Air conditioner using cooling/dehumidifying energy recovery technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
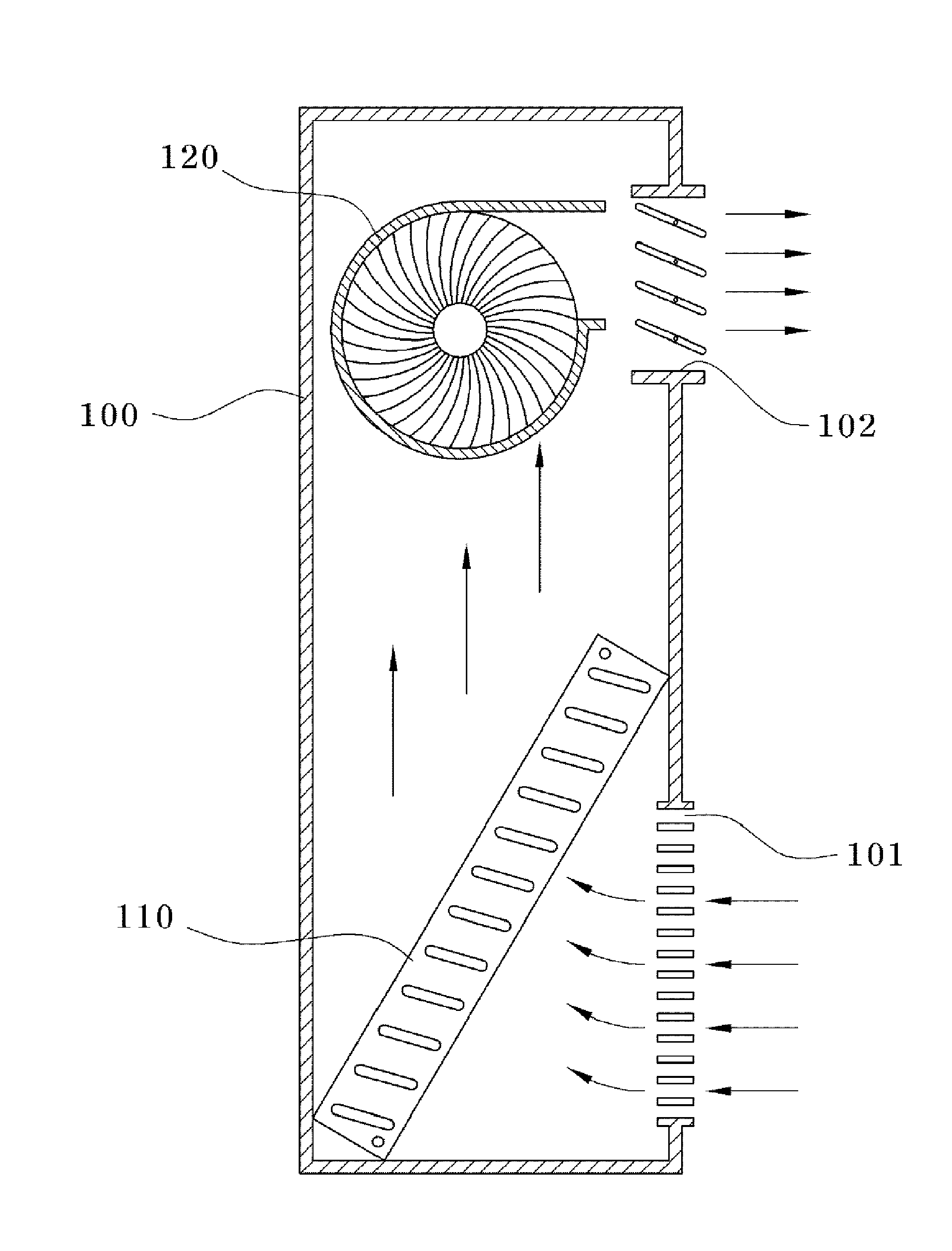
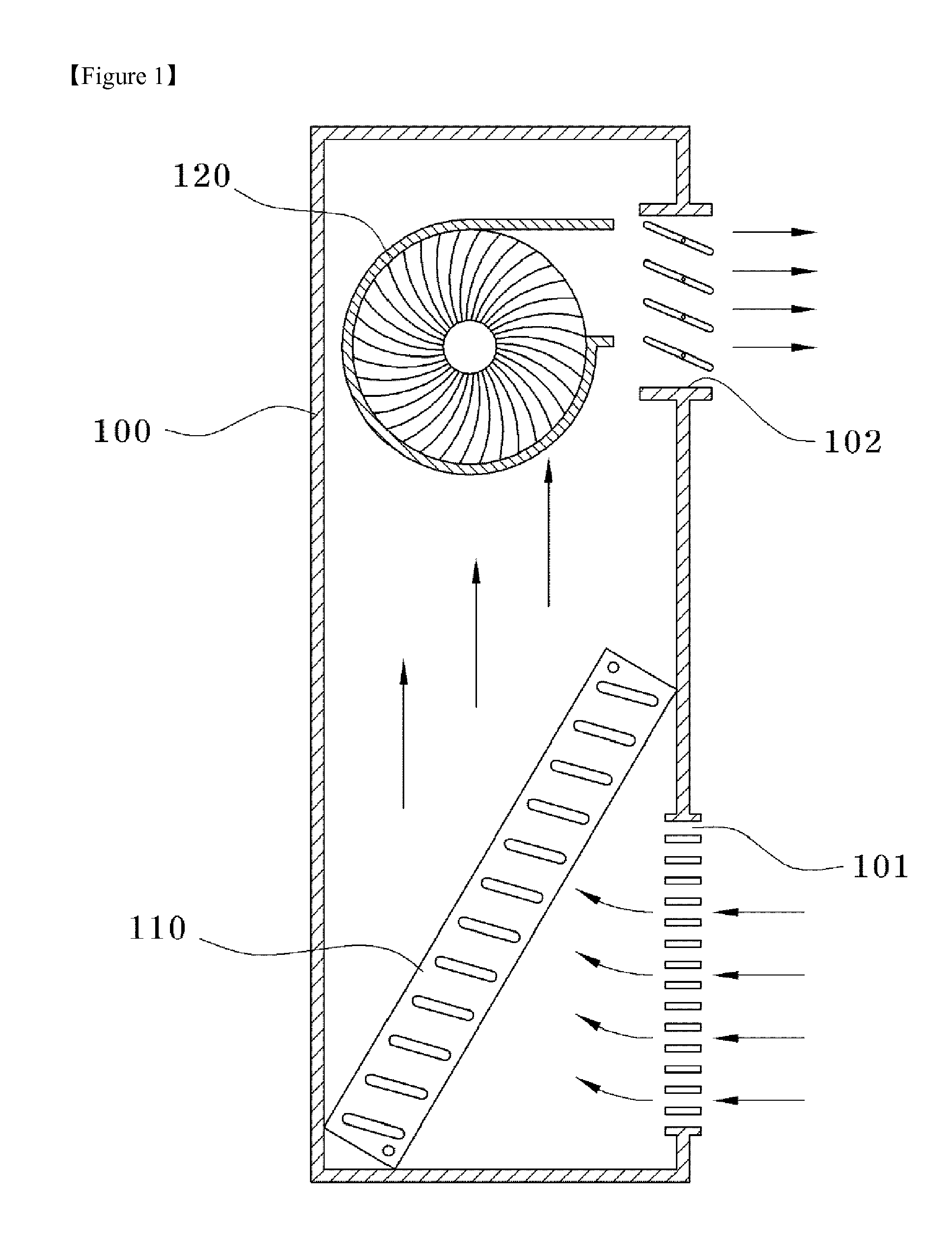
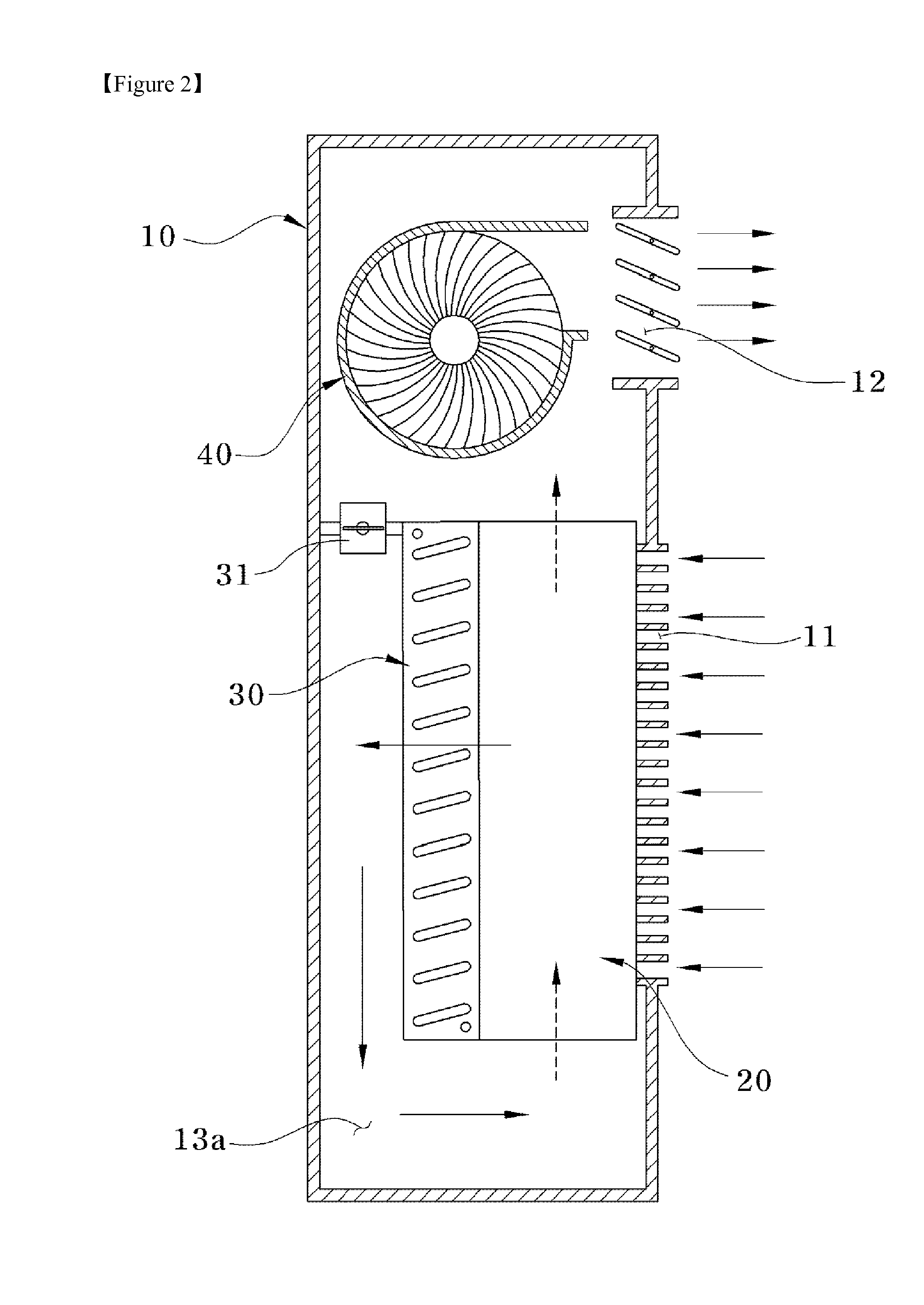
[0024]In a first embodiment, as shown in FIG. 2, all of the intake hole 11 and discharge hole 12 are formed in the front surface of the main body 10, and the heat exchanger 20 and cooling coil 30 are disposed, in turn, downstream from the intake hole 11, and a separate air passage 13a is provided downstream of the cooling coil 30.
[0025]The heat exchanger 20 disposed downstream from the intake hole 11 performs heat exchange between air introduced into the main body 10 and cooled air, such that the introduced air is previously cooled, thereby ultimately enhancing cooling efficiency. As shown in FIG. 3, the heat exchanger 20 is a stacked plate type heat exchanger in which plate type first and second heat exchanging plates 20A and 20B are alternately stacked. Heat exchanger