Chemokines with amino-terminal modifications
a technology of amino-terminal modifications and chemokines, which is applied in the field of amino-terminal modification (nterminal modification) chemokines, can solve the problems of relative short biological half-lives of these proteins, and achieve the effect of decreasing the number of functional receptor molecules and decreasing the function of receptors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Expression and Purification of N-Terminal-Modified Chemokines
[0165] The amino acid sequences of the full-length human chemokines SDF-1α and SDF-1β (hSDF-1α and hSDF-1β, GeneSeq accession numbers R75419 and R75420) are provided as SEQ ID NO:s 1 and 2, respectively, and SEQ ID NO:s 3 and 4 are the nucleotide sequences of cDNA molecules encoding hSDF-1α and hSDF-1β (GeneSeq accession numbers Q74089 and Q74091). The amino acid sequences of the mature hSDF-1α and hSDF-1β proteins begin at amino acid 22 (lysine) in both SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with hSDF-1α or hSDF-1β cDNA as a template was used to make expression constructs encoding mature hSDF-1α and hSDF-1β proteins, or mature hSDF-1α and hSDF-1β proteins fused to the C-terminus of an expression / purification accessory sequence such as GroHEK (SEQ ID NO:5, AAKDVKHHHHHHGSGSDDDDK). Cloning NdeI / XbaI-restricted hSDF-1α, hSDF-1β, GroHEK / hSDF-1α, and GroHEK / hSDF-1β PCR products (generally referred to as t...
example 2
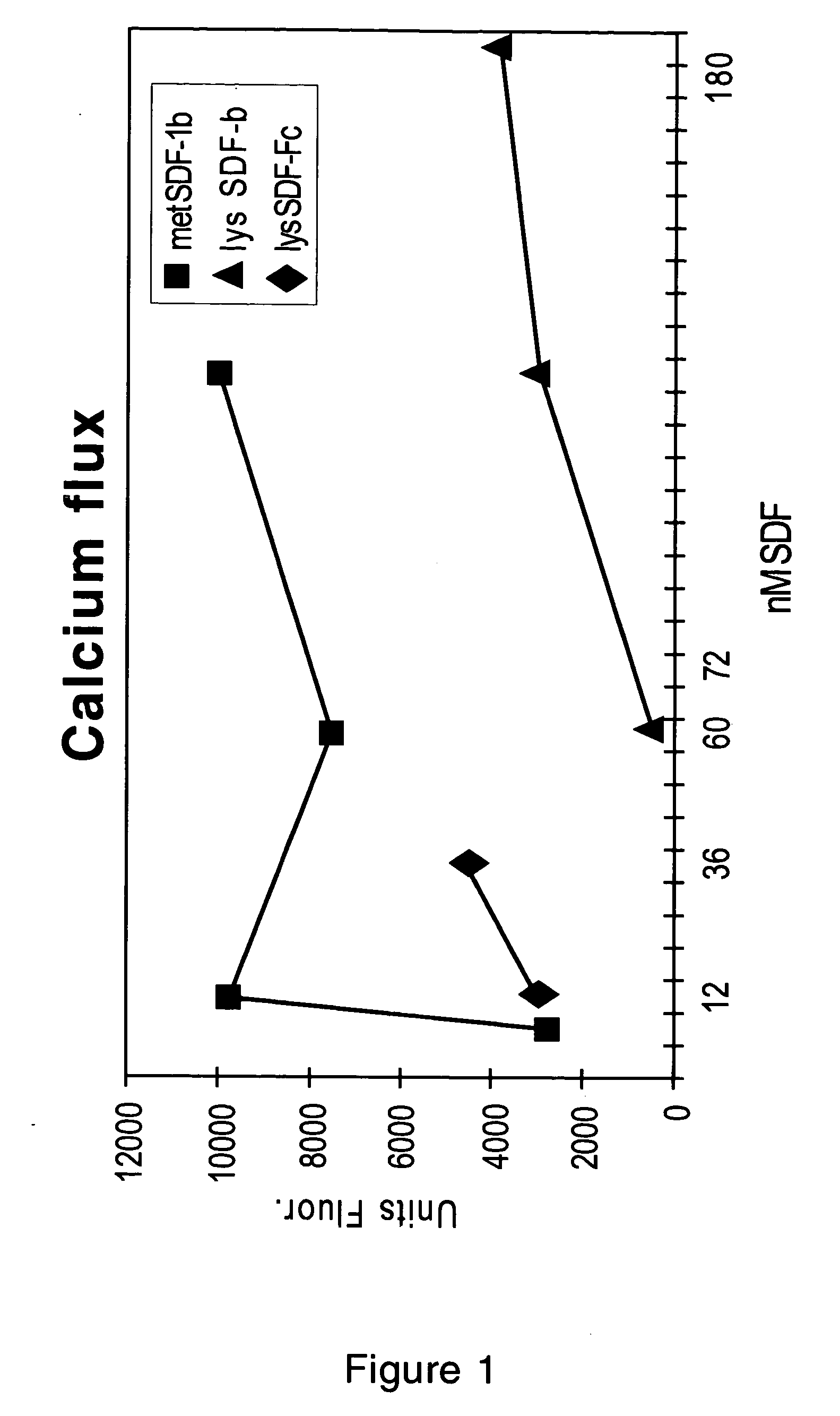
Stimulation of Calcium Flux by N-Terminal-Modified Chemokines
[0171] When chemokines bind to receptors present within the membranes of cells, a calcium flux may be induced. When N-terminal-modified chemokines bind to these receptors, the duration, intensity, or other properties of the calcium flux may be altered, or the calcium flux may be inhibited. The calcium fluxes induced by the binding of met-hSDF-1β, lys-hSDF-1β, and lys-hSDF-1α-Fc were measured using the following protocol, and the effects of the binding of mature chemokines (lys-) to chemokine receptors were compared to the effects of binding displayed by N-terminal-modified chemokines (met-). The lys-hSDF-1α-Fc protein (or “chemokine-Fc protein”) has the same chemokine N-terminus as a mature hSDF-1α or hSDF-1β protein, but this chemokine domain has been fused to the Fc domain of a human IgG4 molecule so that when expressed the Fc regions interact to form a dimer. This protocol can also be used to assay the calcium flux ind...
