Fault-tolerant magnetic bearing position sensing and control system
a technology of applied in the field of fault-tolerant magnetic bearing position sensing and control system, can solve the problems of inaccurate rotor position control, faulty position sensor, and inability to control bearing properties, such as magnetic field strength, during operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
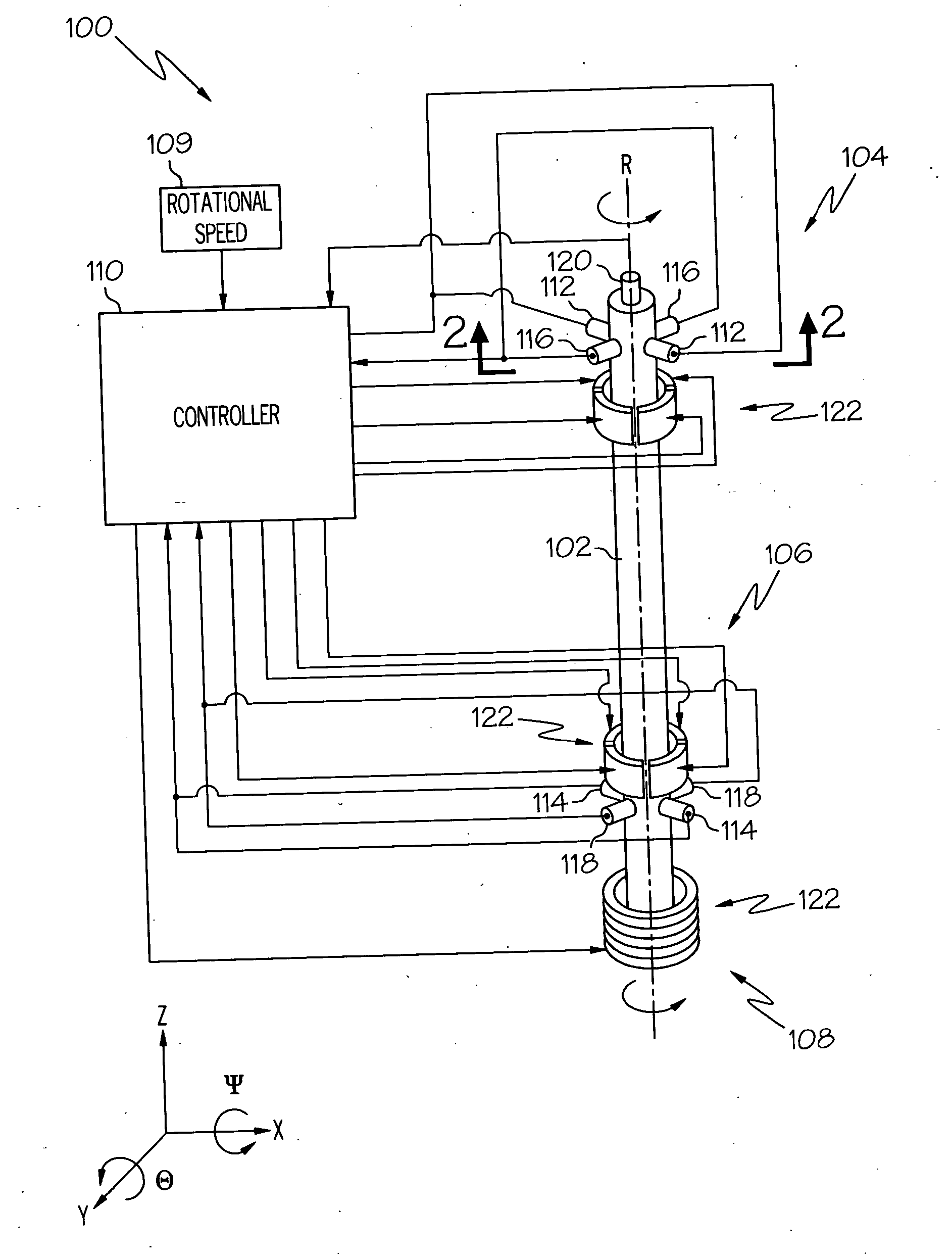
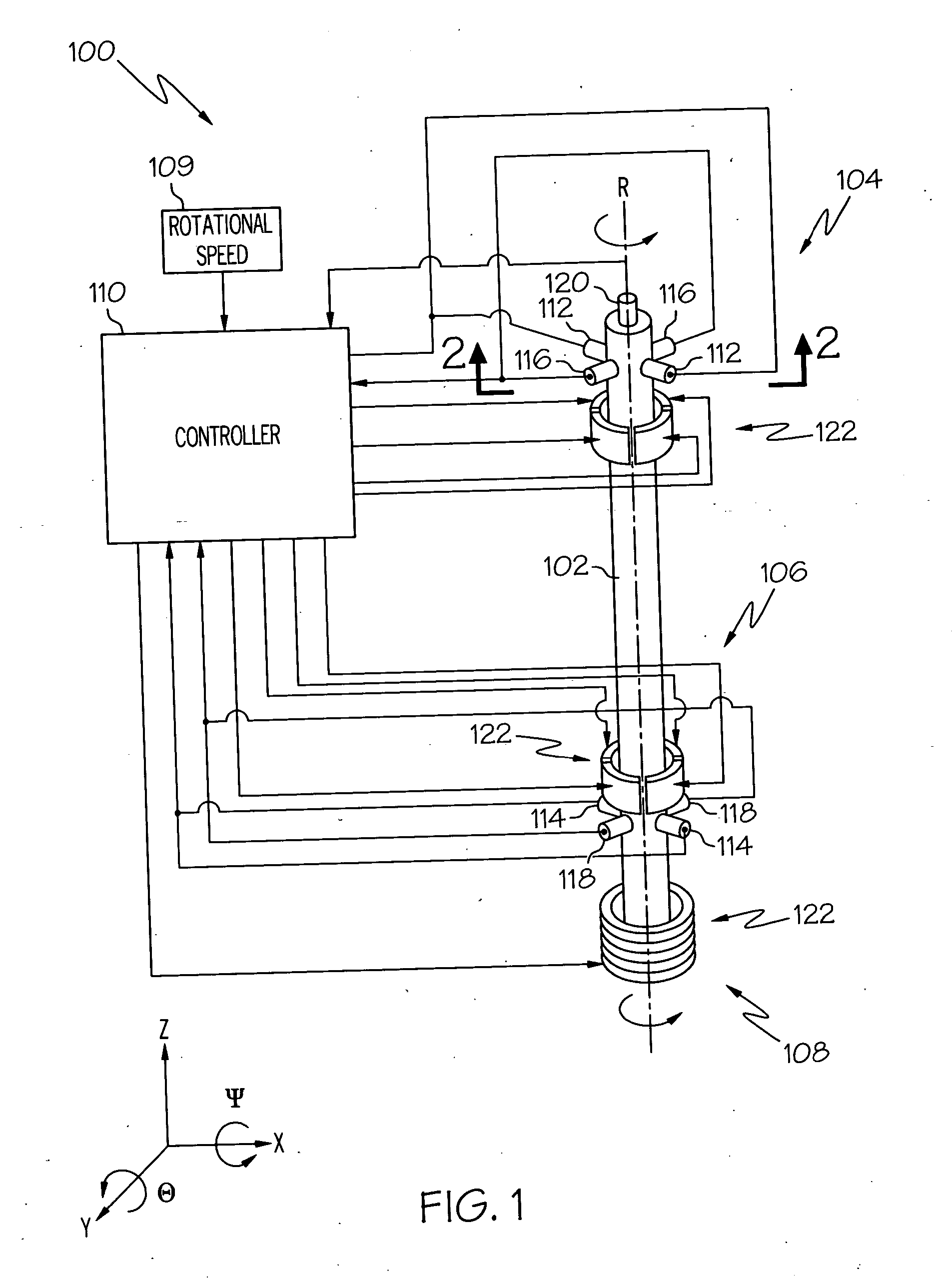
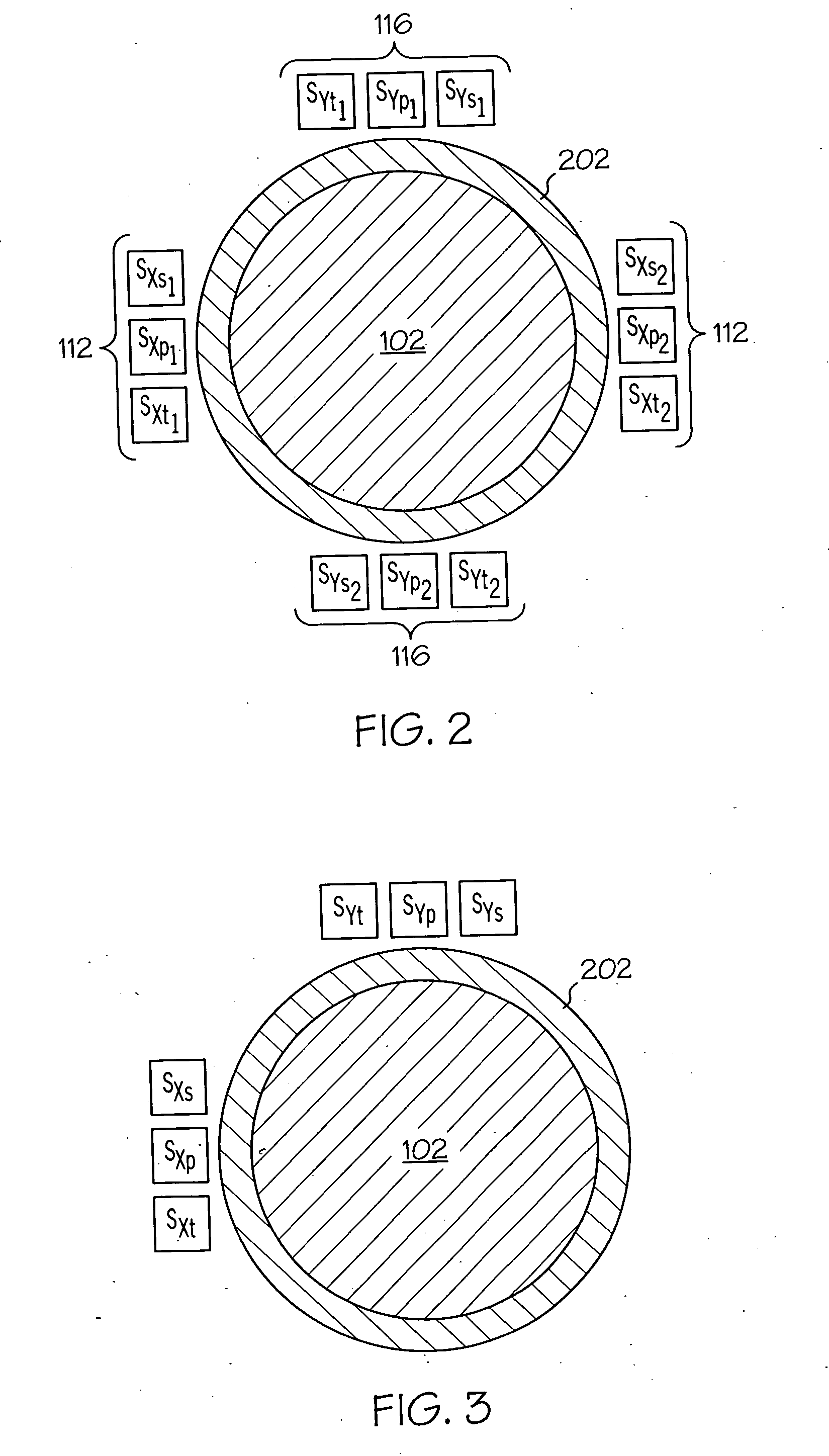
[0014] The following detailed description of the invention is merely exemplary in nature and is not intended to limit the invention or the application and uses of the invention. Furthermore, there is no intention to be bound by any theory presented in the preceding background of the invention or the following detailed description of the invention. In this regard, before proceeding with the detailed description, it is to be appreciated that the magnetic bearing system described herein is not limited to use with a particular configuration. Thus, although the magnetic bearing control system and method that is explicitly depicted and described is implemented using independent radial and axial bearing assemblies, it will be appreciated that other magnetic bearing configurations may also be used with the control system and method described herein. For example, the control system and method may also be used with a combination bearing configuration, or a conical bearing configuration.
[0015...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com