Dither system for a quantizing device
a quantizing device and dithering technology, applied in the field of dithering systems for quantizing devices, can solve the problems of limited passage of high frequencies, and therefore high harmonics, and reduce the degree of harmonic distortion in adcs, so as to achieve easy conversion and reduce quantization noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
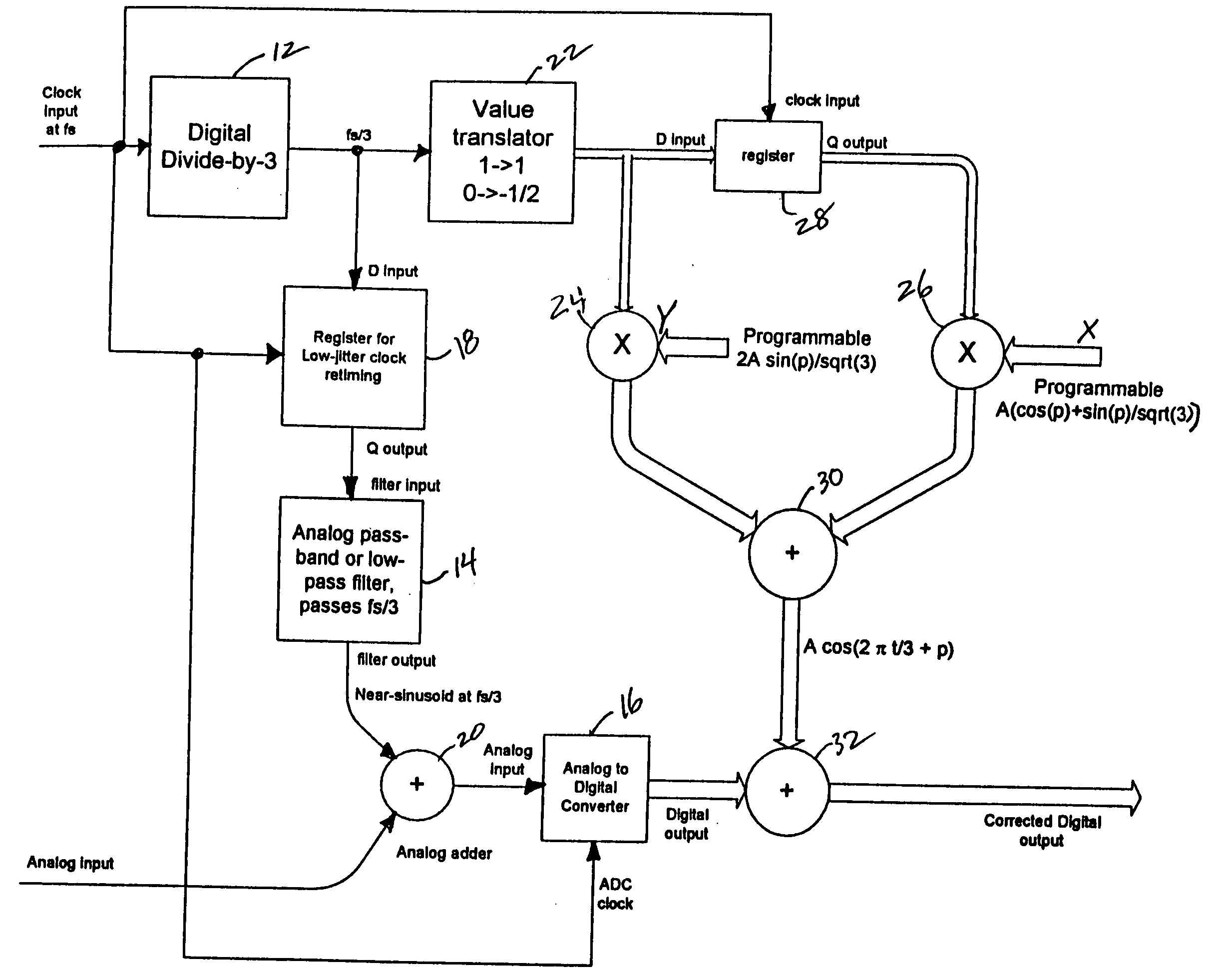
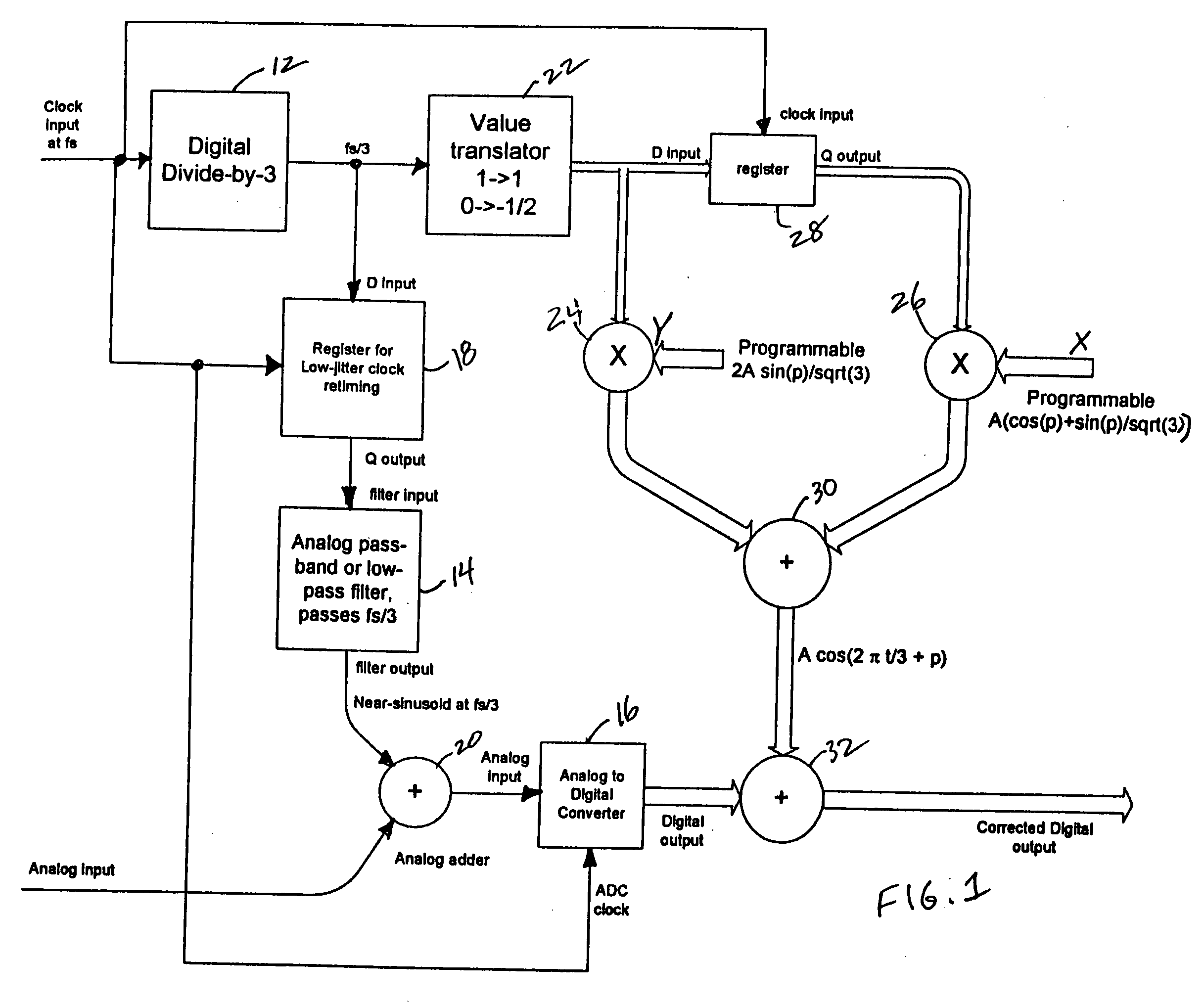
[0018] Referring now to FIG. 1, a clock signal having a sample frequency of fs is input to a divide-by-three circuit 12 to generate the following sequence:
W(t)=(1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, . . . )
or alternatively
W(t)=(1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, . . . )
or any other sequence having a repetition period of fs / 3 such that its harmonics are at (2fs / 3, 3fs / 3. 4fs / 3. 5fs / 3. 6fs / 3, . . . ). These frequencies alias to sampled frequencies (fs / 3, DC, fs / 3, fs / 3, DC, . . . ). A simple bandpass or lowpass analog filter 14 applied to the digital sequence removes DC and most of the harmonics prior to entry into a multi-stage ADC 16, although the filter performance is not critical as the non-DC harmonics all lie on fs / 3. More importantly the serial digital stream is re-clocked with a low-phase-noise, or low-jitter, register device 18, as noise on its output is being sampled by the ADC 16. The resulting output from the analog filter 14 is a near-sinusoid at fs / 3 which is input to an adder 20 t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com