Stochastic block allocation for improved wear leveling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
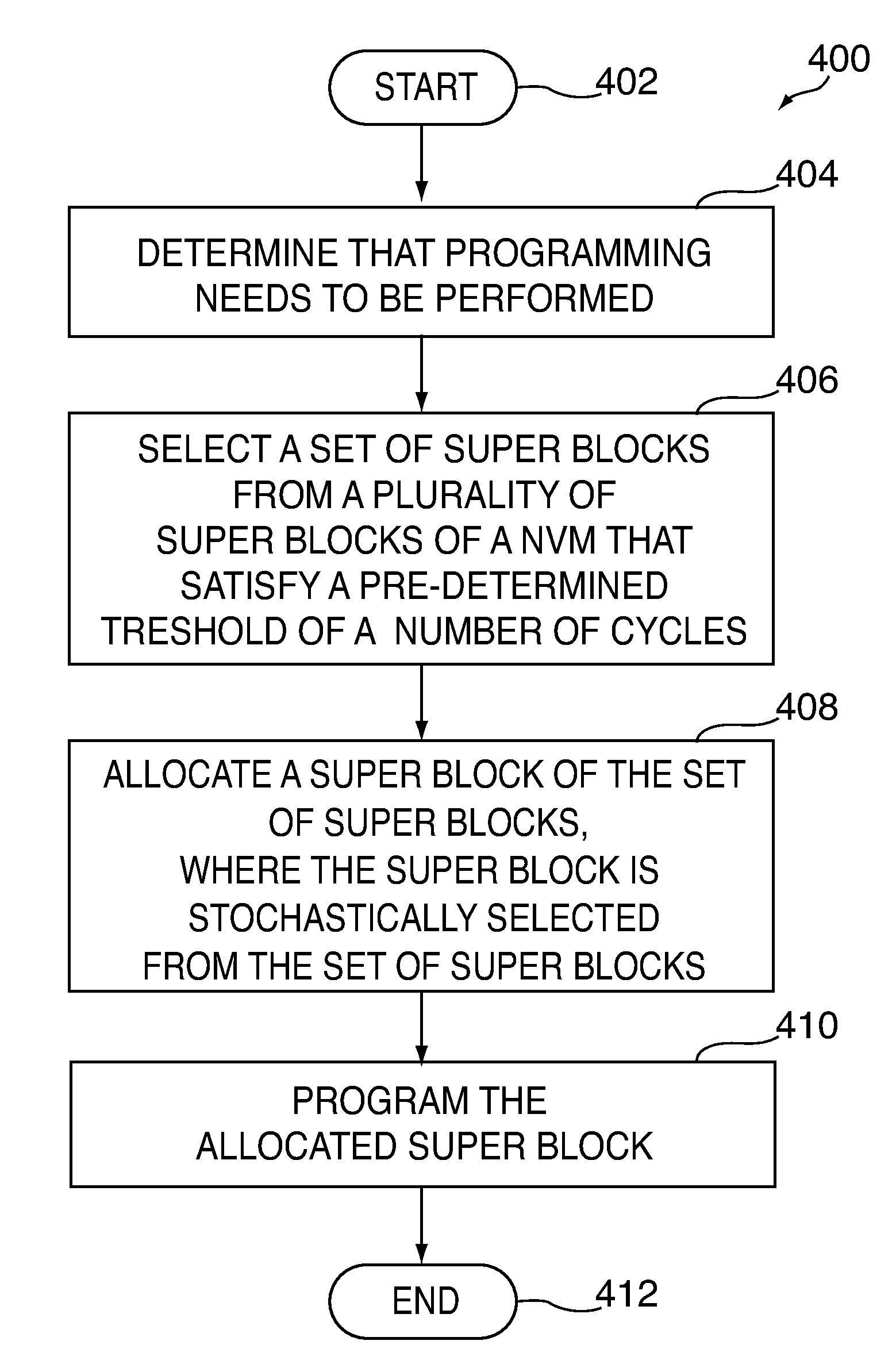
[0014]Systems and methods for stochastic block allocation for improved wear leveling are provided. As used herein, “stochastic” block allocation can refer to the non-deterministic selection of a block, where one or more blocks or super blocks have a random or probabilistic chance of being allocated.
[0015]A NVM interface of a system can probabilistically allocate a block or super block based on statistics associated with the block or super block. The block or super block may be allocated for any suitable programming purposes including, for example, host writing, garbage collection, and wear leveling. In some embodiments, in order to allocate a particular super block, a set of super blocks can be selected from multiple super blocks of a NVM based on a pre-determined threshold of a number of cycles (e.g., erase cycles and / or write cycles). For example, if the NVM interface determines that a lower-cycled super block needs to be allocated for dynamic host writes and garbage collection (“...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com