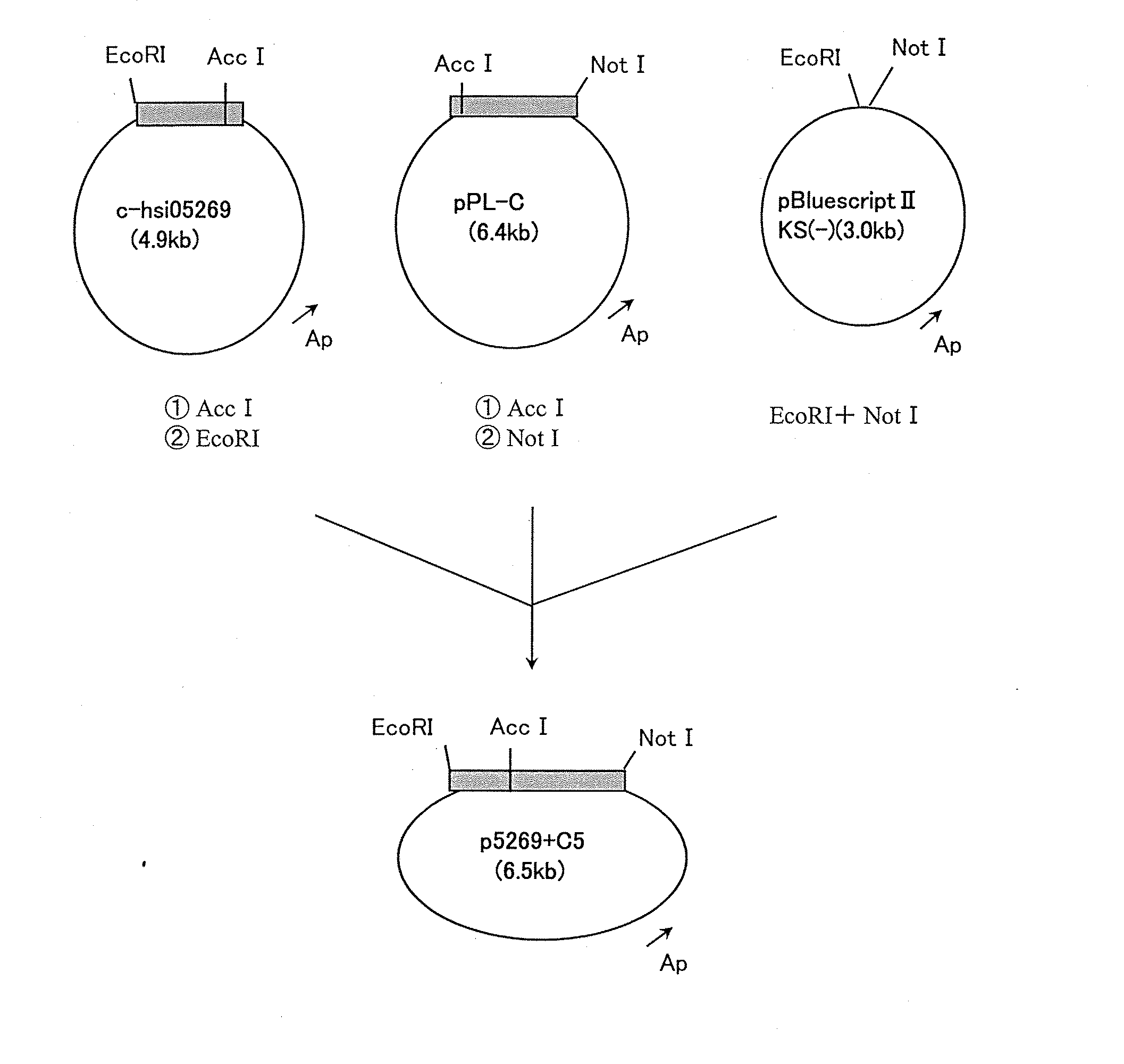
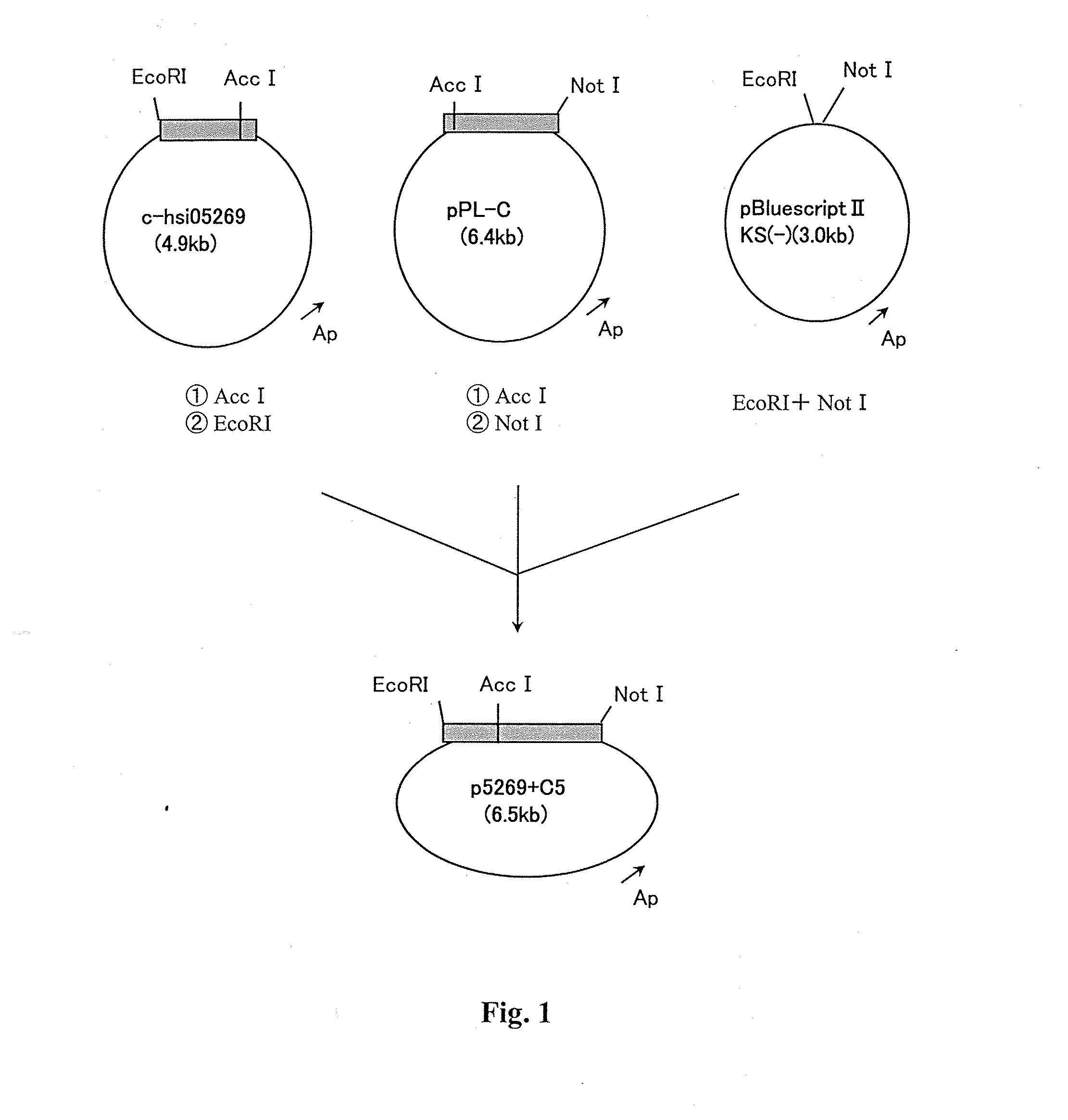
Polypeptides having phospholipase a2 activity
a polypeptide and activity technology, applied in the field of phospholipase a2 polypeptides, can solve the problems of difficult purification and isolation from tissues or cells, undesirable use of non-specific chemicals, and specific cytoplasmic phospholipas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cloning of cDNA Encoding the Human-Derived Polypeptide of the Present Invention
[0294] Unless otherwise noted, the genetic engineering techniques in the following examples were carried out according to the known methods described in Molecular Cloning, Second Edition.
(1) Preparation of a cDNA Library Derived from Human Small Intestine
[0295] Total RNA was extracted from human small intestine using an RNA extraction kit (#27-9270-01) produced by Pharmacia. Thereafter, mRNA was extracted and purified in accordance with the polyA(+)RNA purification method described in literature [J. Sambrook, E. F. Fritsch & T. Maniatis, Molecular Cloning Second Edition, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press (1989)].
[0296] A cDNA library was prepared from each of polyA(+)RNA according to the oligo-cap method [Gene, 138, 171 (1994)]. BAP (bacterial alkaline phosphatase) treatment, TAP (tobacco acid pyrophosphatase) treatment, RNA ligation, single-stranded cDNA synthesis and RNA removal were carried out ...
example 2
Analysis of Expression Using RT-PCR Method
[0315] A 5′-end DNA primer having the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 13 and a 3′-end DNA primer having the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 14 were designed and synthesized based on the information on the nucleotide sequence determined in Example 1.
