Set-associative cache memory having variable time decay rewriting algorithm
a technology of variable time decay and cache memory, which is applied in the direction of memory address/allocation/relocation, digital storage, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective replacement algorithm, inability to implement, and inability to replace data which will be used soon,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
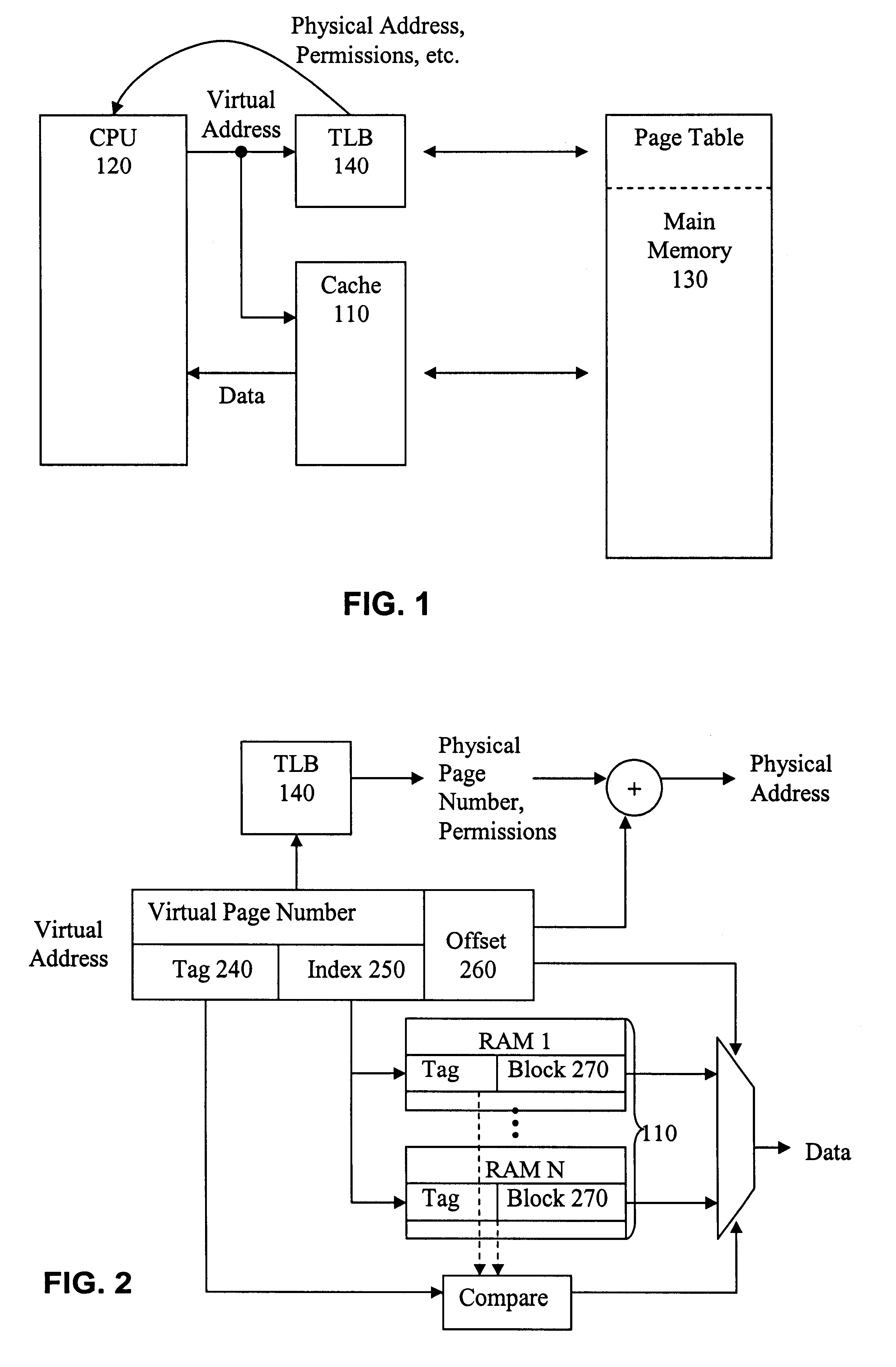
The present invention will now be described in detail with reference to the drawings, which are provided as illustrative examples of the invention so as to enable those skilled in the art to practice the invention. Notably, the figures and examples below are not meant to limit the scope of the present invention. Moreover, where certain elements of the present invention can be partially or fully implemented using known components, only those portions of such known components that are necessary for an understanding of the present invention will be described, and detailed descriptions of other portions of such known components will be omitted so as not to obscure the invention. Further, the present invention encompasses present and future known equivalents to the known components referred to herein by way of illustration.
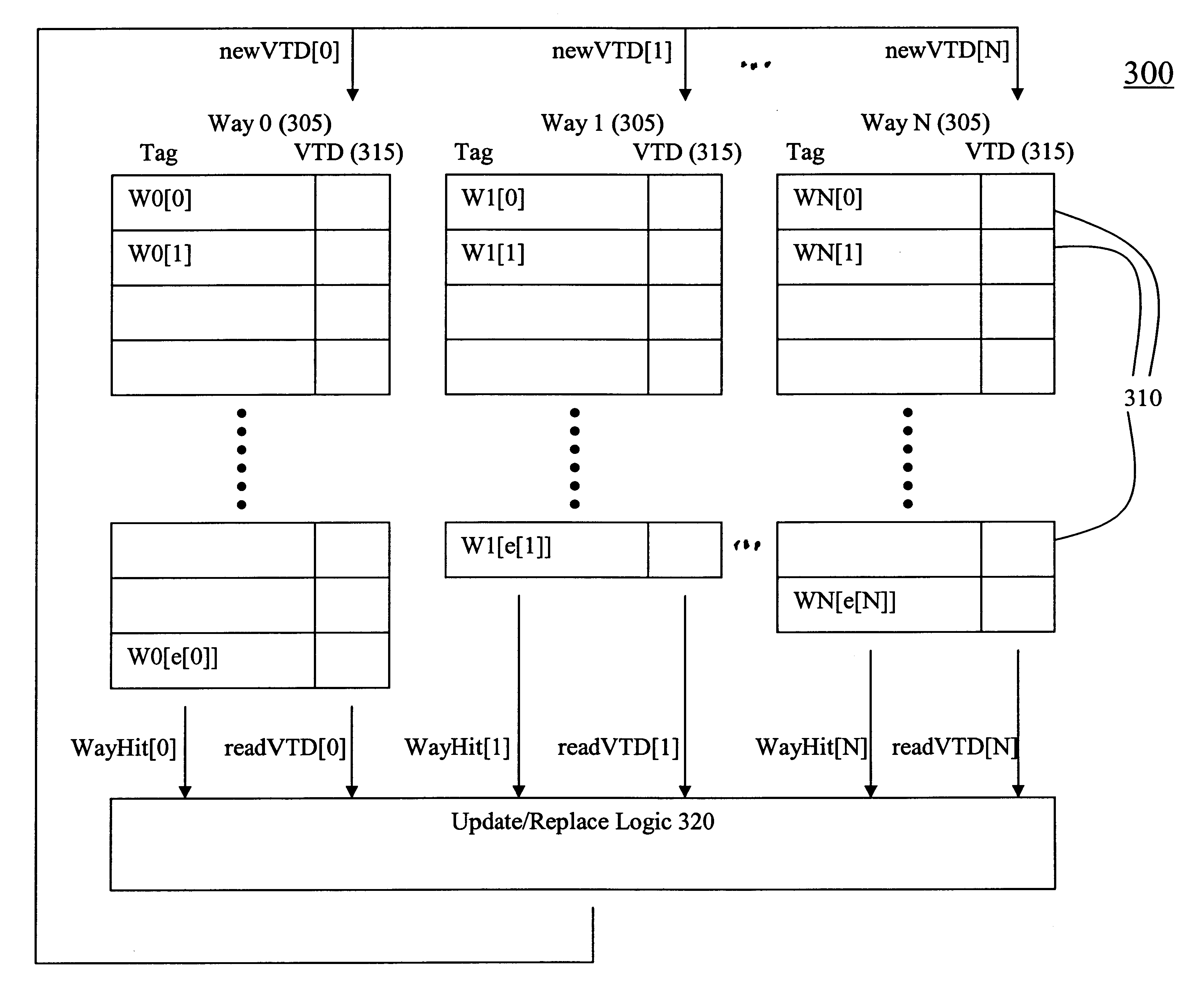
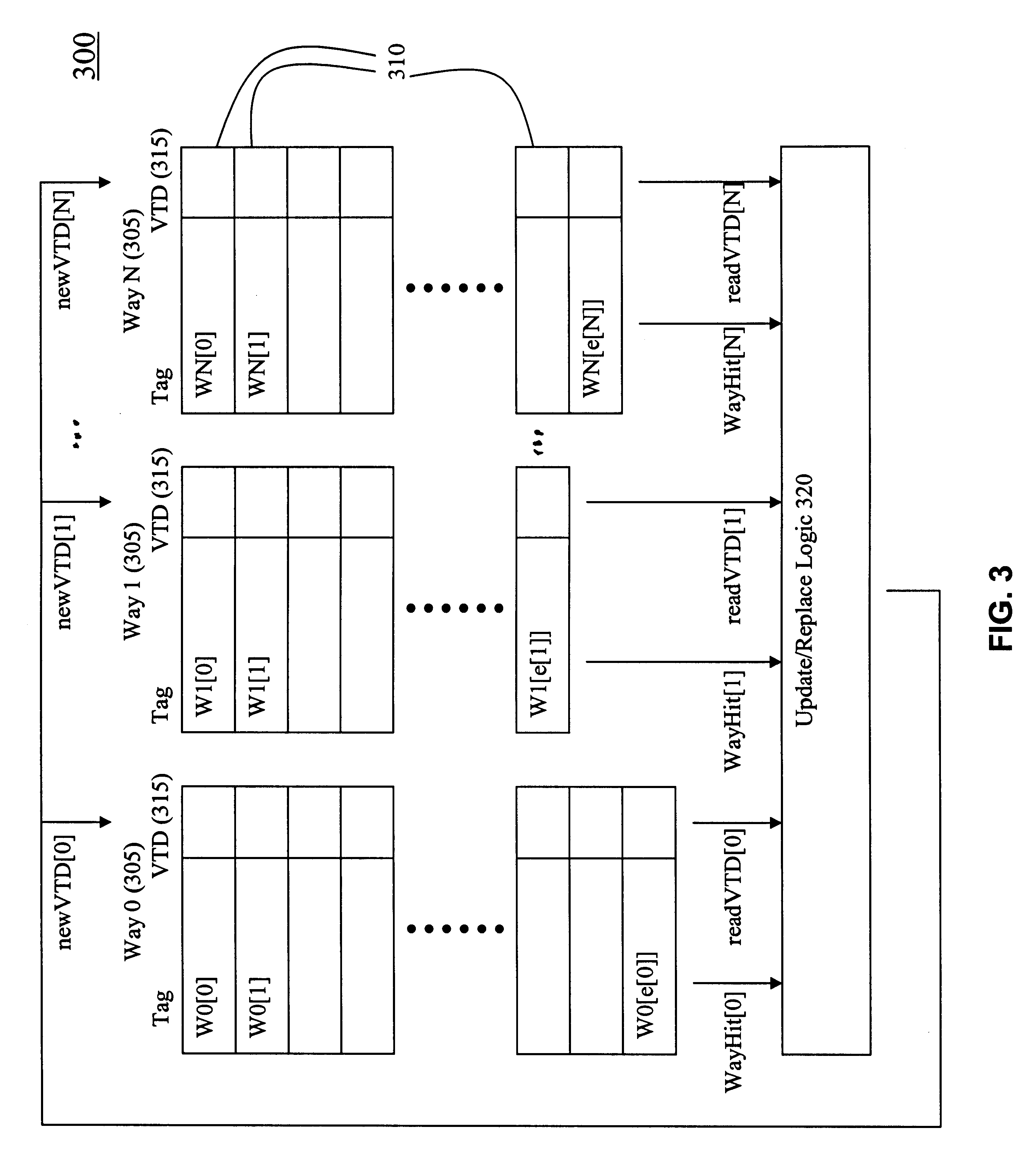
A top-level block diagram of one example implementation of a cache memory in accordance with the invention is shown in FIG. 3. As shown in FIG. 3, memory 300 is an N-W...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com