All-or-none switchover to address split-brain problems in multi-chassis link aggregation groups
a multi-chassis link and all-or-none technology, applied in the field of network systems and methods, can solve problems such as significant switchover tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
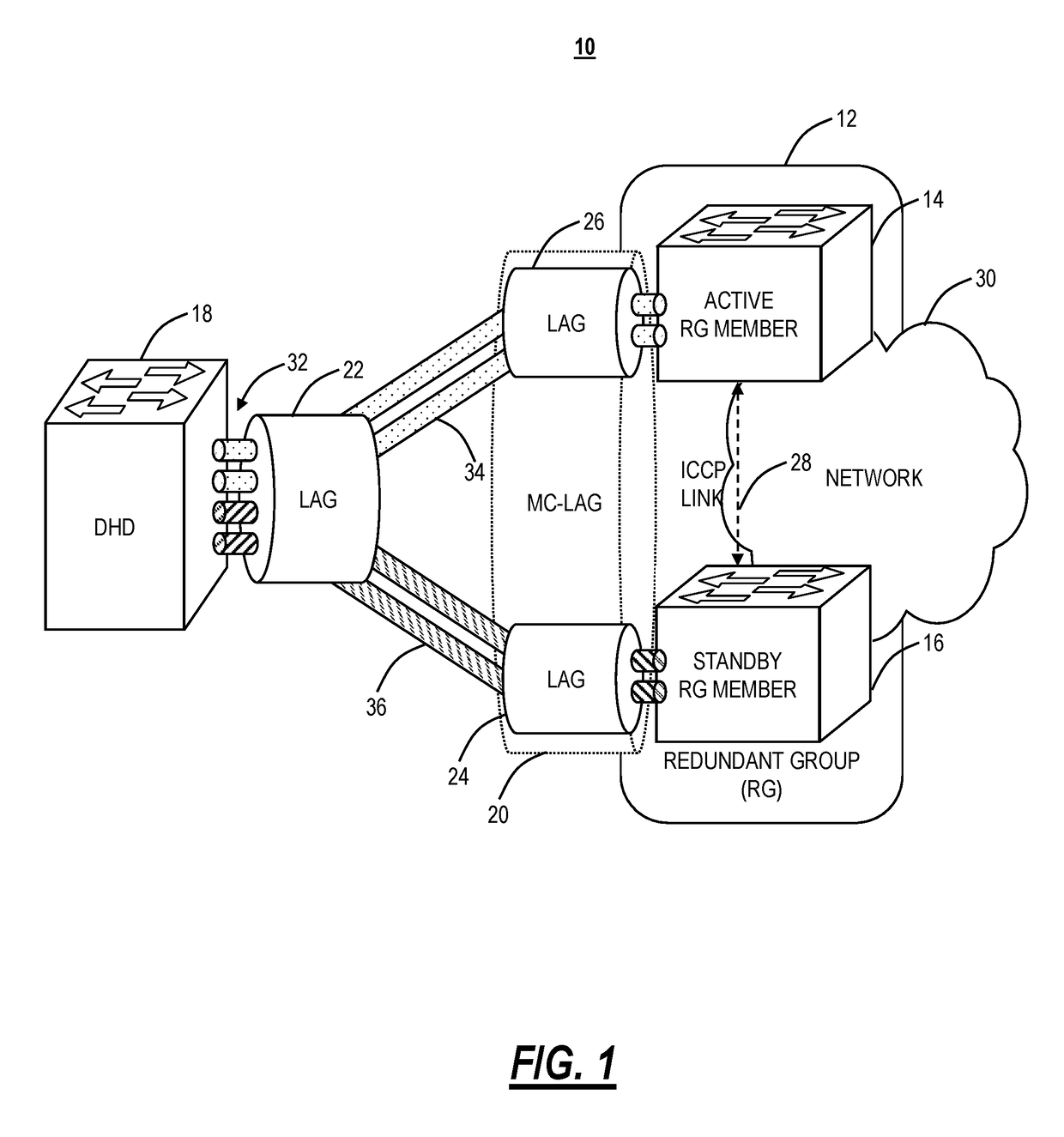
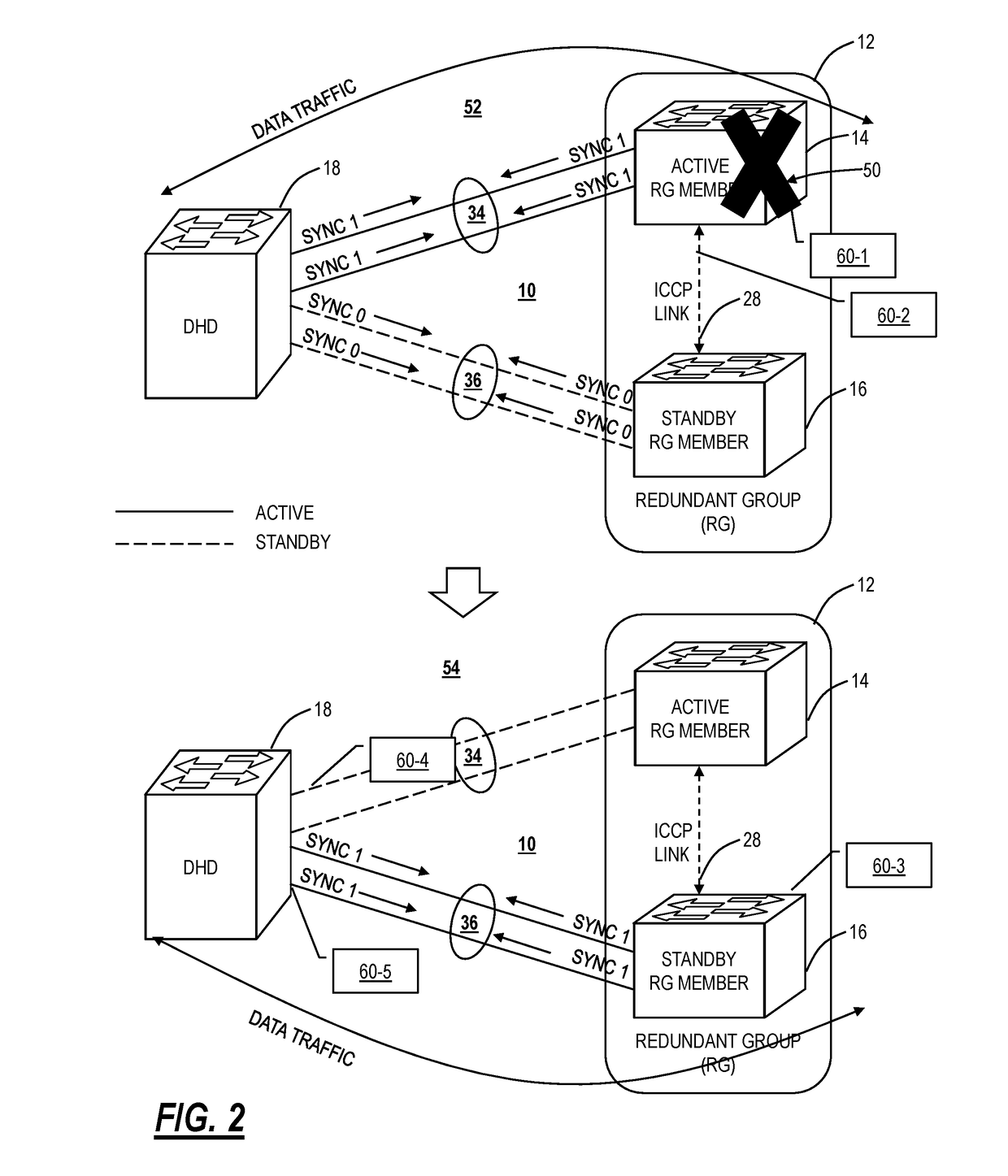
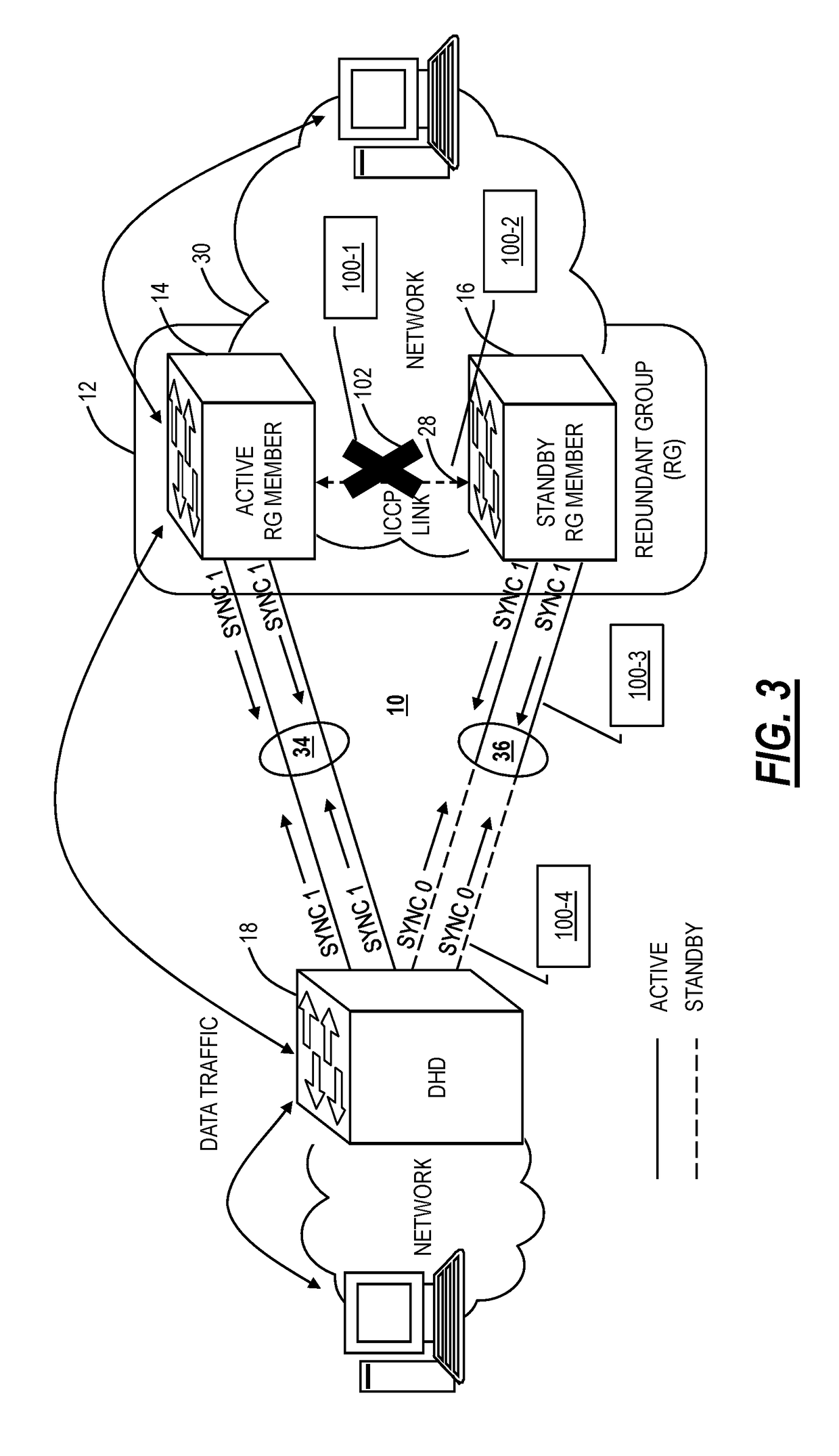
[0025]In various embodiments, the present disclosure relates to systems and methods performing an all-or-none switchover to address split-brain problems in Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation Groups (MC-LAGs). In particular, the systems and method solve the split-brain problem in an active / standby MC-LAG in a triangle topology (a DHD connected to a plurality of RG members). The proposed systems and methods are implemented between the RG members only without the involvement of the DHD; thus, the systems and methods can interoperate with any vendor's DHD. Also, the systems and methods do not change system MAC addresses thereby avoiding increased switchover time.
Active / Standby MC-LAG
[0026]FIG. 1 illustrates an active / standby MC-LAG 10. MC-LAG 10 simply means dual-homing an endpoint to two or more upstream devices, i.e., allowing two or more upstream nodes to share a common endpoint thereby providing node-level redundancy. The MC-LAG 10 includes a Redundant Group (RG) 12 which includes RG me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com