Bioindex mechanism for increasing the relative speed of biometric indentification against large population samples
a biometric and relative speed technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of increasing reduce the field of template keys (xt) database, increase the range of keys searched, and reduce the overall search time. the effect of time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
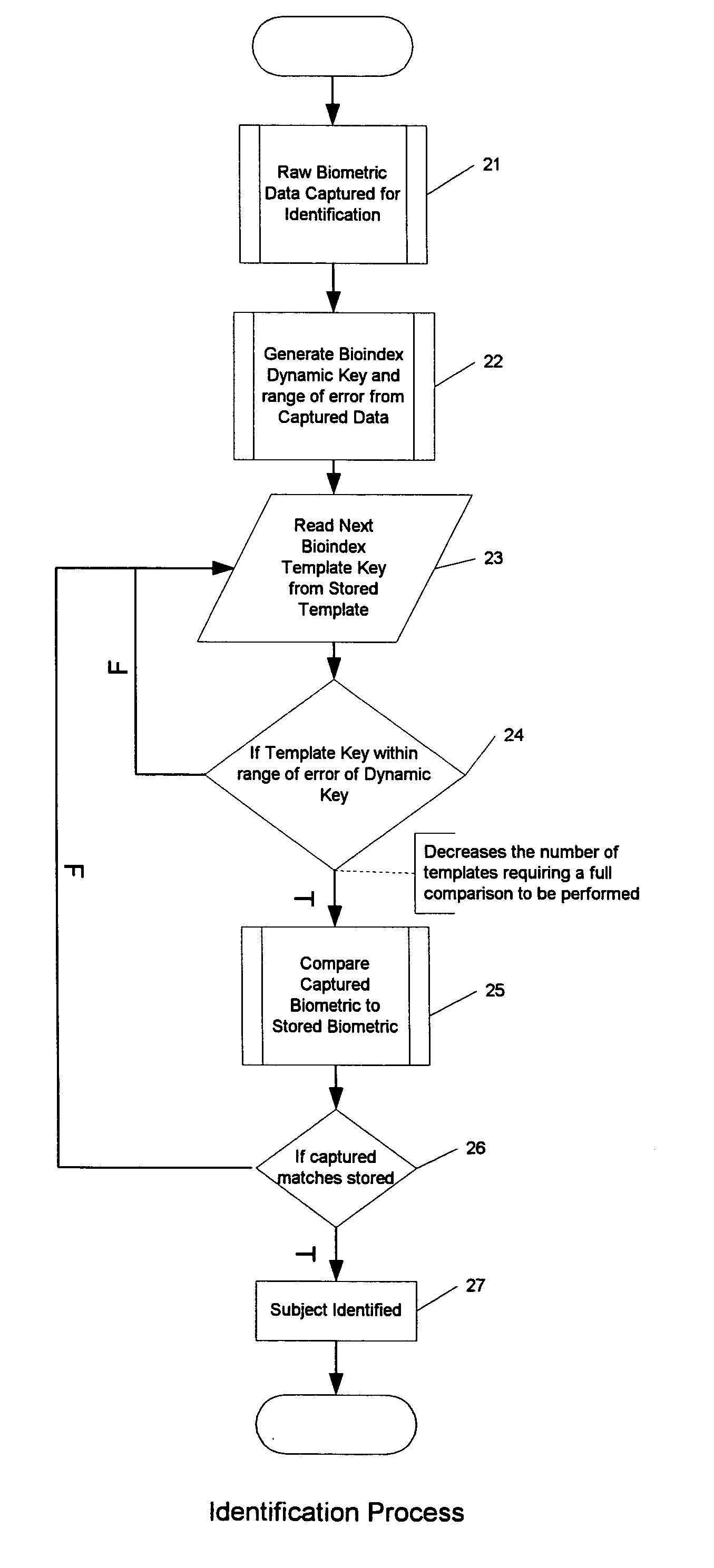
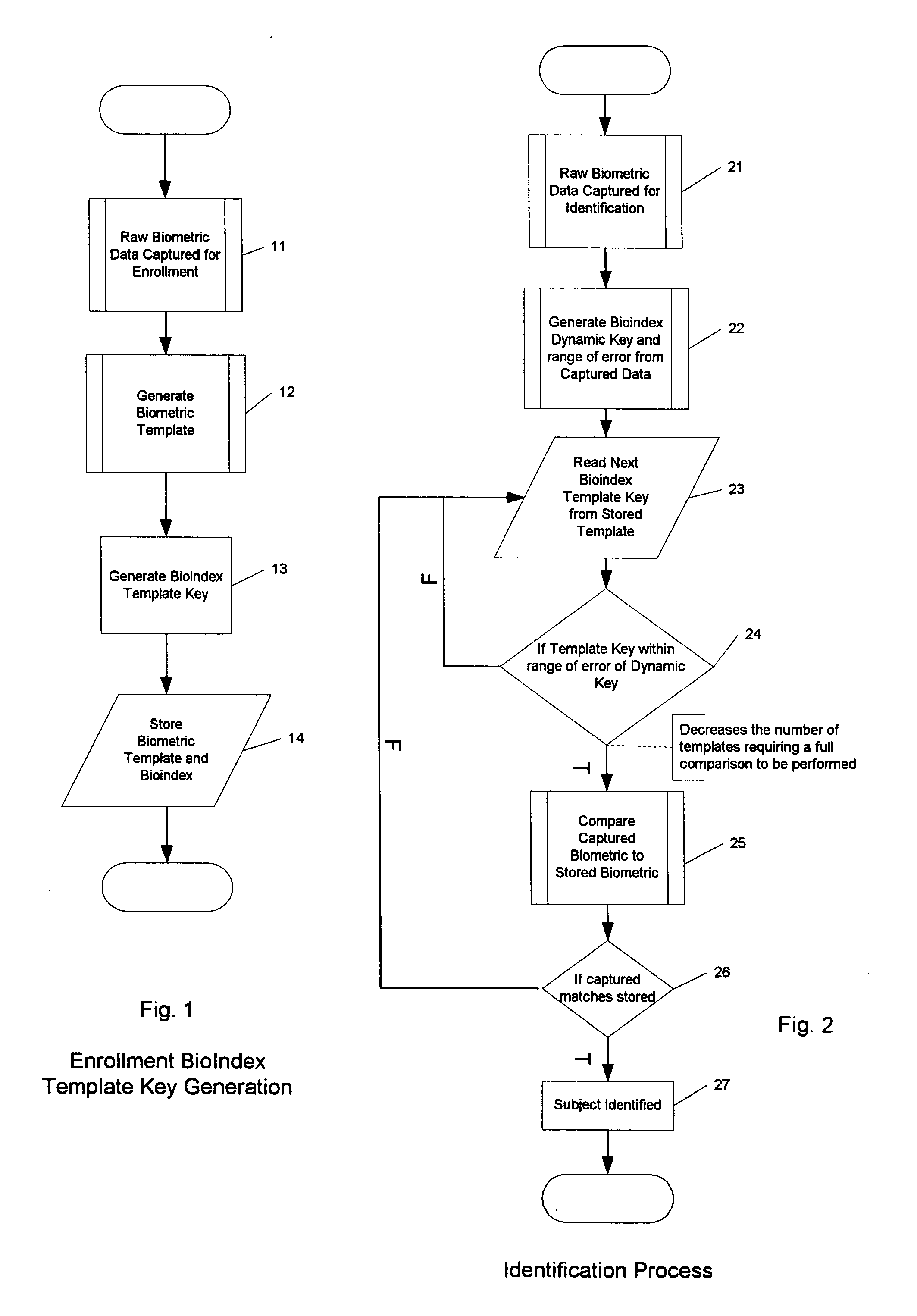
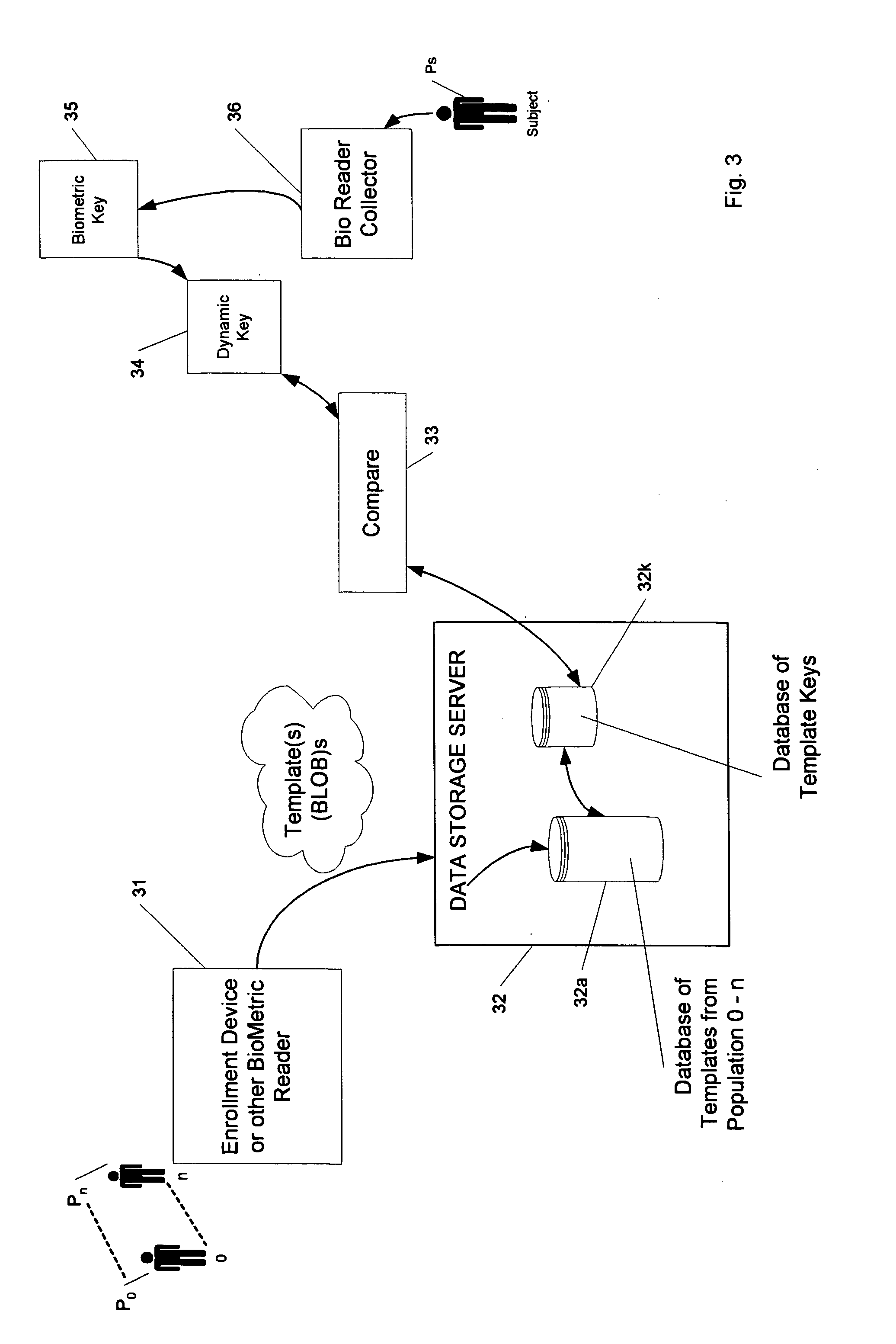
[0018]The solution proposed here is to generate a single long number from the biometric template itself. This number preferably may be represented as an eight-byte integer and stored in any kind of database. This number can then be used as a key in the database just as any other number to speed searches and selectively extract the data from the database. This key would not necessarily be a unique key, but the more near unique the generated key is, the faster the identification process can be.
[0019]We begin with raw biometric data capture at an ‘enrollment’ facility or station in an initial phase 11 of generating a bioindex template key. An enrollment station can be one that has a mechanism for sensing or registering a measurement or set of measurements that identify an individual human being. For example, facial recognition systems could be used. Such systems analyze the characteristics of a person's face images input through a digital video camera, by measuring overall facial struc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com