Thermal physical vapor deposition source using pellets of organic material for making OLED displays
a technology of physical vapor deposition and organic material, which is applied in the direction of vacuum evaporation coating, chemical vapor deposition coating, coating, etc., can solve the problems of non-uniform vapor flux of organic material to emanate along a length the width dimension of the slit is reduced, and the formation of an organic layer thereon that will have a non-uniform layer thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
The term “substrate” denotes at least a portion of an OLED display, which includes one or more layers onto which another organic layer is to be formed.
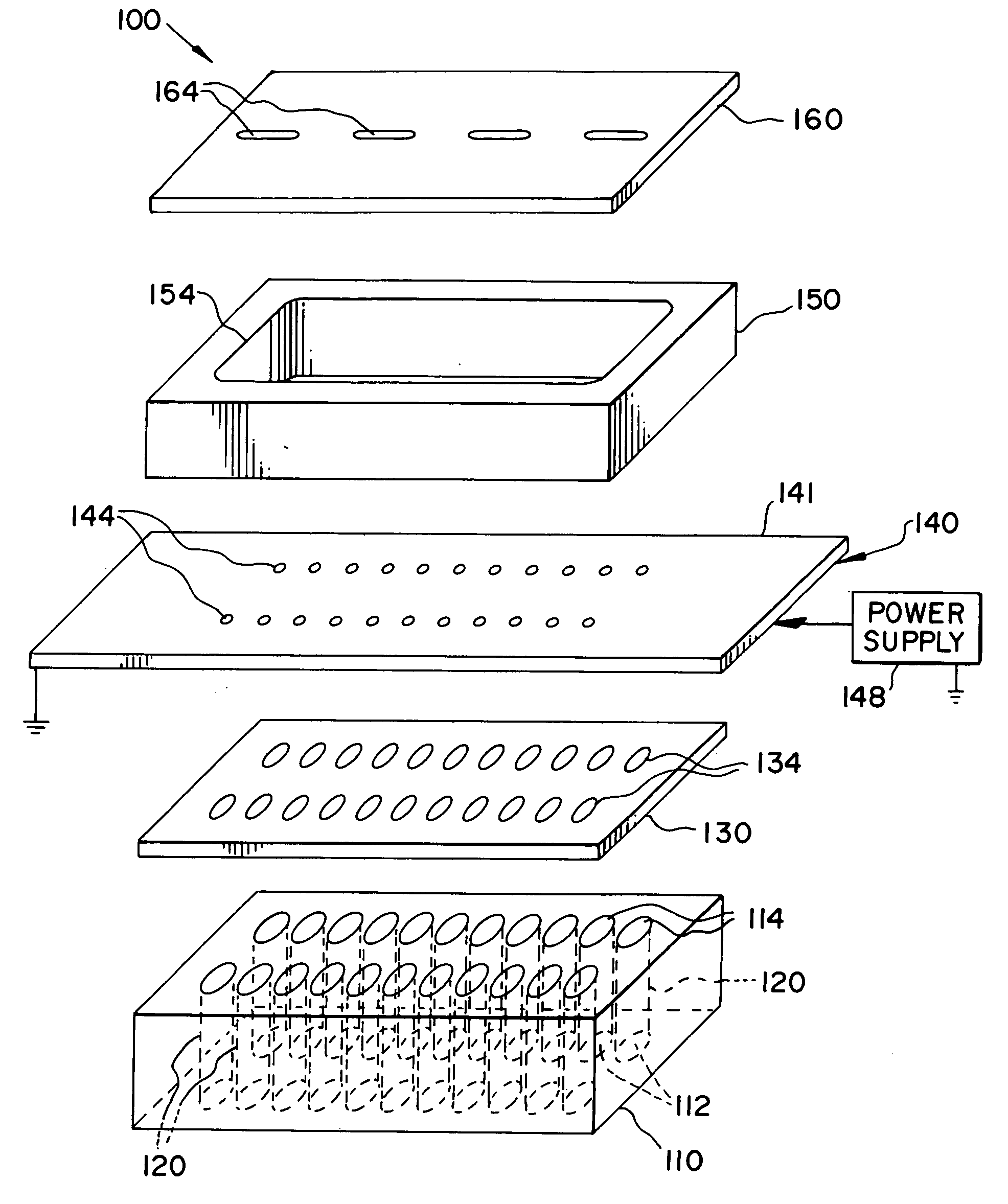
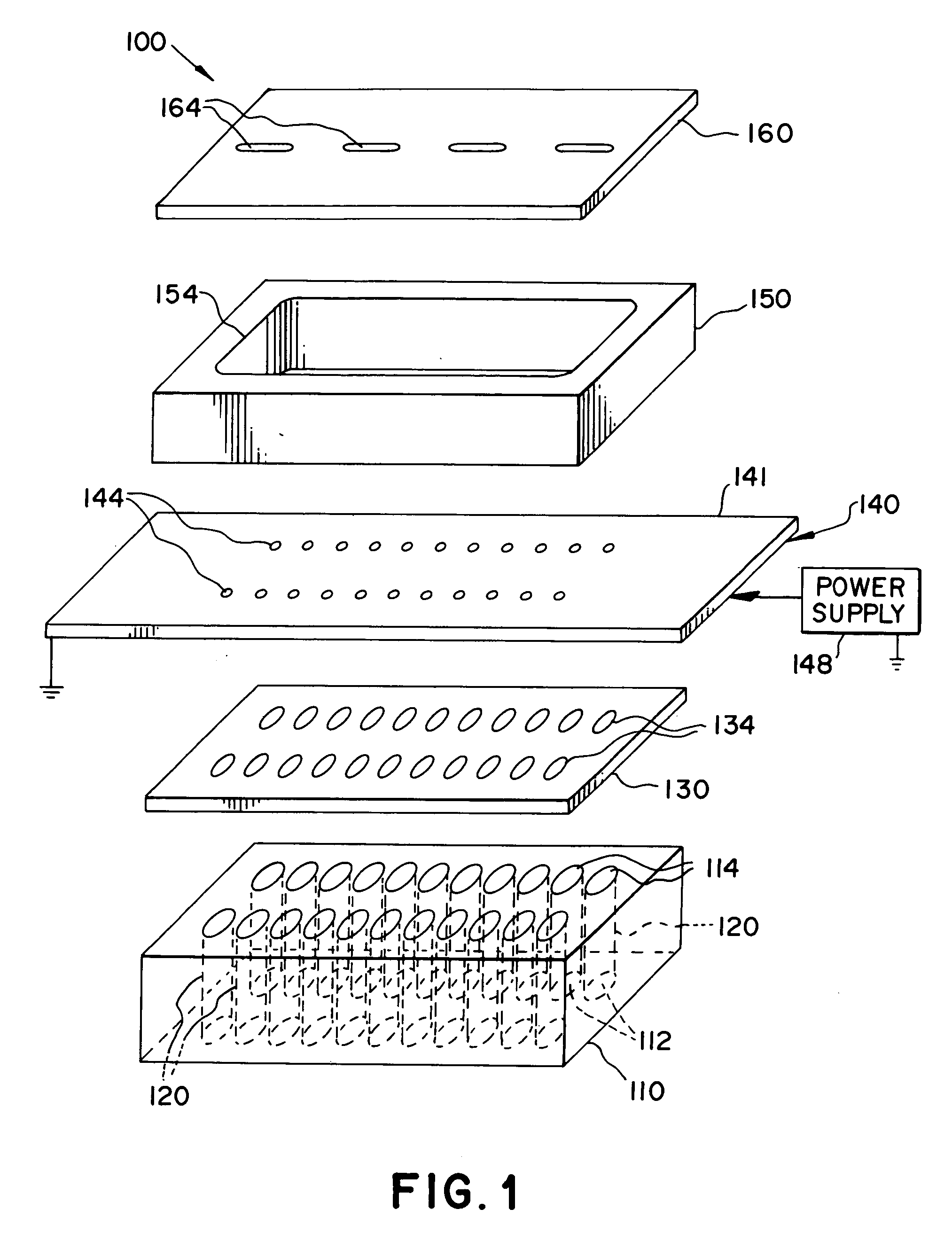
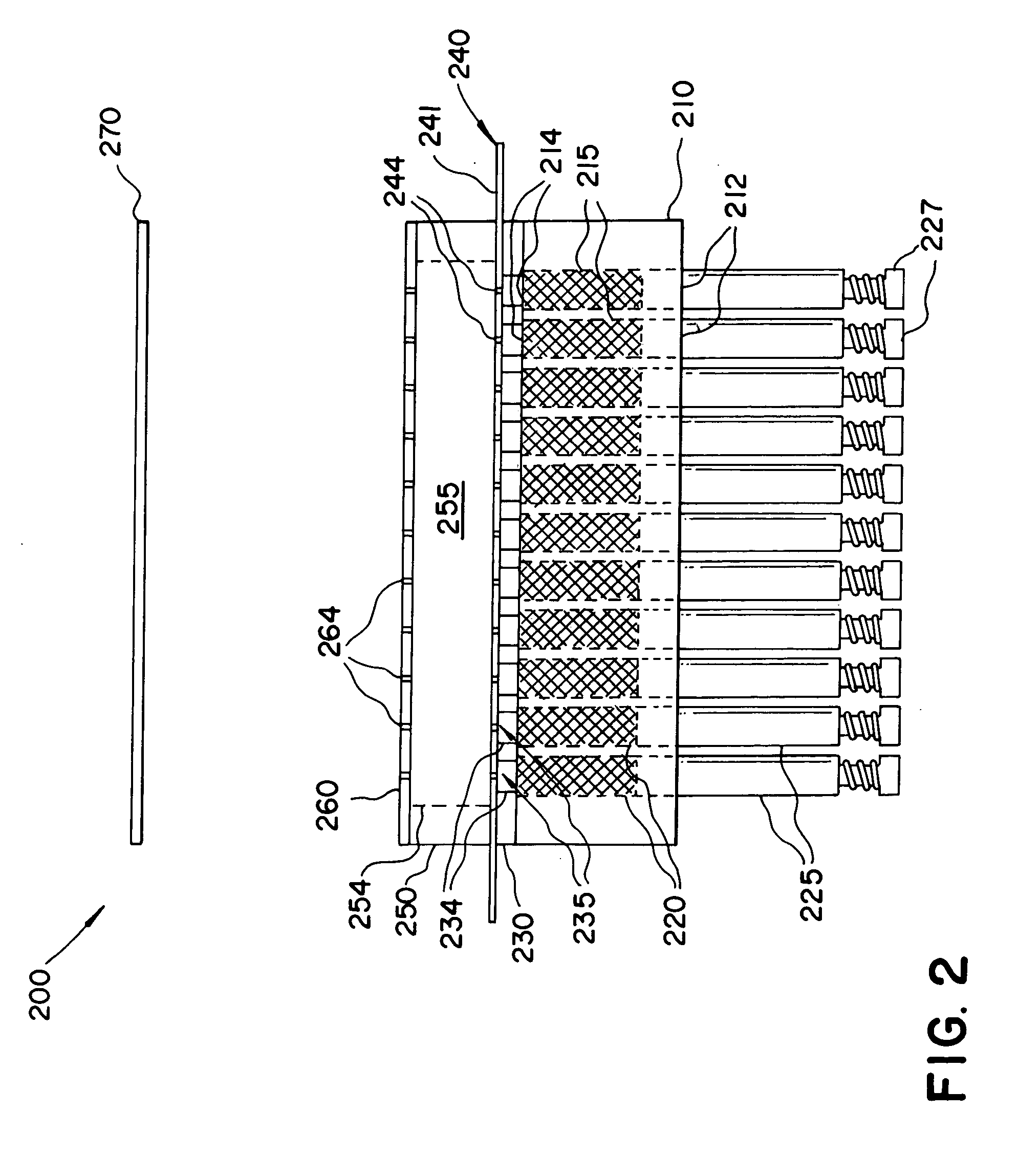
Turning to FIG. 1, a thermal physical deposition source 100 is illustrated, wherein a housing 110, defining a plurality of spaced passages 120, each spaced passage 120 having a closed first end 112 and an open second end 114 is shown. The spaced passages 120 can be of any shape and size and are fabricated such that compacted pellets 215 (see FIG. 2) of organic materials can be inserted through the open second end 114.
The housing 110 can be formed from thermally insulating materials such as high temperature glasses like quartz, alumino-boro-silicate glass and ceramics like alumina, zirconia, boron nitride, or magnesia. The purpose of using thermally insulating materials is to manage the thermal characteristics of the housing 110 when compacted pellets 215 used have more than one organic component, the details of which will be desc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com