intake and discharge holes 21A, 21B, 22A, 22B are formed in each of the first and second heat exchangers 20A, 20B so that air passing through the heat exchanger 20 is cross-flowed.
[0026]In other words, as shown in FI...
second embodiment
[0038]As shown in FIG. 4, a second embodiment relates to an air conditioner in which the intake hole 11 for sucking the indoor air is formed in the rear surface of the main body 10, and the discharge hole 12 for discharging the cooled air to the indoor space is formed in the front surface of the main body 10. Therefore, the second embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except that installation positions of the heat exchanger 20, cooling coil 30 and air passage 13b are opposed to those in the first embodiment. That is, in the second embodiment, the intake hole 11 is formed in the rear surface of the main body 10, and the heat exchanger 20 and cooling coil 30 are disposed, in turn, downstream from the intake hole 11, and the air passage is formed between the front surface of the main body 10 and the cooling coil 30 and also at the lower side of the heat exchanger 20, and thus a reversed “L”-shaped air passage 13b is formed. Further, a damper 31 may be further provided at an up...
third embodiment
[0041]As shown in FIG. 6, a third embodiment relates to an air conditioner in which the intake hole 11 is formed in both side surfaces of the main body 10. Except that, unlike the first embodiment, the intake hole 11 is formed in the side surfaces of the main body 10, the rest configuration, i.e., the heat exchanger 20, cooling coil 30 and air passage 13c of the third embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment. As described above, if the intake hole 11 is formed in the side surfaces of the main body 10, it is prevented that the cooled air is introduced again into the main body 10 through the intake hole 11 due to the drawing force of the fan while the cooled air is discharged through the discharge hole 12.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com