Heat exchanger and components and methods therefor
a technology of heat exchangers and components, applied in the field of heat exchangers, can solve the problems of prone failure of braze joints, prone to external clogging of all monoblock cores, and prone to bar and plate monoblock cores
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
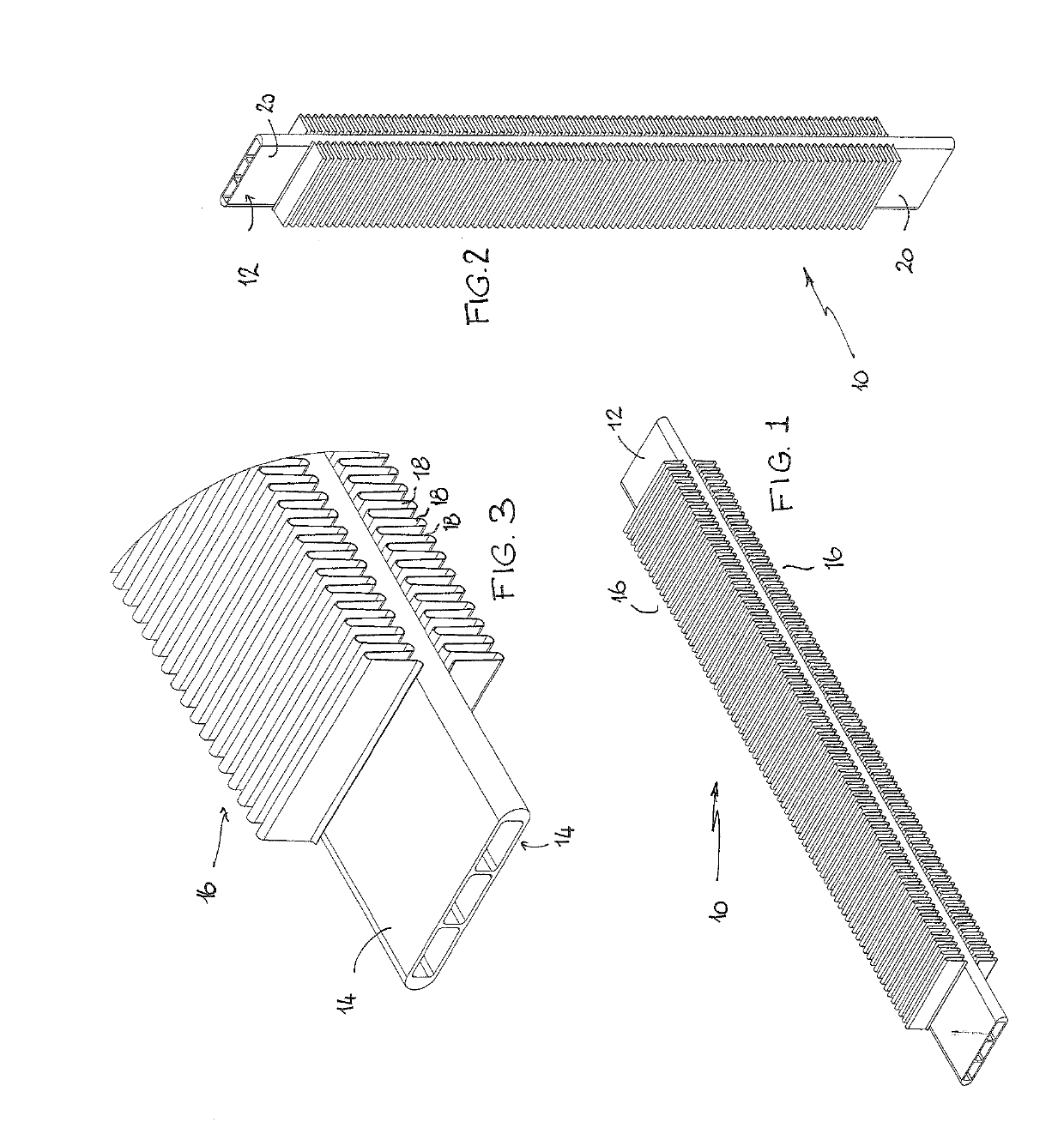
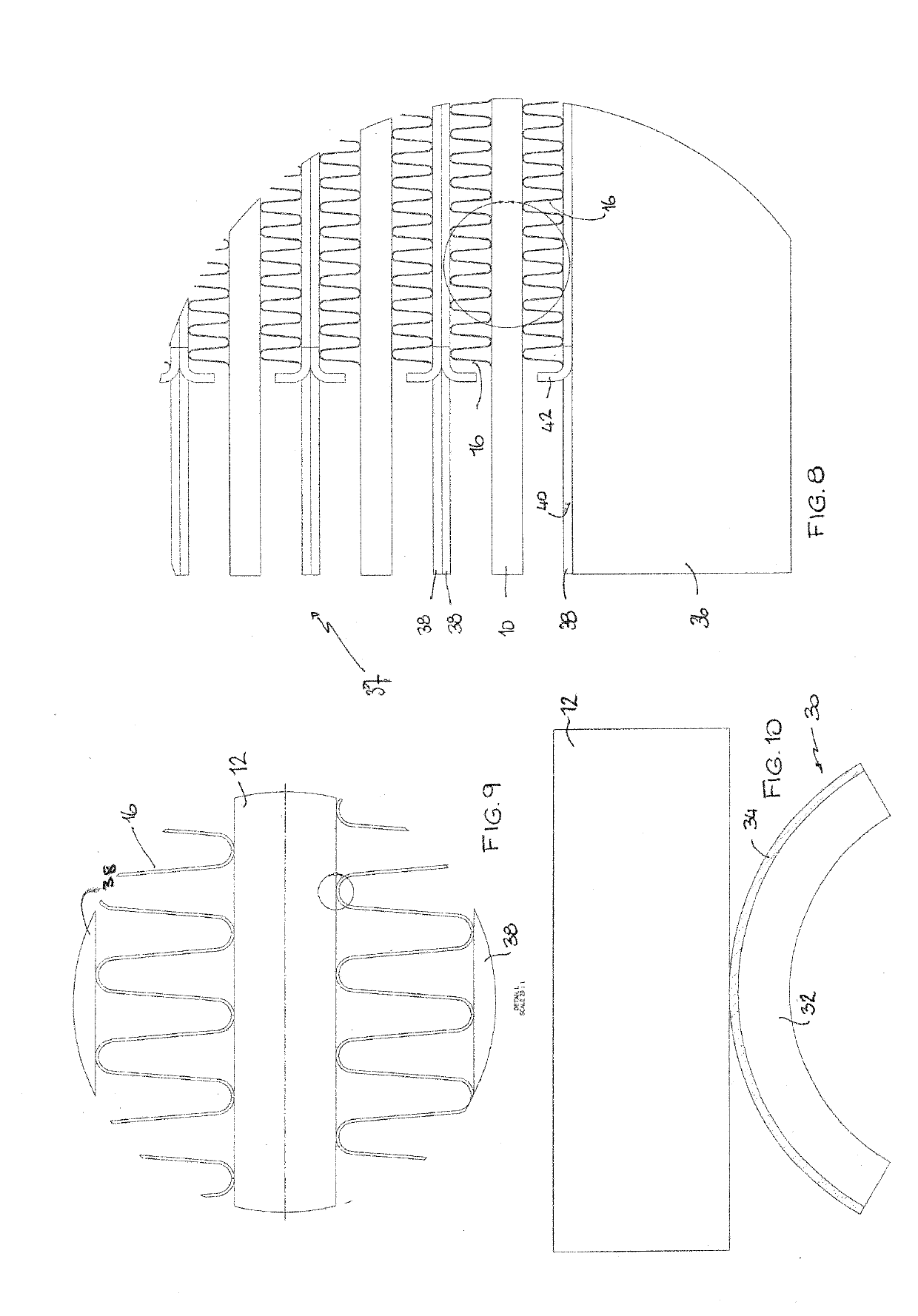
[0110]FIGS. 1 and 2 illustrate the form of the tubular component 10 according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. The tubular component 10 includes a tube portion 12. The tube portion 12 is oblong in transverse section as shown in FIG. 3 with 2 flat longitudinal sides 14. Fin portions 16 are bonded to respective flat sides 14. As shown most clearly in FIG. 3, the fin portions 16 are in the form of metal strip which has been folded, bent, corrugated or otherwise shaped into repeated folds 18 of troughs and peak. The folds 18 are sinuous in shape and are of equal height and equal spacing between the folds. The fin portions 16 extend for a substantial portion of the length of the tube portion 12. However, the fin portions 16 fall short of the ends of the tube portion 12 and define end portions 20 which are free of the fin portions on both sides 14.
