Interactive method and system for teaching decision making
a decision-making and decision-making technology, applied in the field of decision-making, can solve the problems of horrifying deterioration in the ethical conduct or character of people today, poor character, and all too often fail to see the corresponding responsibility that accompanies each and every choice, so as to increase student understanding, develop students' abilities, and expand student awareness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
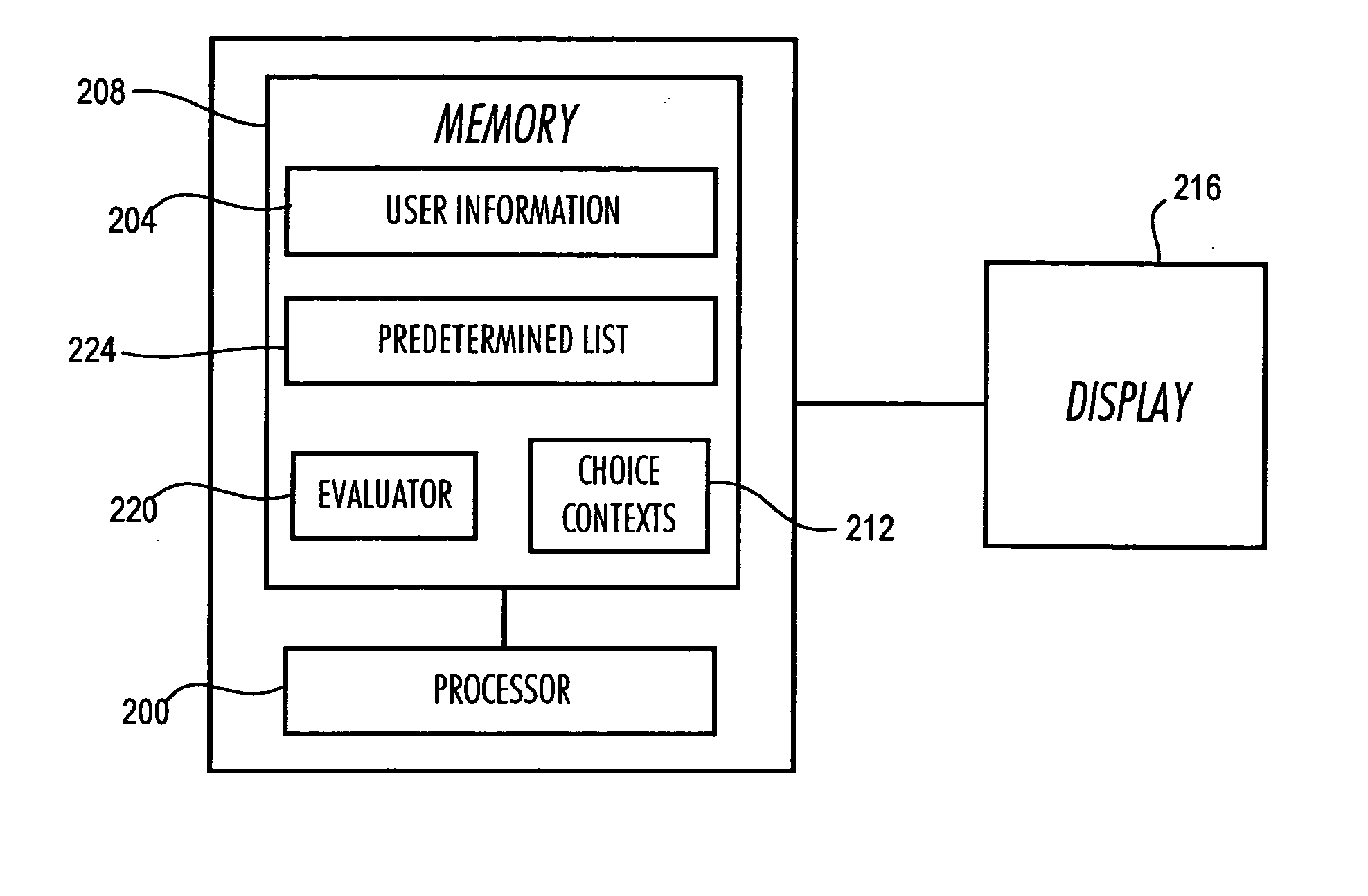
