems of not producing phytotoxicity and compound not producing phytotoxicity, and achieve the effects of effective control of harmful insects, low toxicity, and reduced amoun
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
synthesis example 1
Synthesis of 1-(2-chloro-5-pyridylmethyl)-5-methyl-2-nitroiminohexahydro-1-,3,5-triazine
[0035] 0.6 g of 1-(2-chloro-5-pyridylmethyl)-3-nitroguanidine and 0.4 g of bis(chloromethyl)methylamine were suspended in dried THF. To the suspension, a solution of 0.52 g of triethylamine in THF was added dropwise with cooling. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 hour, and then poured into ice water. The mixture was extracted with dichloromethane. After the extract was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, dichloromethane was distilled off. The residue was recrystallized from methanol to obtain 0.78 g of the title compound. This compound is No. 1 in Table 1. m.p.: 150-154.degree. C.
synthesis example 2
Synthesis of 1-(2-chloro-5-pyridylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-nitroiminohexahydro-1,-3,5-triazine
[0036] To a stirring mixture of 1 g of 1-(2-chloro-5-pyridylmethyl)-3-nitr-oguanidine, 0.28 g of 70% ethylamine in water and 20 ml of ethanol, 0.71 g of 37% formalin solution was added dropwise with heating. The reaction mixture was heated under reflux for two hours. After being allowed to cool to room temperature, the crystals formed, which were filtrated off and recrystallized from methanol to obtain 1.15 g of the title compound. This compound is No. 2 in Table 1. m.p.: 124-125.degree. C.
synthesis example 3
Synthesis of 1-(2-chloro-5-pyridylmethyl)-3,5-dimethyl-2-nitroiminohexahyd-ro-1,3,5-triazine
[0037] 1 g of 1,5-dimethyl-2-nitroiminohexahydro-1,3,5-triazine was dissolved in 20 ml of dried DMF. To the solution, 0.27 g of 60% sodium hydride was added with cooling. The mixture was stirred for 1 hour at room temperature until evolution of hydrogen was ceased and then the mixture was heated with stirring further for 1 hour at 50.degree. C. To the mixture, a solution of 0.9 g of 2-chloro-5-pyridylmethylchloride in 8 ml of dried DMF was added dropwise at 40-50.degree. C. After this addition, the reaction mixture was heated with stirring it for two hours at 70-80.degree. C. The mixture was poured into ice-water and extracted with dichloromethane. The extract was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and dichloromethane was distilled off. The residue was purified by a column chromatography to obtain 1.3 g of the title compound. This compound is No.5 in Table 1. m.p.: 116-117.degree. C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com