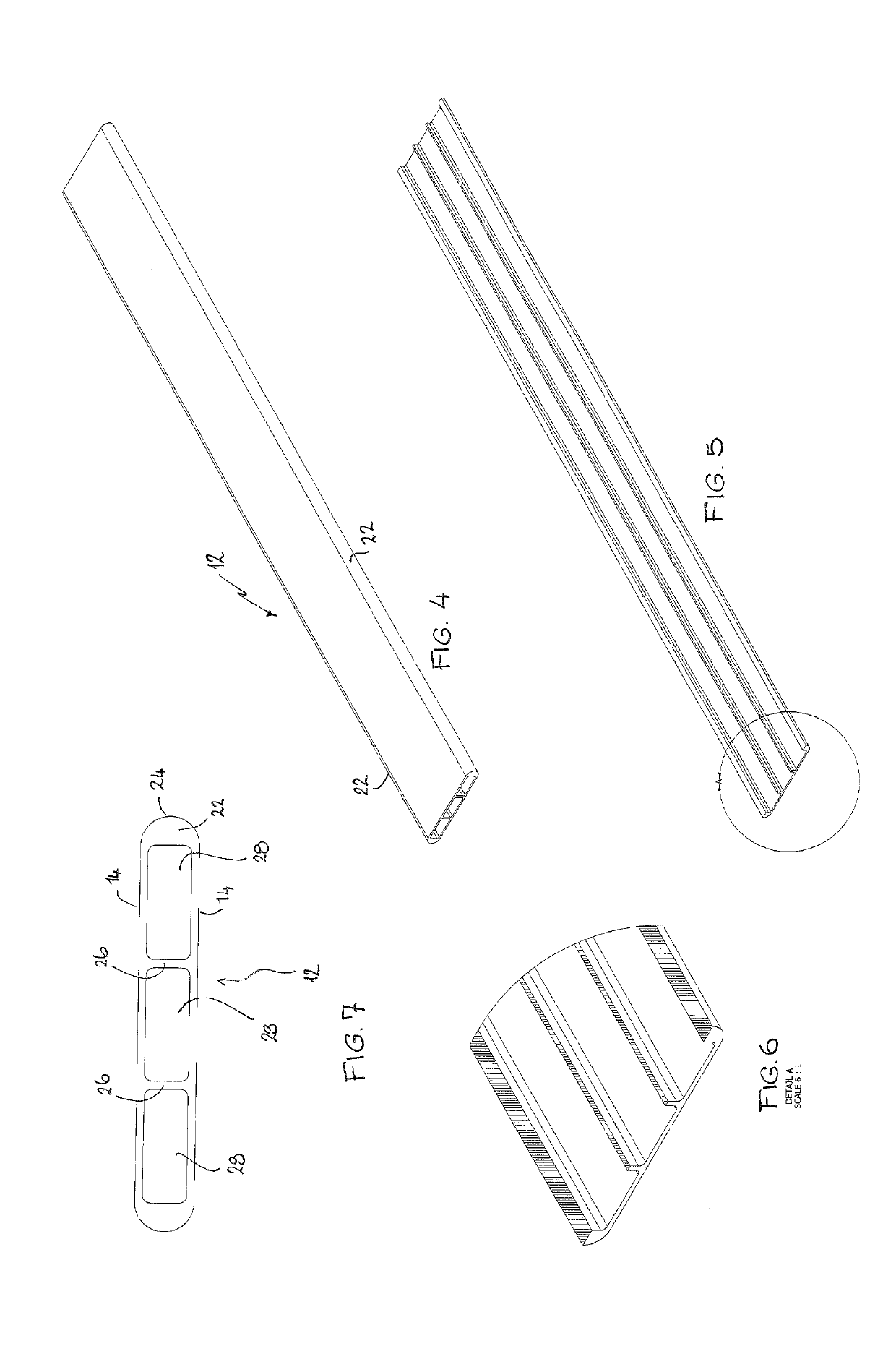
[0111]FIGS. 4-7 show the form of the tube portion 12 in greater detail. The tube portion 12 is extruded from a heat treatabl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com