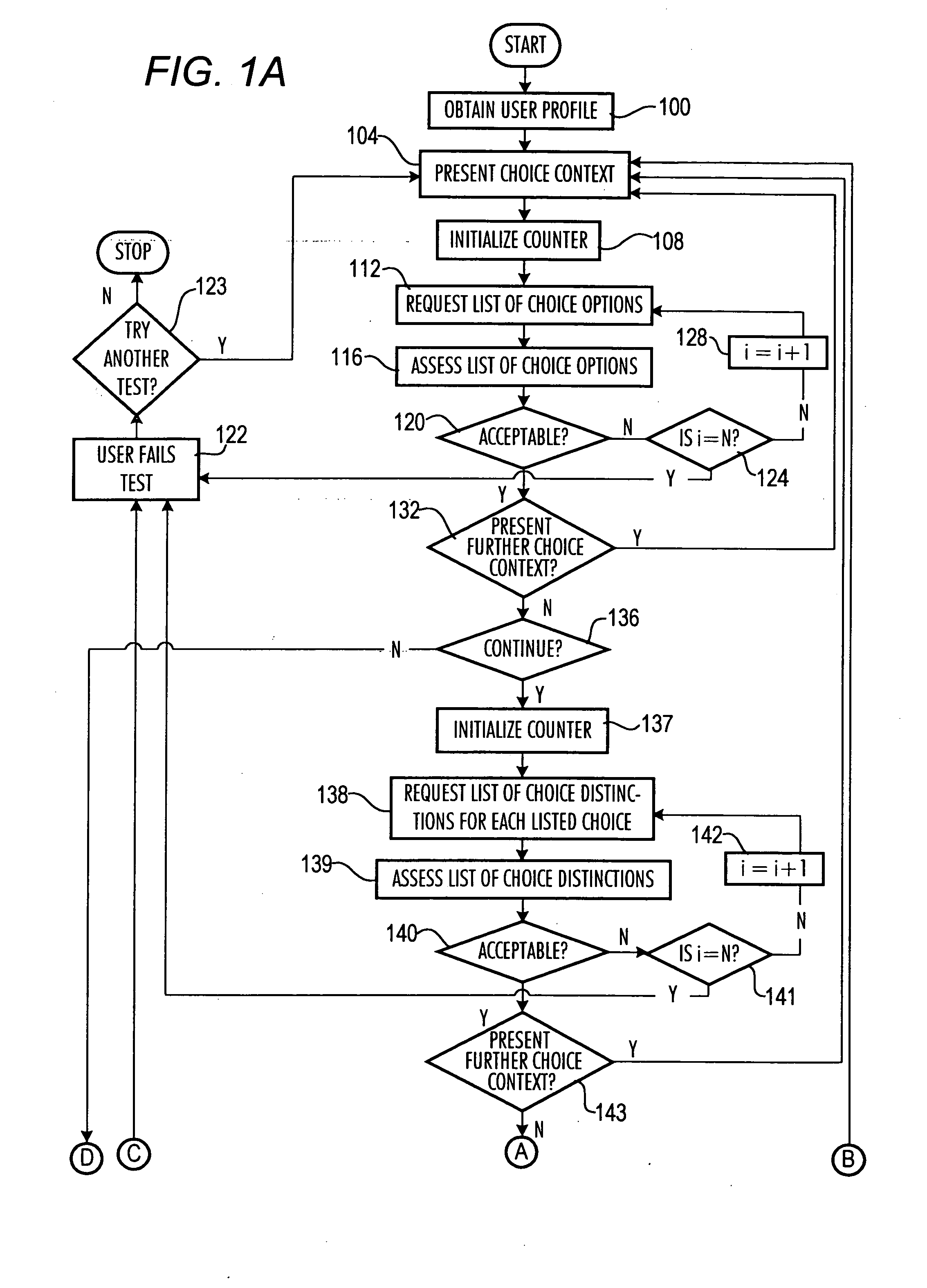
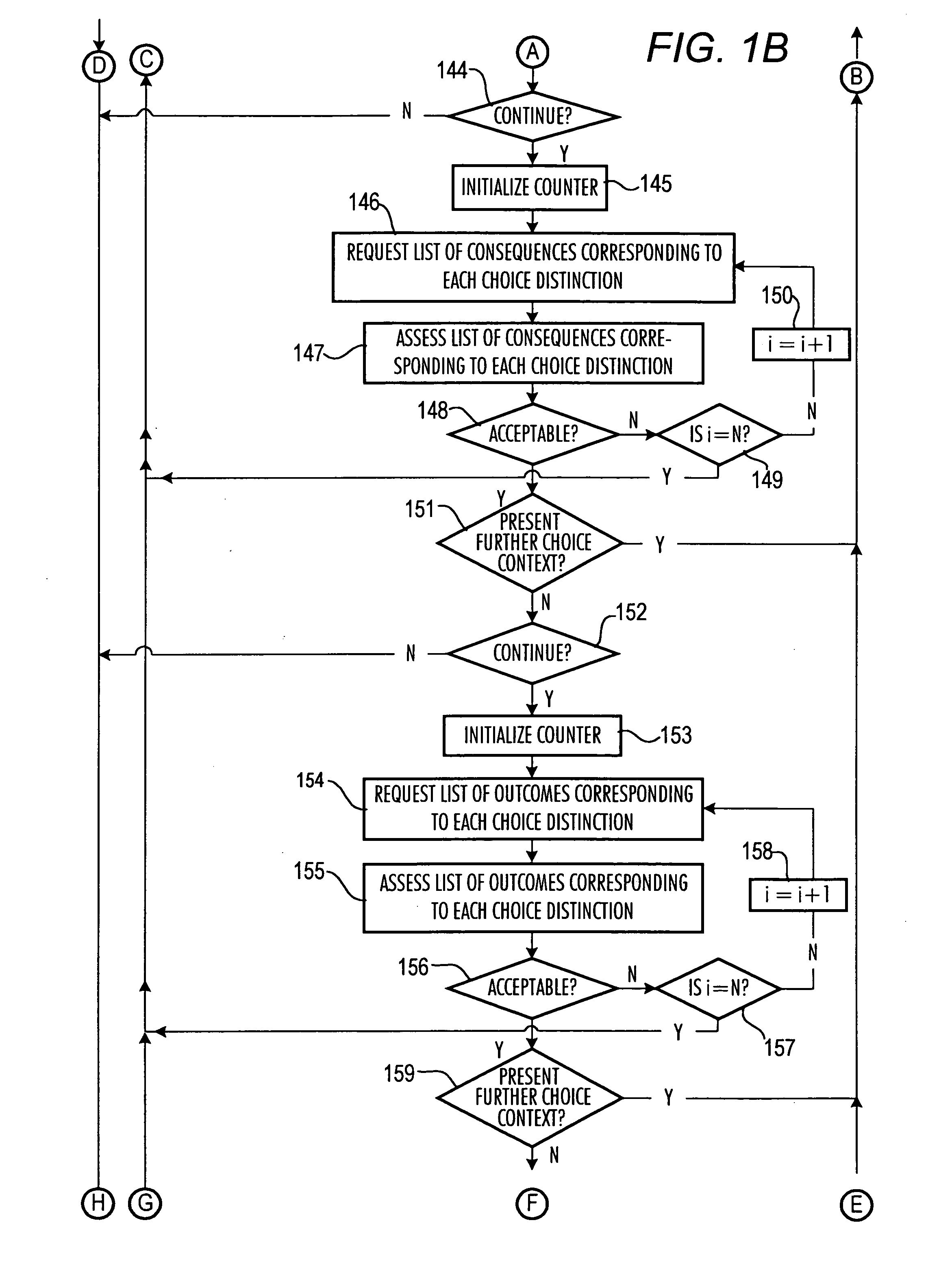
[0052] FIGS. 1A-D and 2 depict an interactive algorithm according to the present invention. The processor 200 (FIG. 2) initially obtains a (via step 100, FIG. 1A) profile of the user from user information 204 (FIG. 2). The profile may be stored in memory 208 as shown and / or obtained from the user through a series of queries. The user then is presented with a choice context (step 104FIG. 1) from a plurality of choice contexts 212 in memory 208, and a counter “i” is initialized (step 108FIG. 1A), e.g., set equal to one. The counter tracks the number of iterations through the loop defined by steps 112, 116, 120, 124 and 128.
[0053] The processor 200 can select which choice context to present using a random or pseudorandom number generator (in which event each of a plurality of choice contexts would be assigned a unique number or id) or a predetermined ordering of the choice contexts based on the user's profile information. The id can include a first field for setting, e.g., home, school...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com