Static random access memory and method thereof
a random access memory and random access technology, applied in static storage, information storage, digital storage, etc., can solve the problems of low mos capacitance value in low-voltage operation, inability to read disturb voltage undesired, and inability to read disturb voltage, etc., to improve writability, improve writability, and improve write margin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
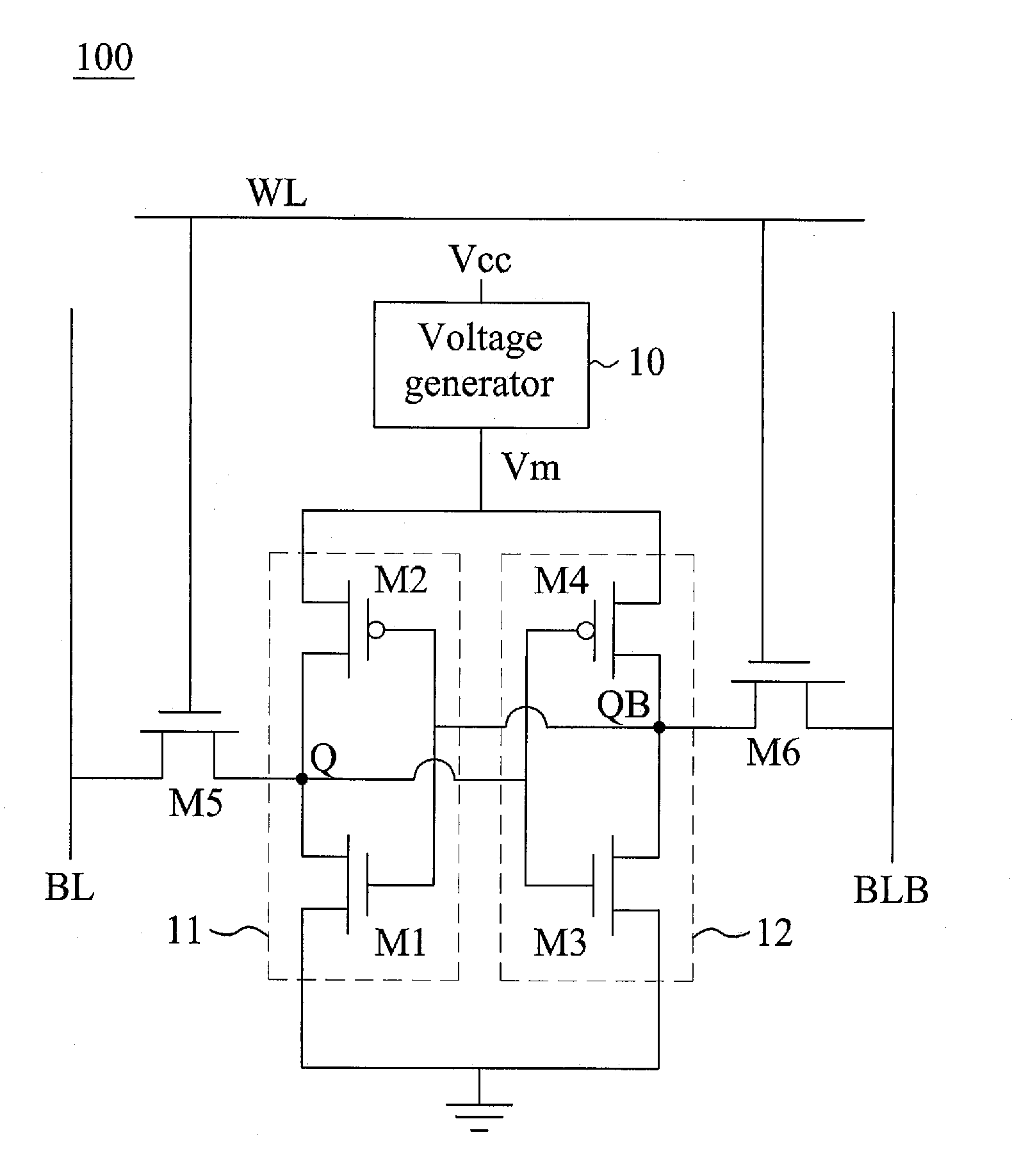
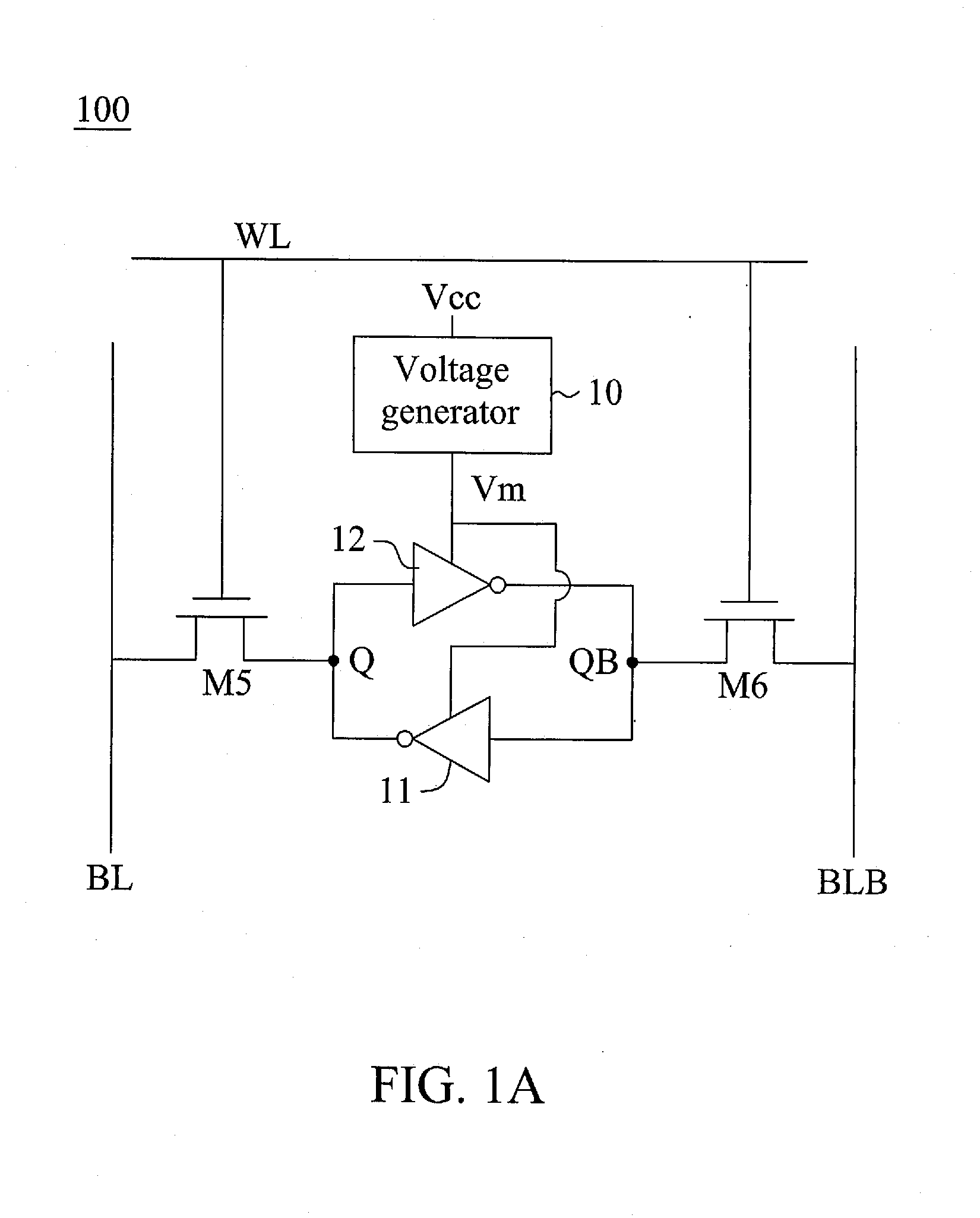
