Remote materialization of low velocity data
a technology of low-speed data and materialization, applied in the field of remote data materialization, can solve the problems of increasing the likelihood that the data no longer reflects the current data of the remote data source, and the probability of b>130 increases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0007]The following description is provided to enable any person in the art to make and use the described embodiments and sets forth the best mode contemplated for carrying out some embodiments. Various modifications, however, will remain readily apparent to those in the art.
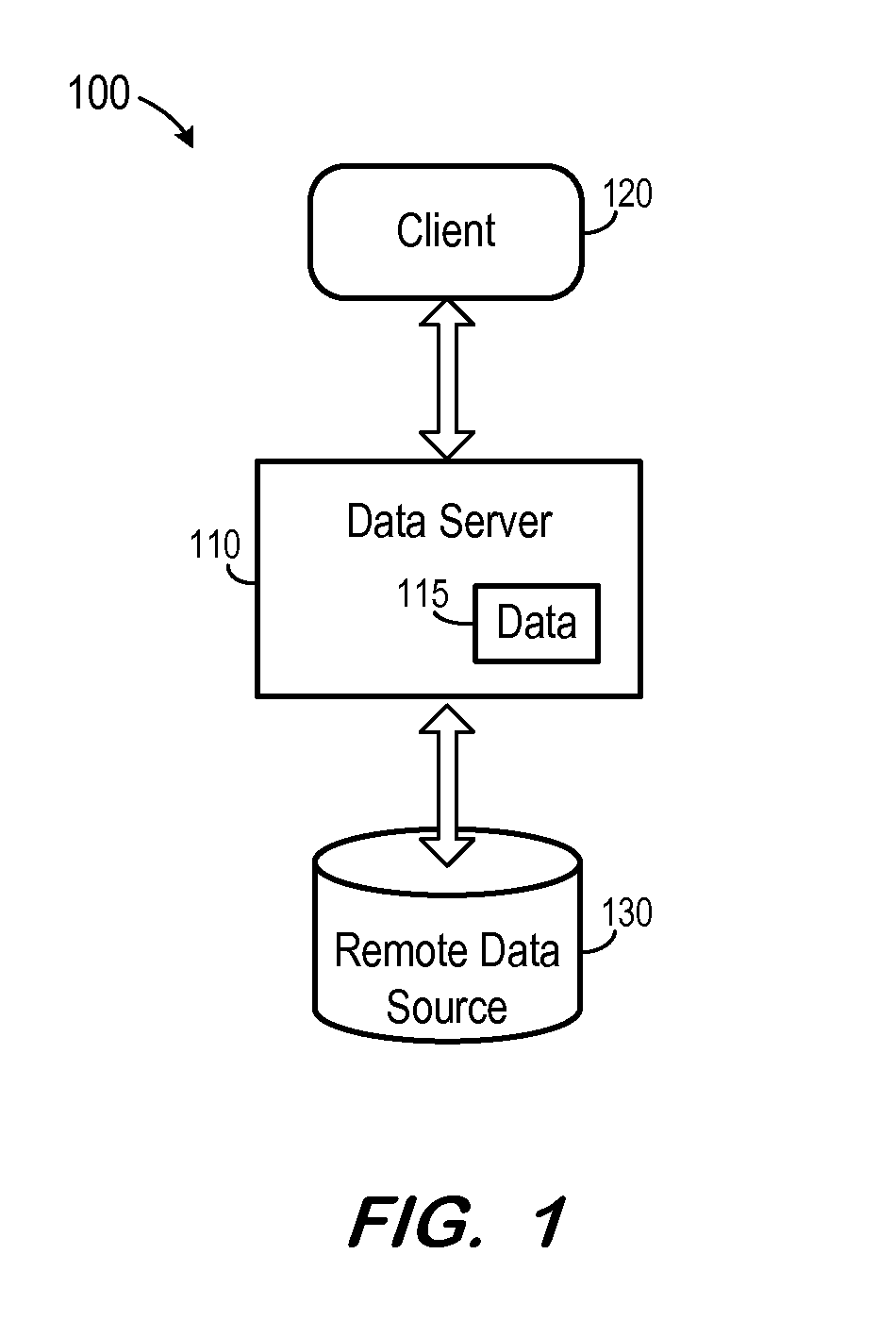
[0008]FIG. 1 is a block diagram of system 100 according to some embodiments. System 100 includes data server 110, client 120, and remote data source 130. Generally, data server 110 receives queries from client 120 and provides results thereto based on data of data 115 and / or remote data source 130. Data server 110 may support multi-tenancy for multiple unrelated clients by providing multiple logical database systems which are programmatically isolated from one another.
[0009]Data 115 may be stored in Random Access Memory (e.g., cache memory for storing recently-used data) and one or more fixed disks (e.g., persistent memory for storing their respective portions of the full database). Alternatively, data server 11...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com