[0316] PCR was carried out using 20 μl of a reaction solution containing 1.0 μmol / l each of the two primers (SEQ ID NOS: 13 and 14), 2 μl of a cDNA library prepared from each of the mRNAs of various human organs, a mixed solution of dNTPs (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP) containing 200 μmol / l each of the components, 200 μmol / l each of dNTPs (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP), 2.5 units of Taq Gold polymerase (Perkin Elmer) and 1× Taq Gold (Mg plus) buffer (Perkin Elmer) under the following conditions.
[0317] That is, using a thermal cycler, PTC-200 (MJ Research), PCR was carried out, after heating at 95° C. for 10 minutes, by 35 cycles, one cycle consisting of reaction at 94° C. for one minu...
example 3
Analysis of Expression of mRNA by Northern Hybridization
[0319] PCR was carried out using 50 μl of a reaction solution containing 0.2 μmol / l each of the two primers (SEQ ID NOS: 13 and 14), a mixed solution of dNTPs (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP) containing 200 μmol / l each of the components, 200 μmol / l each of dNTPs (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP), 2 μl of Human Kidney Marathon-Ready cDNA, 2.5 units of Ampli Taq Gold polymerase (Perkin Elmer) and 1× Taq Gold buffer under the following conditions.
[0320] That is, using a thermal cycler, PTC-200, PCR was carried out, after heating at 95° C. for 10 minutes, by 35 cycles, one cycle consisting of reaction at 94° C. for one minute and reaction at 60° C. for one minute, followed by heating at 72° C. for 8 minutes.
[0321] A 5 μl aliquot of the resulting PCR reaction mixture was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis to confirm that an about 0.6 kb DNA fragment was amplified, The DNA fragment was then purified using QIAEX II Gel Extraction Kit (Q...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap