Use of treating elements to facilitate flow in vessels
a technology of treating elements and facilitating the flow of streams, which is applied in fluid dynamics, chemical/physical/physico-chemical processes, chemical apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of significant loss of bed vessel productivity and profitability, damage to the vessel and its internals, and the passage of the internal processing portion of the bed vessel, so as to improve the flow distribution of one or more streams
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
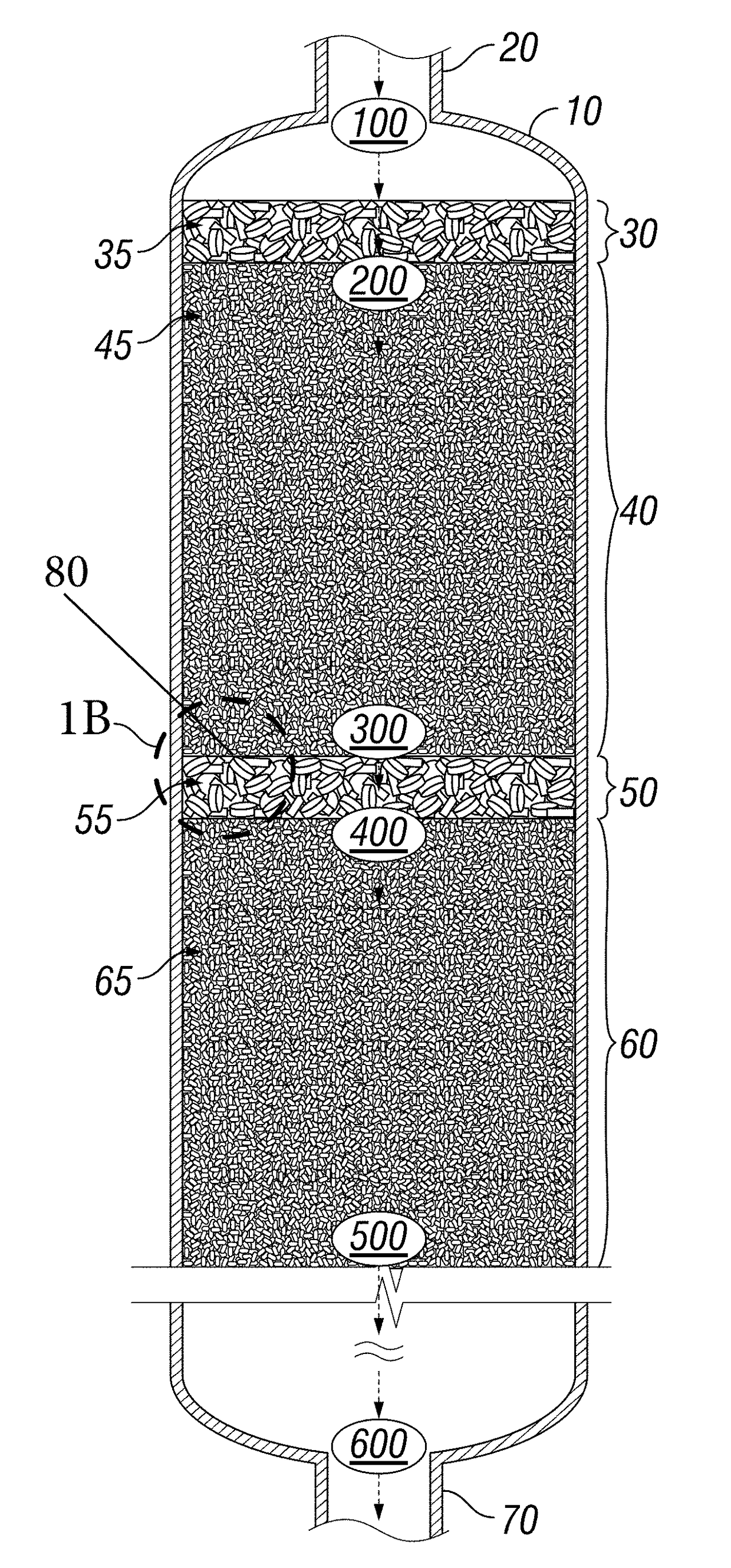
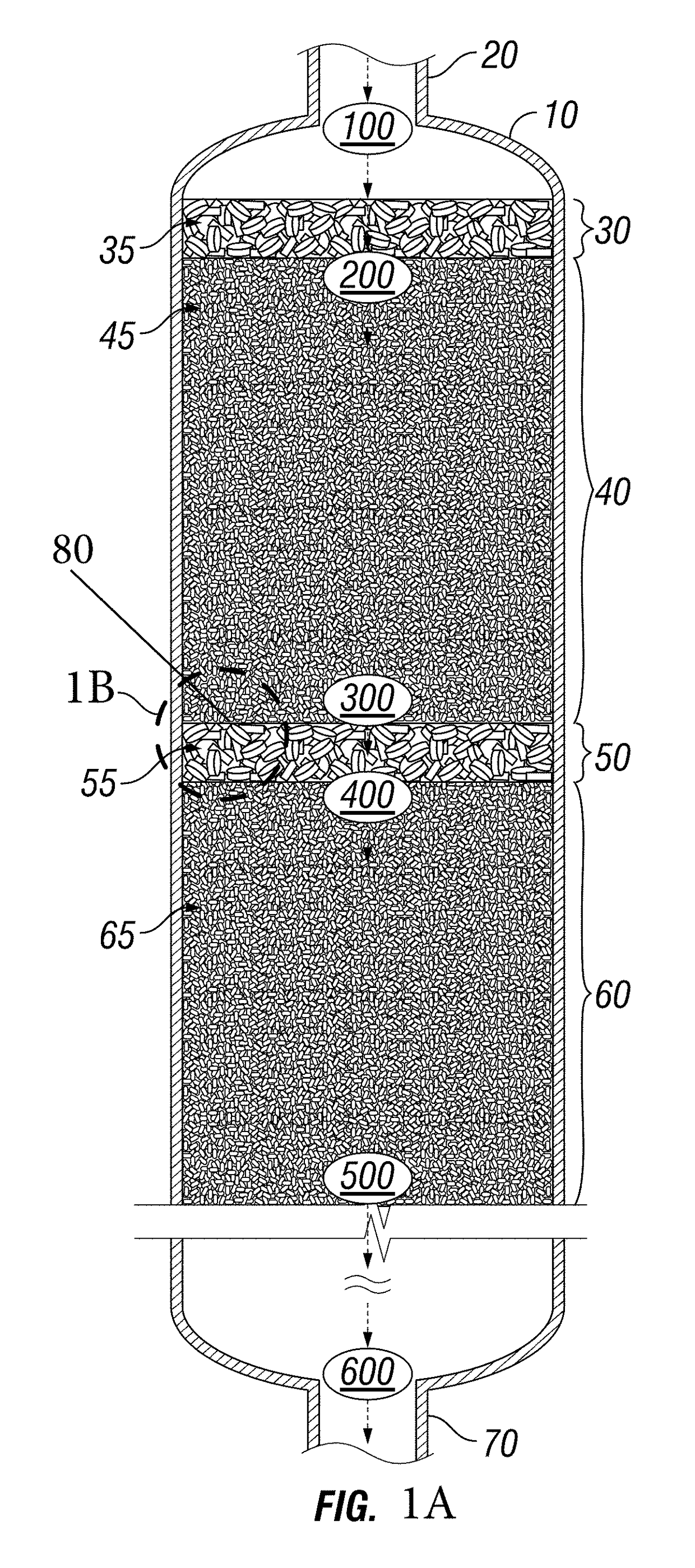
[0030]In accordance with the presently disclosed subject matter, various illustrative embodiments of methods for facilitating the redistribution and lateral redispersion of the flow of one or more streams within bed vessels are provided.
