Non-contact type human iris recognition method for correcting a rotated iris image
a human iris and image correction technology, applied in the field of non-contact iris recognition methods, can solve the problems of inability to accurately detect the deformed or slanting eye image and many errors in the real application of the conventional iris recognition system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] In the following description, for purposes of explanation rather than limitation, specific details are set forth such as the particular architecture, interfaces, techniques, etc., in order to provide a thorough understanding of the present invention. For purposes of simplicity and clarity, detailed descriptions of well-known devices, circuits, and methods are omitted so as not to obscure the description of the present invention with unnecessary detail.
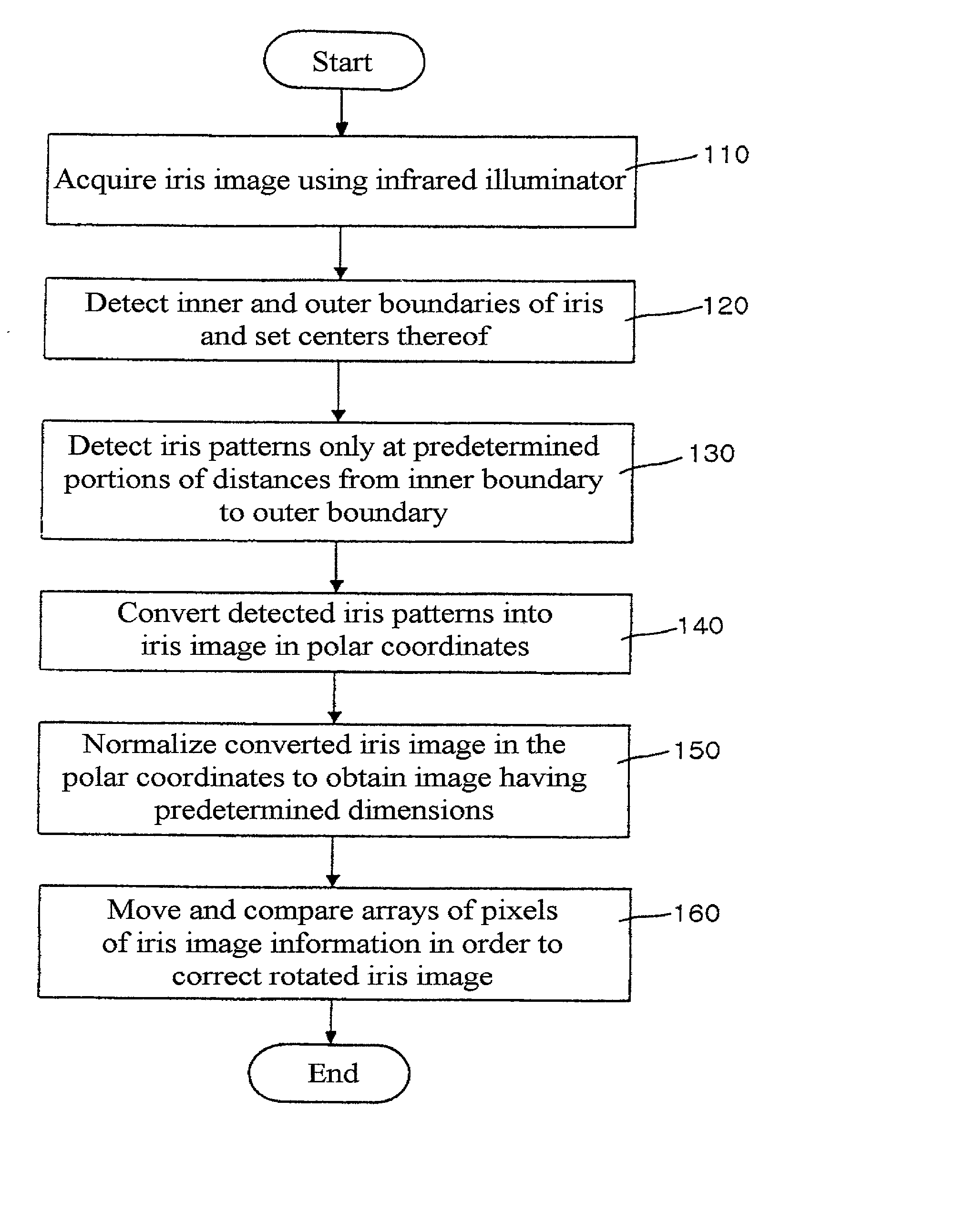
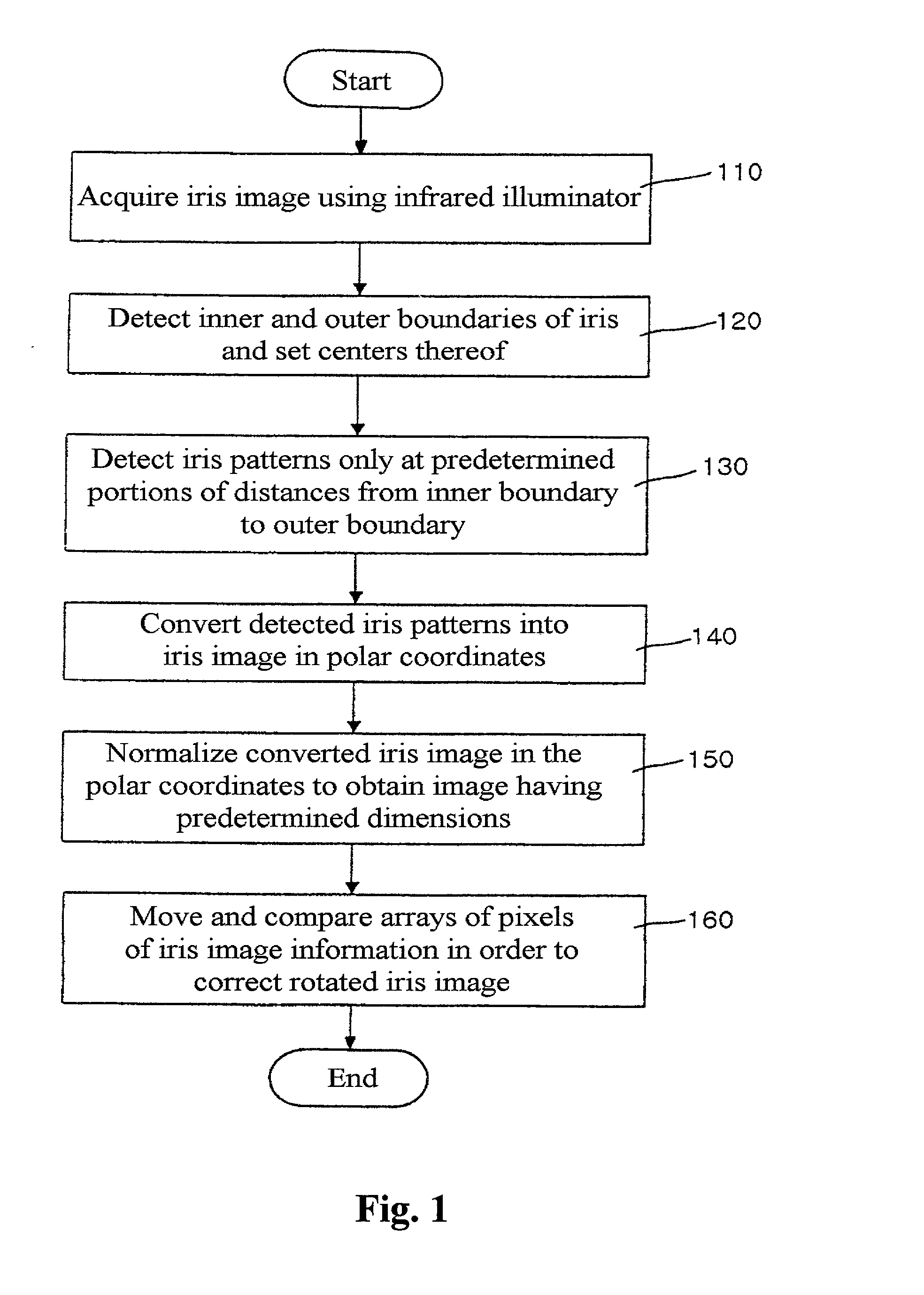
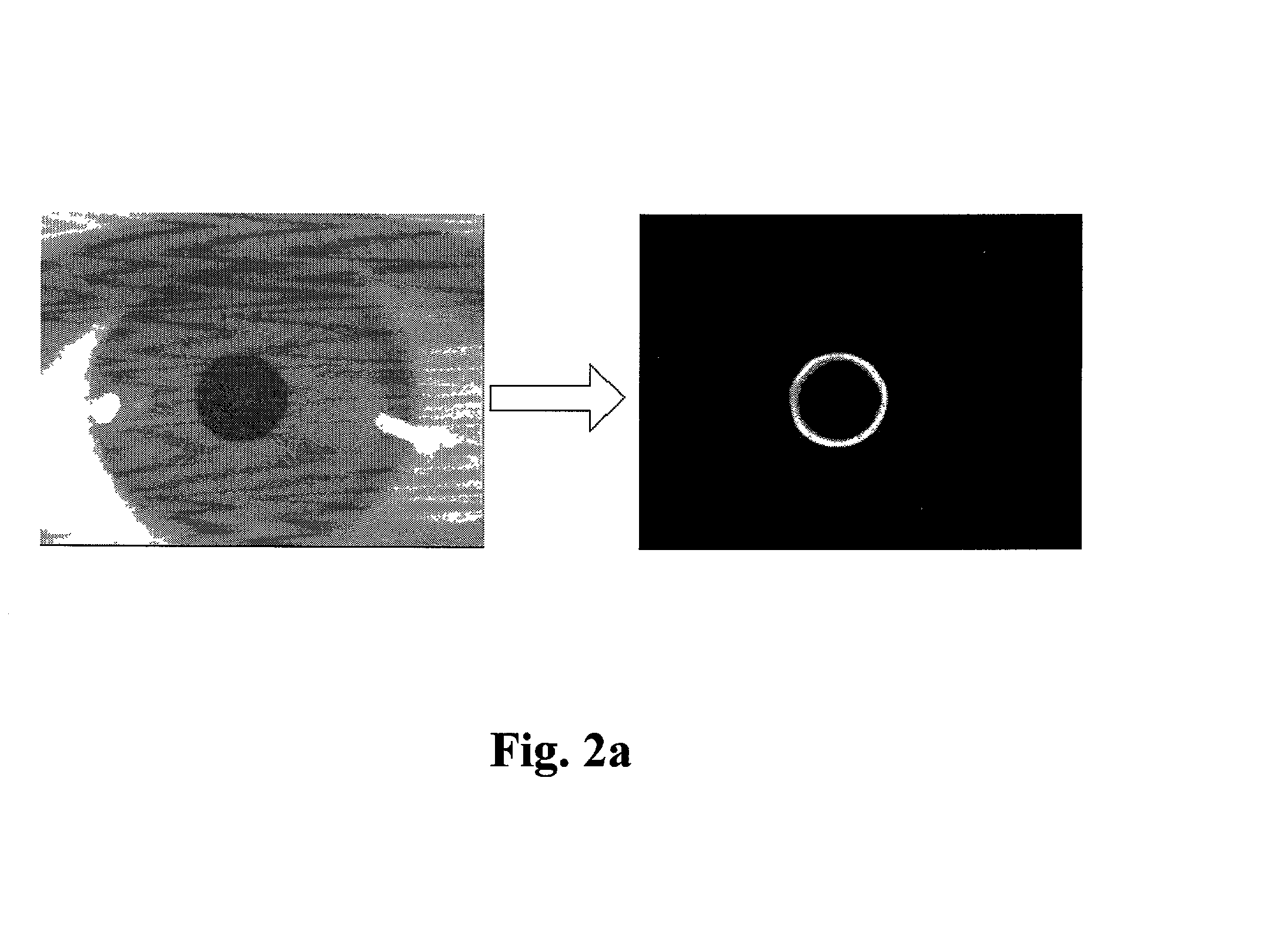
[0022] FIG. 1 is a flowchart illustrating the operation steps of normalizing the iris image of a person according to the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, in step 110, the eye image is acquired using any commercially available image acquisition device equipped with an infrared illuminator and a visible light rejection filter. The image acquisition device typically generates a reflective light to be gathered in the pupil of the eye region, so that information indicative of the iris image can be generated. In step 120, the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com