Method and system for processing financial transactions
a financial transaction and system technology, applied in the field of financial transaction processing methods and systems, can solve the problems of not performing data mining in real-time and not performing all mpps, and achieve the effects of preventing possible fraudulent purchases, increasing the risk of fraud on-line transactions, and reducing the risk of fraud
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0060] A description of preferred embodiments of the invention follows.
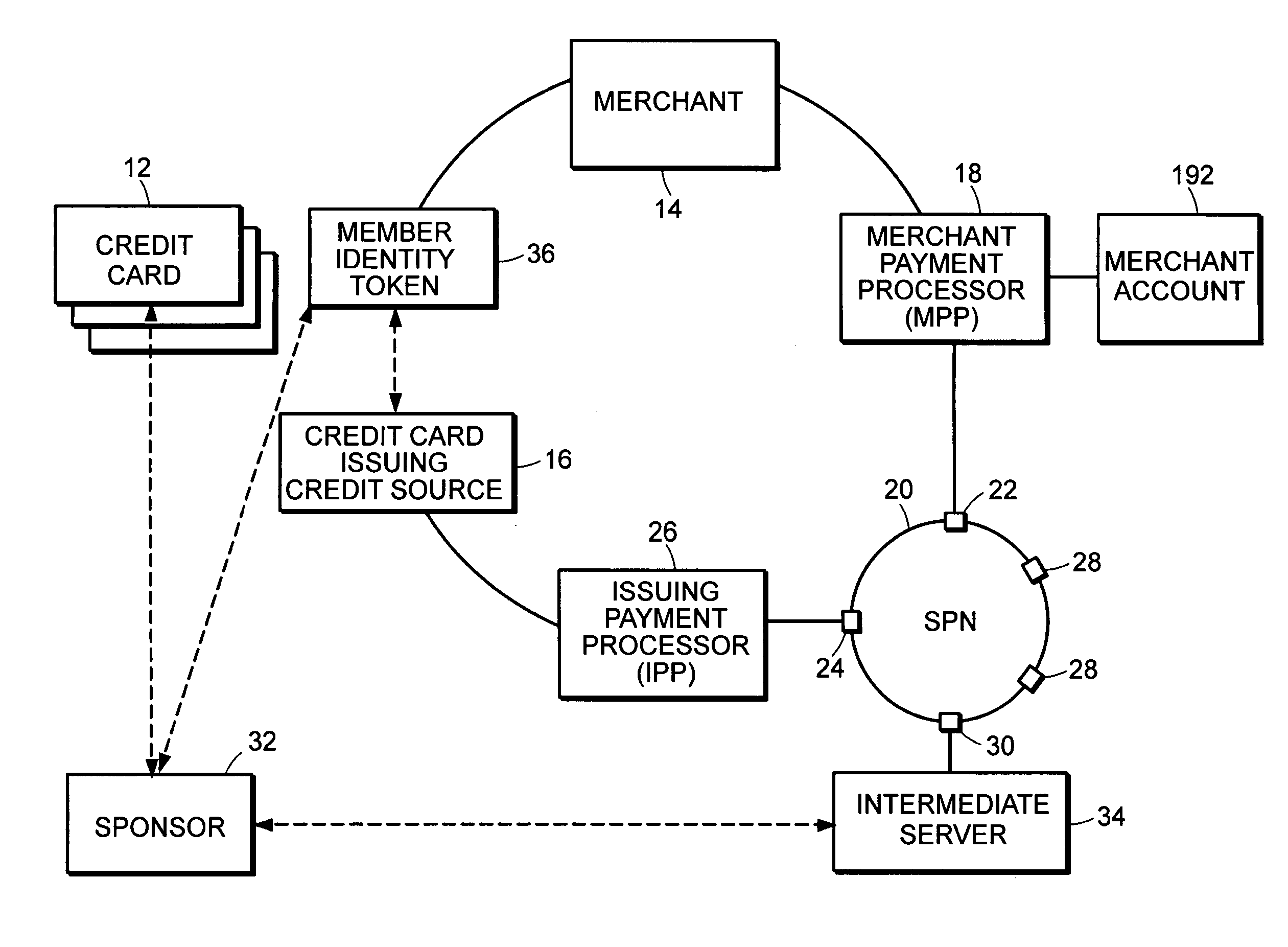
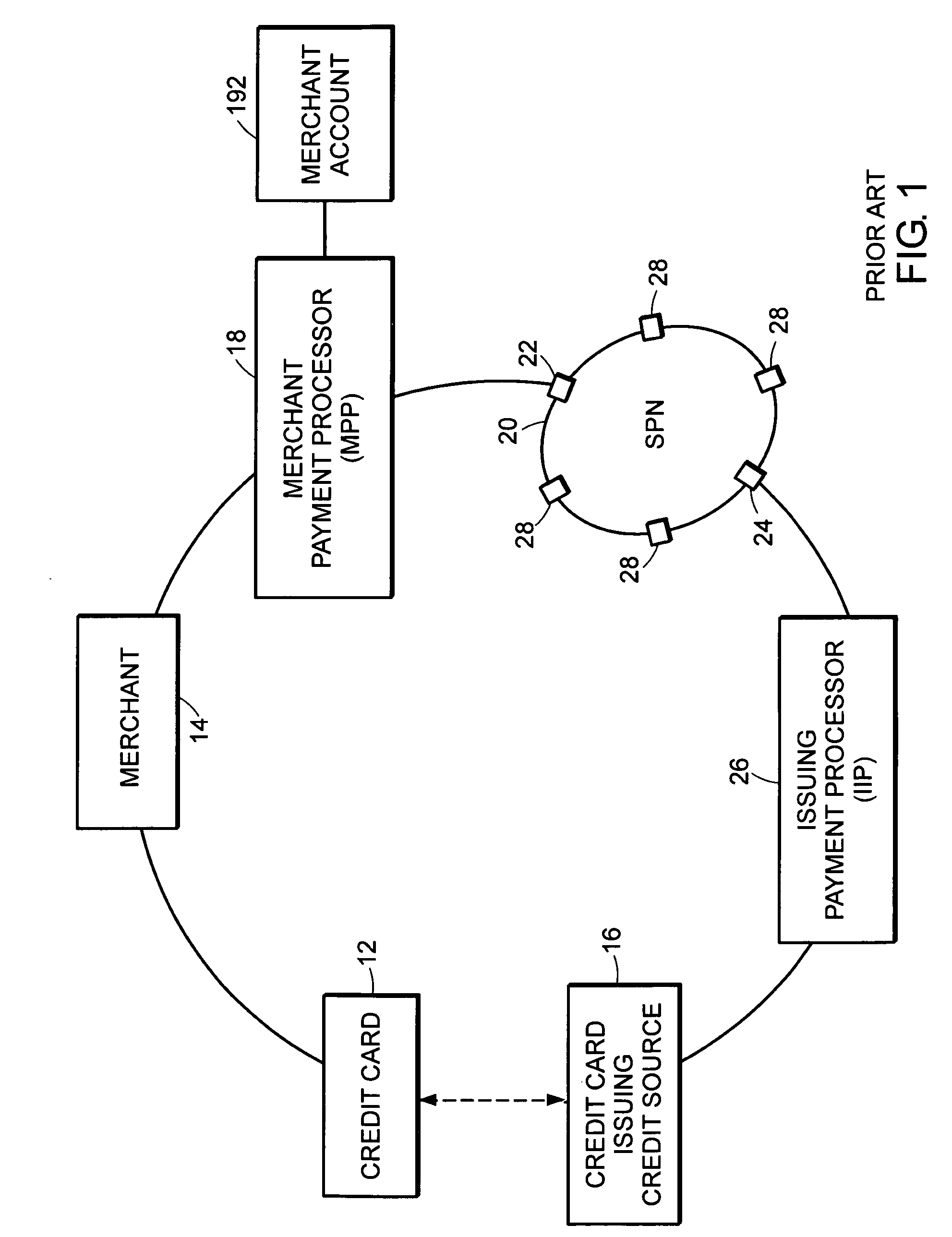
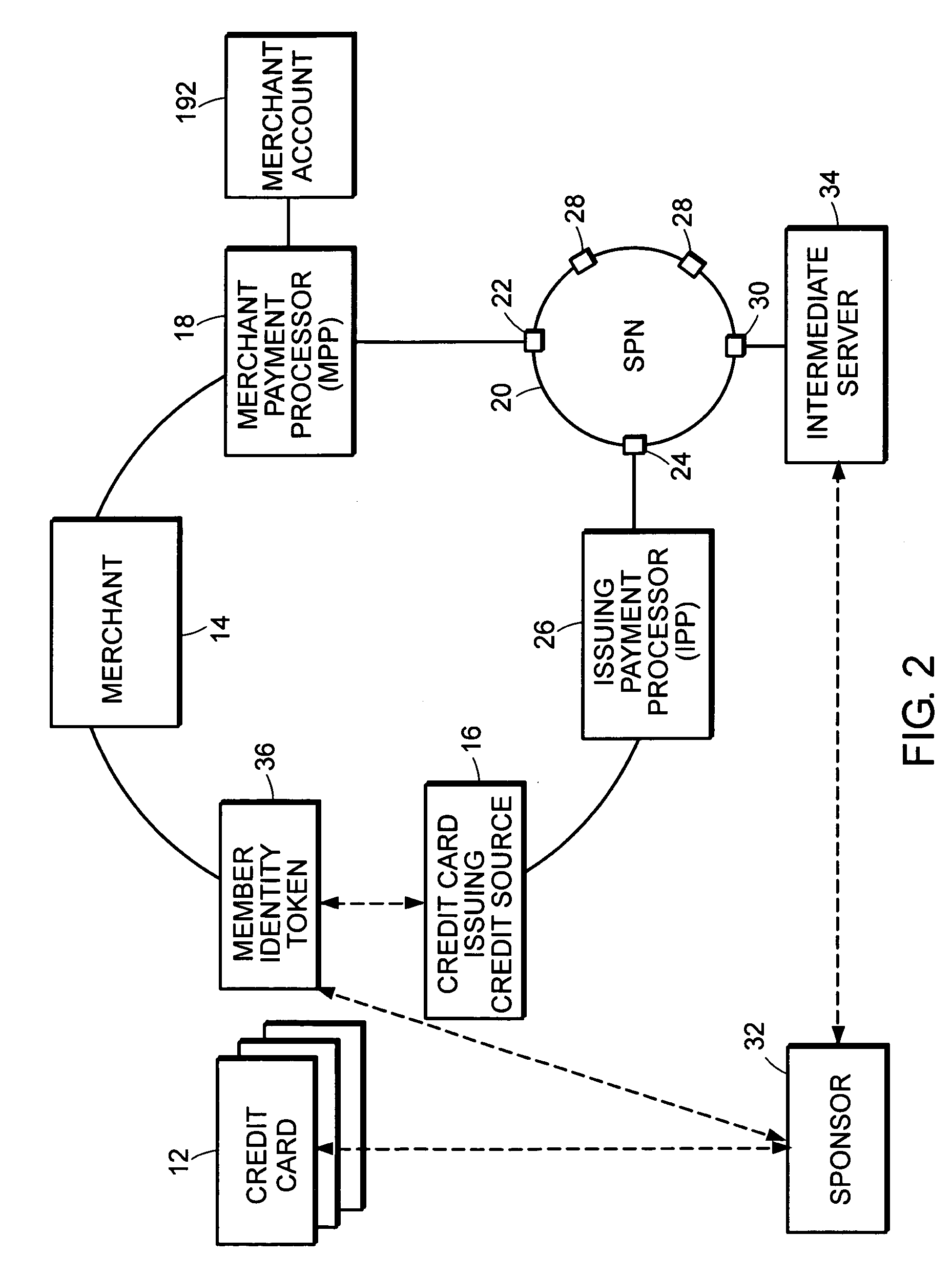
[0061] In one embodiment, the FIG. 2 financial transaction network includes network elements that are defined and function equivalently to the essential elements discussed in existing FIG. 1 network such as credit card 12, credit card issuing credit source 16, merchant 14, MPP 18 and associated access point 22, IPP 26 and associated access point 24, and merchant account 192. To provide enhanced financial transaction capabilities, intermediate server 34, associated access point 30, sponsor 32, and member identity token 36 are included in the financial transaction network of FIG. 2. An important aspect of the present invention is that the additional elements do not impact payment transactions that rely on the existing FIG. 1 financial transaction network architecture contained within the FIG. 2 financial transaction network architecture.
[0062] The FIG. 2 financial transaction network enables the purchase of goods...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com