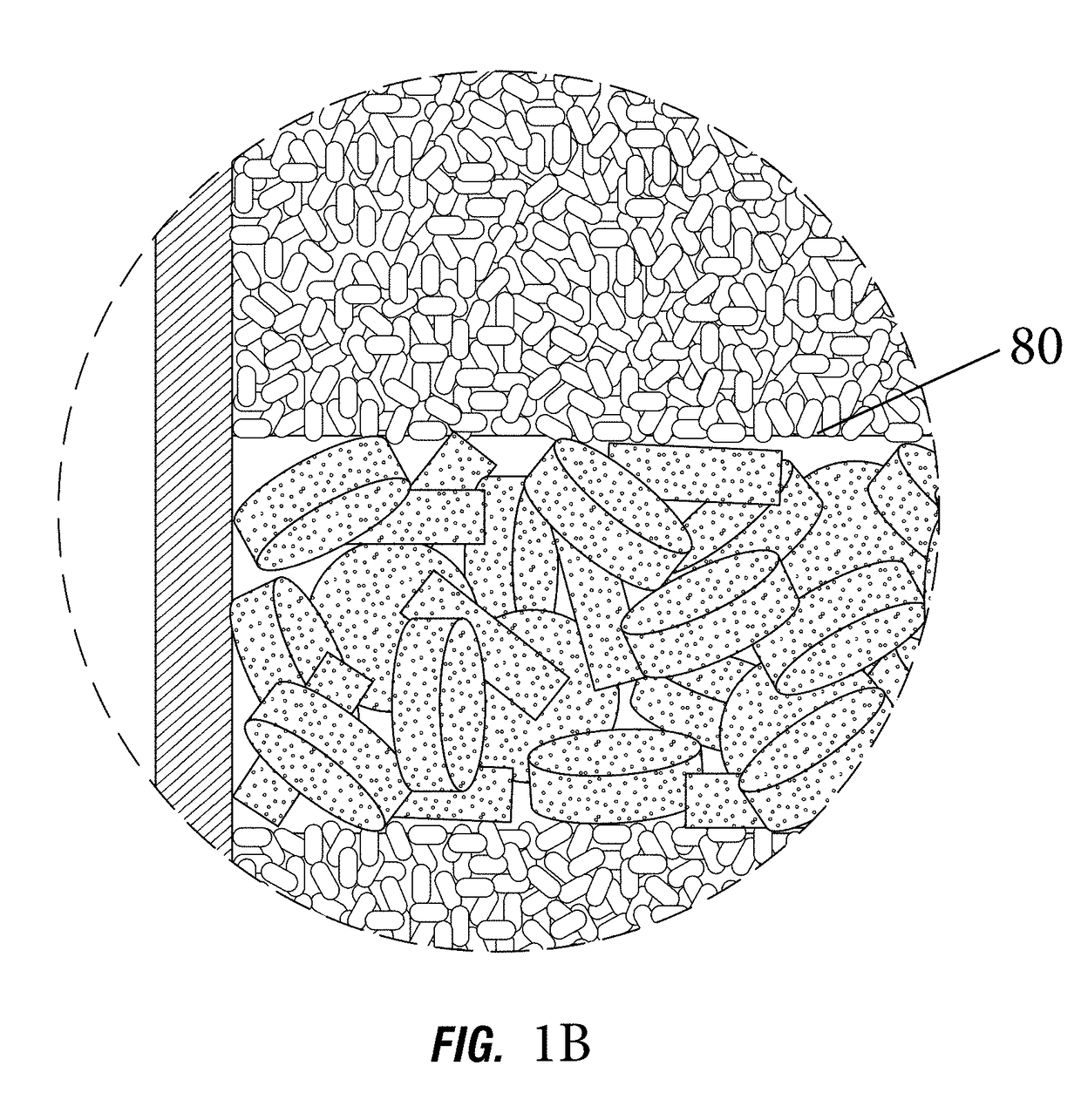
[0031]The concept of “redistribution” as described in the presently disclosed subject matter concerns the division and dispersion of process streams across and throughout the internals contained within a bed vessel. Such division and dispersion is facilitated by redistribution treating zones disposed to counter negative stream coalescing effects which cause stream channeling and which, at best, prevent achievement of the designed performance of the processing zones installed within the bed vessel and, at worst, cause unsafe operating circumstances which increase operating risk.
[0032]In certain illustrative embodiments, disposed within such bed vessels are internal materials and structures as well as multiple operating zones. One type of operating zon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com