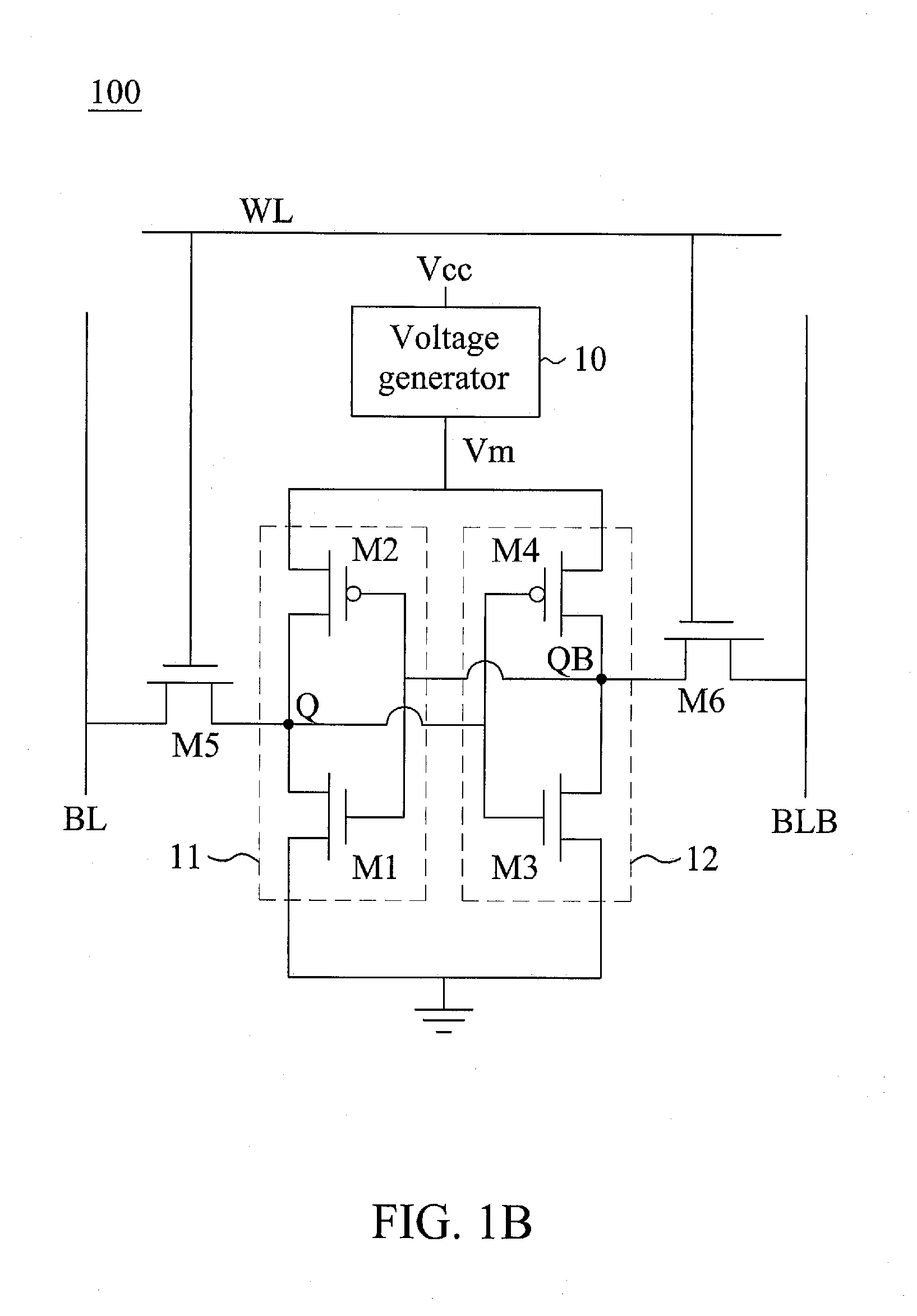
[0018]FIG. 1A shows a circuit diagram illustrated of a static random access memory (SRAM) 100 according to one embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 1B shows a detailed circuit diagram of the SRAM 100 of FIG. 1A. One SRAM cell is representatively shown, and a plurality of the same SRAM cells may be arranged in an array of rows and columns to form a SRAM device. Although a 6-T SRAM is illustrated in the following embodiment, it is appreciated that the present invention may be embodied in other SRAM with different number of transistor, or may be embodied in a dual-port SRAM.
[0019]The SRAM 100 of the embodiment includes a voltage generator 10 that is coupled to receive a positive power supply voltage Vcc, and is configured to controllably generate a first power supply voltage Vm, wherein the first power supply voltage is with a reduced level and is higher than a retention voltage during a specific period. The positive power supply voltage Vcc of the embodiment may be as low as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com