example 3
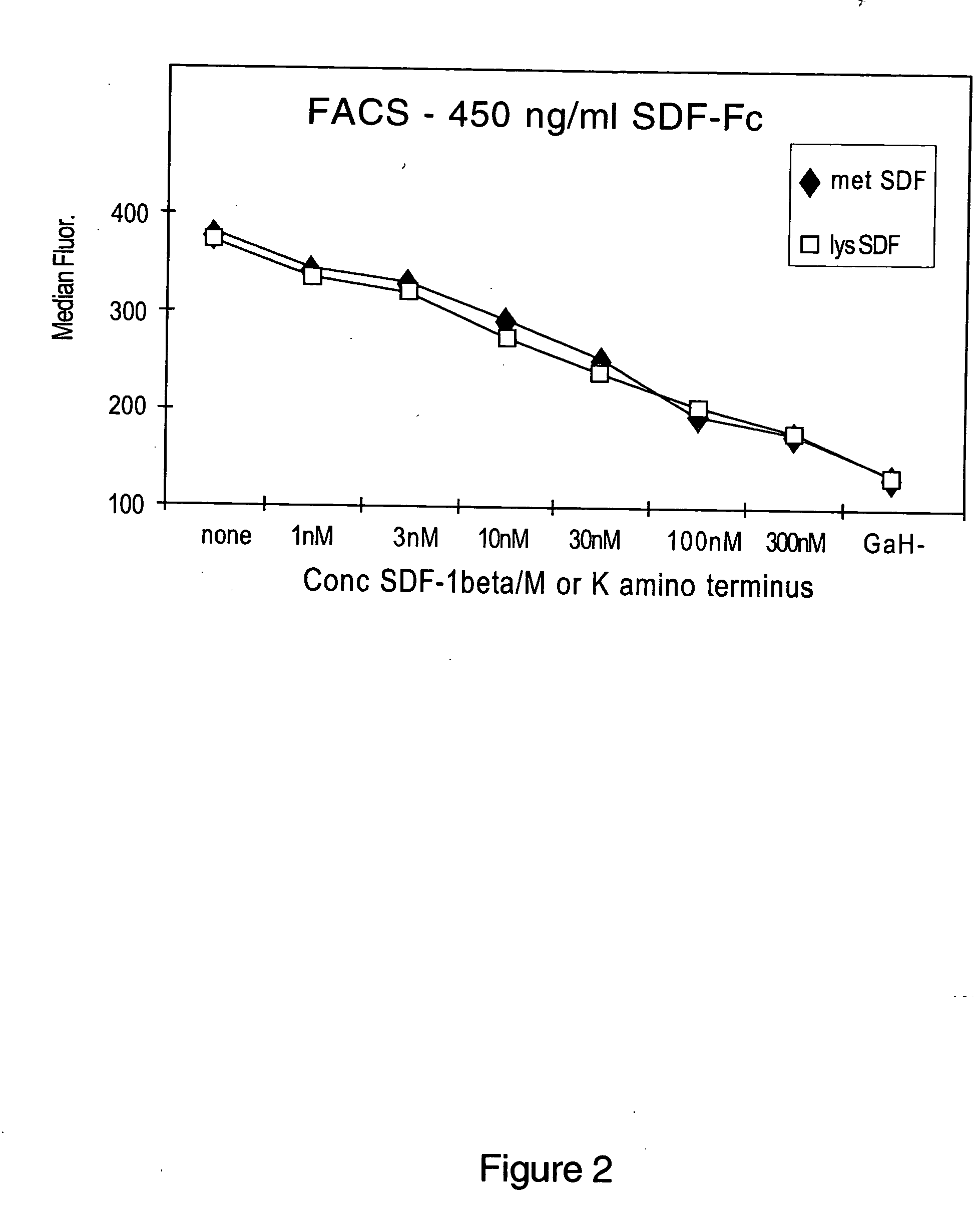
Stimulation or Inhibition of Chemotaxis by N-Terminal-Modified Chemokines
[0174] N-terminal-modified chemokines can be tested for their ability to stimulate or inhibit chemotaxis by any of the following assays for chemotactic activity. These assays (which will identify proteins that induce or prevent chemotaxis) measure the ability of a protein to induce the migration of cells across a membrane as well as the ability of a protein to induce the adhesion of one cell population to another cell population. Suitable assays for movement and adhesion include, without limitation, those described in: Current Protocols in Immunology, Ed. by J. E. Coligan, A. M. Kruisbeek, D. H. Margulies, E. M. Shevach, W. Strober, Pub. by Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience (Chapter 6.12, Measurement of alpha and beta Chemokines 6.12.1-6.12.28); Taub et al., J. Clin. Invest. 95:1370-1376, 1995; Lind et al., APMIS 103:140-146, 1995; Muller et al., Eur. J. Immunol. 25: 1744-1748; Gruber et al.,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pharmaceutically acceptable | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Immunogenicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap