Anti-ADDL monoclonal antibody and use thereof
a monoclonal antibody and anti-addl technology, applied in the field of anti-addl monoclonal antibody, can solve the problems of incongruent mechanism and lethal effect of analogous fibrils generated in vitro on cultured brain neurons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
General Materials and Methods
[0084]ADDL Preparation. ADDLs in F12 medium (Biosource, Camarillo, Calif.) were prepared from Aβ1-42 in accordance with established methods (Lambert, et al. (2001) supra). Briefly, Aβ1-42 peptide (American Peptide Co., Sunnyvale, Calif. or California Peptide Research, Inc., Napa, Calif.) was weighed and placed in a glass vial capable of holding a sufficient quantity of HFIP (1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol) to achieve a peptide concentration of 10 mg / mL. HFIP was added to the dry peptide, the vial was capped and gently swirl to mix, and the peptide / HFIP solution was stored at room temperature for at least one hour. Aliquots (50 or 100 μL, 0.5 or 1.0 mg, respectively) of peptide solution was dispensed into a series of 1.5 mL conical centrifuge tubes. The tubes were placed in a SPEEDVAC® overnight to remove the HFIP. Tubes containing the dried peptide film were capped and stored at −70° C. in a sealed container with dessicant.
[0085]Prior to use, the Aβ1-...
example 2
Isolation of Mouse Antibody Variable Region Sequences
[0092]The cDNAs coding for the variable domains of the 20C2 mouse antibody were cloned and sequenced following a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using specially designed primers that hybridize to the 5′-ends of the mouse constant regions and to the murine leader sequences upstream of the V regions. This ensured that the mouse variable region sequences obtained were complete and accurate. In short, mRNA was extracted from mouse hybridoma cell lines using the QIAGEN® OLIGOTEX® Direct mRNA Mini Kit and subsequently converted to cDNA using a first-strand cDNA synthesis kit. The cDNA was then used as template in PCR reactions to obtain the antibody variable region sequences.
[0093]To obtain the light chain variable region sequence, eleven independent PCR reactions were set up using each of the eleven light chain 5′ PCR primers (MKV-1 to MKV-11) and the 3′ PCR primer MKC-1 (Table 1).
[0094]
TABLE 1SEQ5′IDPrimerSequenceNO:MKV-1GAT CTC TAG A...
example 3
Humanization of Mouse Anti-ADDL Antibody Variable Region Sequences
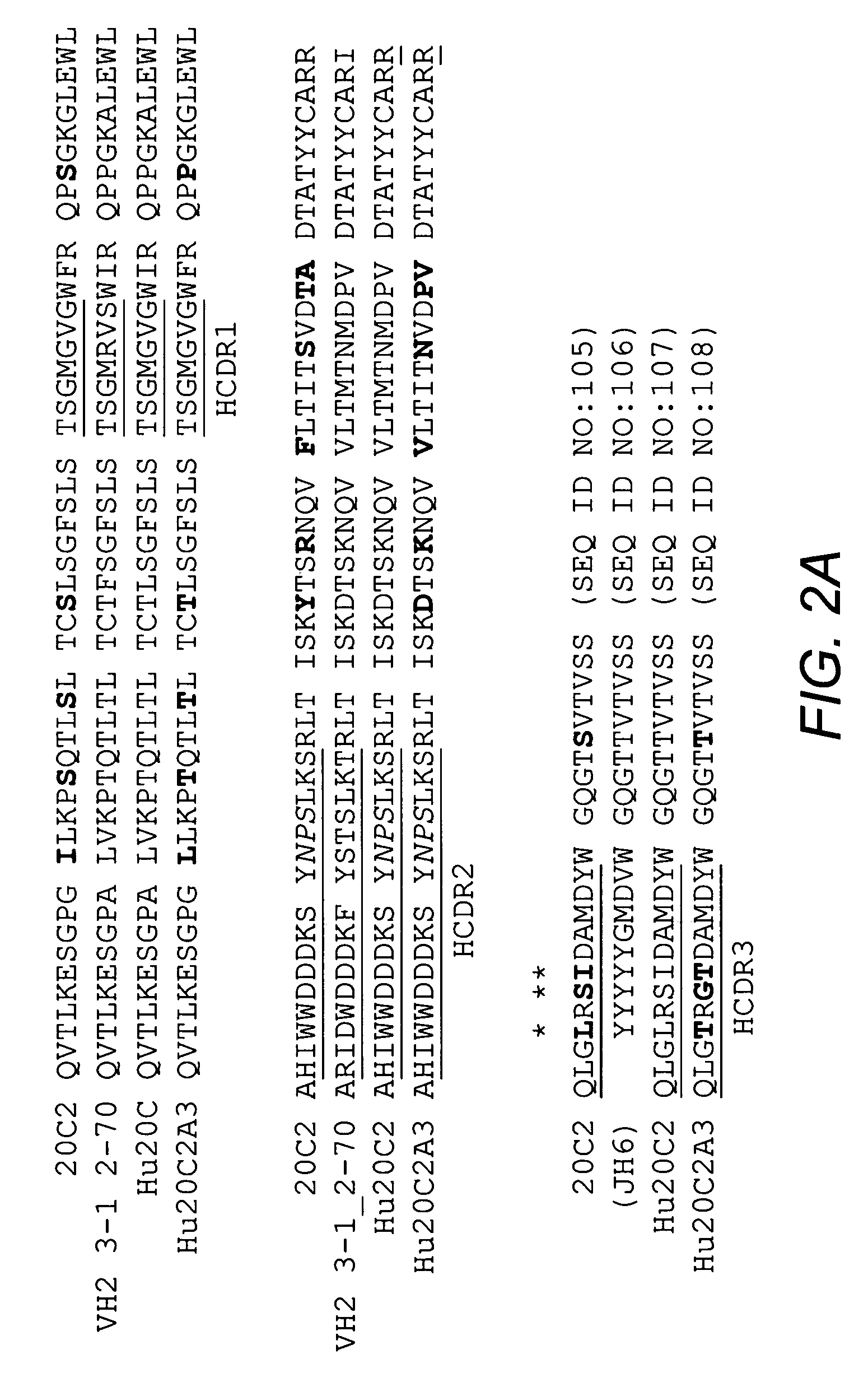
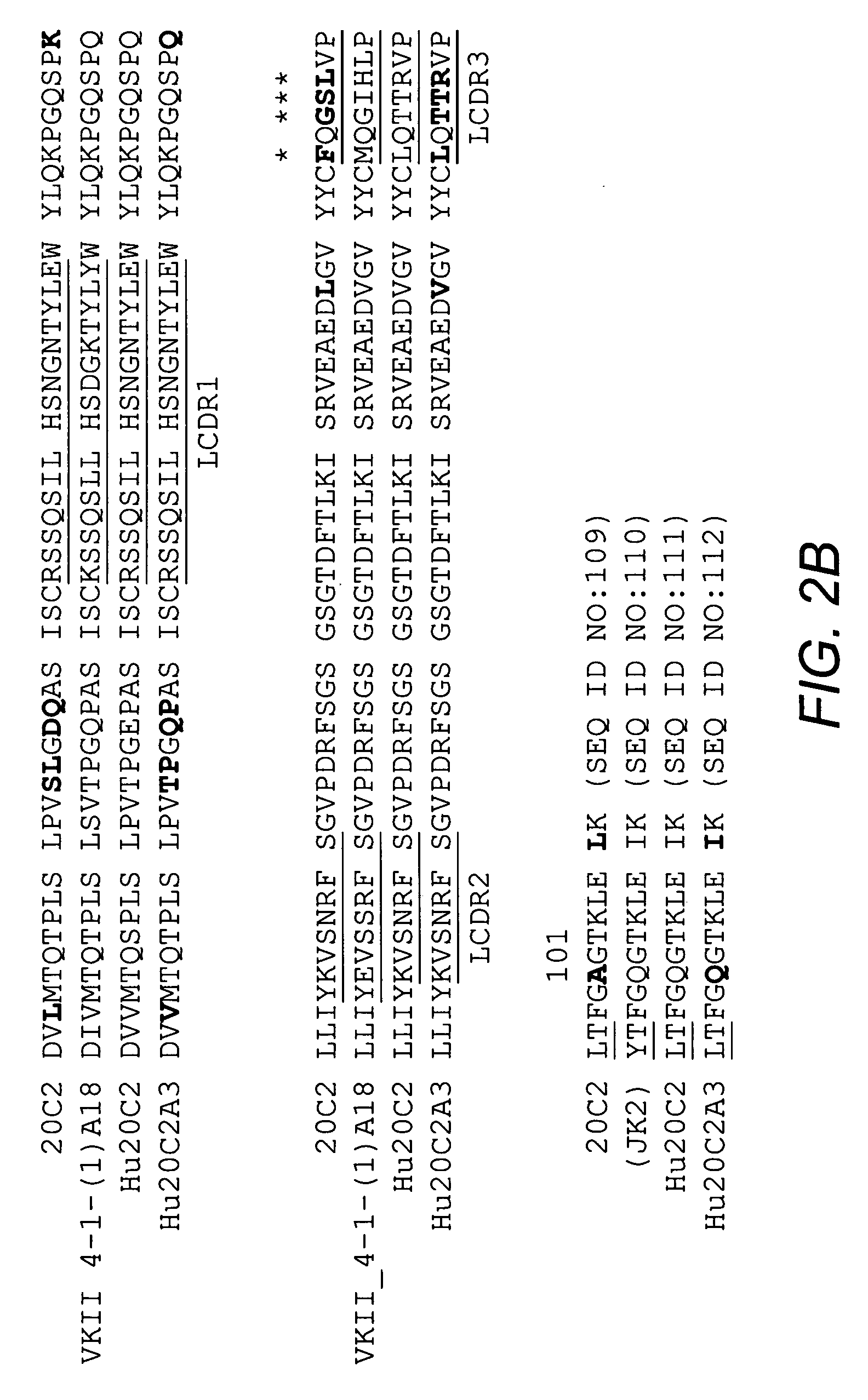
[0098]Mouse antibody heavy and light variable domain nucleic acids obtained from mouse hybridoma cell line 20C2 were humanized using a CDR grafting approach. It will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that humanization of mouse antibody sequences can maximize the therapeutic potential of an antibody by improving its serum half-life and Fc effector functions thereby reducing the anti-globulin response.
[0099]Humanization by CDR grafting was carried out by selecting the human light and heavy chain variable regions from the NCBI protein database with the highest homology to the mouse variable domains. The mouse variable region sequences were compared to all human variable region sequences in the database using the protein-protein Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). Subsequently, mouse CDRs were joined to the human framework regions and the preliminary amino acid sequence was analyzed. All differences betwee...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com