Data transfer optimization through destination analytics and data de-duplication
a data transfer and destination technology, applied in the field of data transfer, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of transferring large quantities of data across slow or congested connections, and increasing the difficulty of transferring large quantities of data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
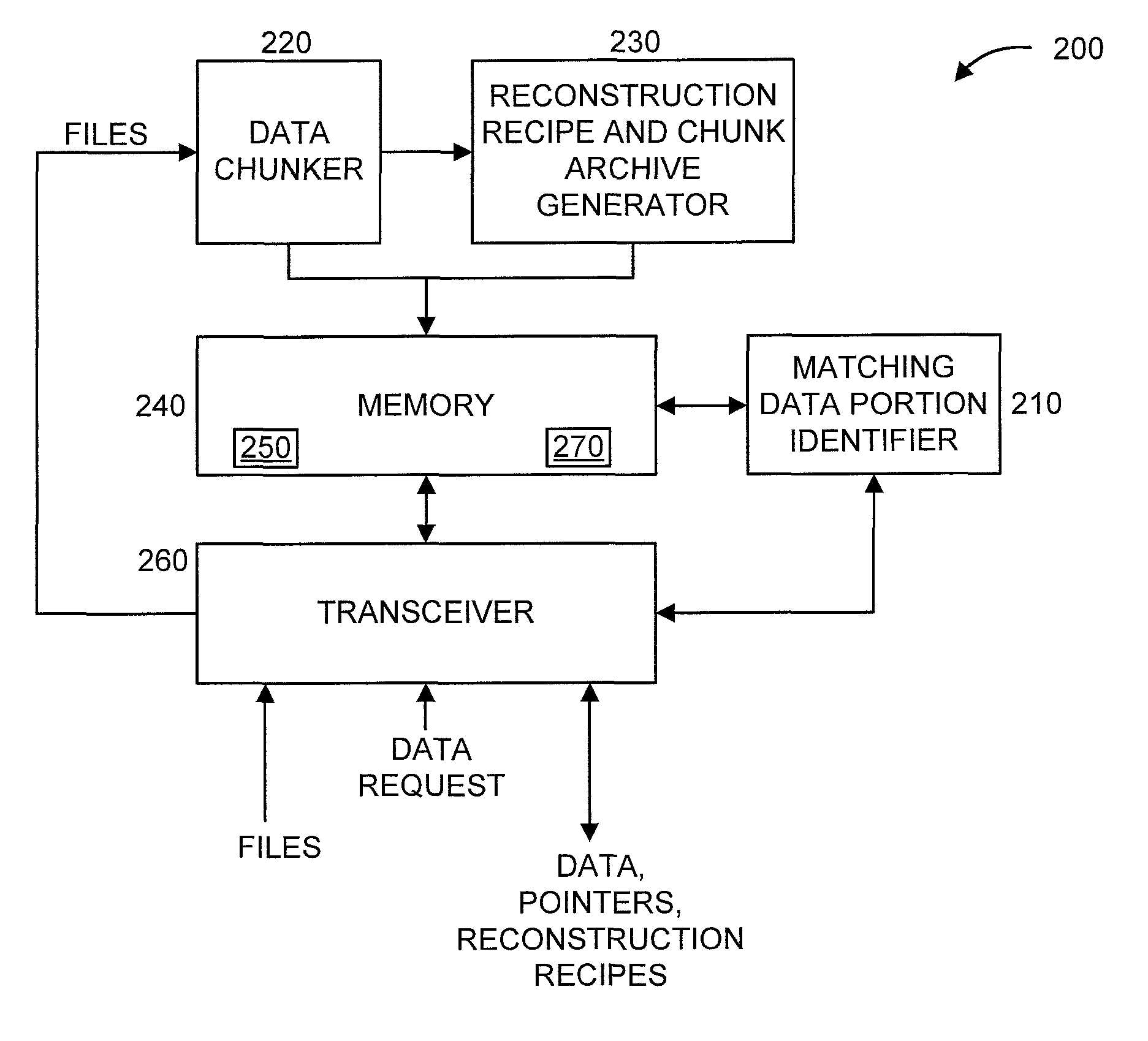
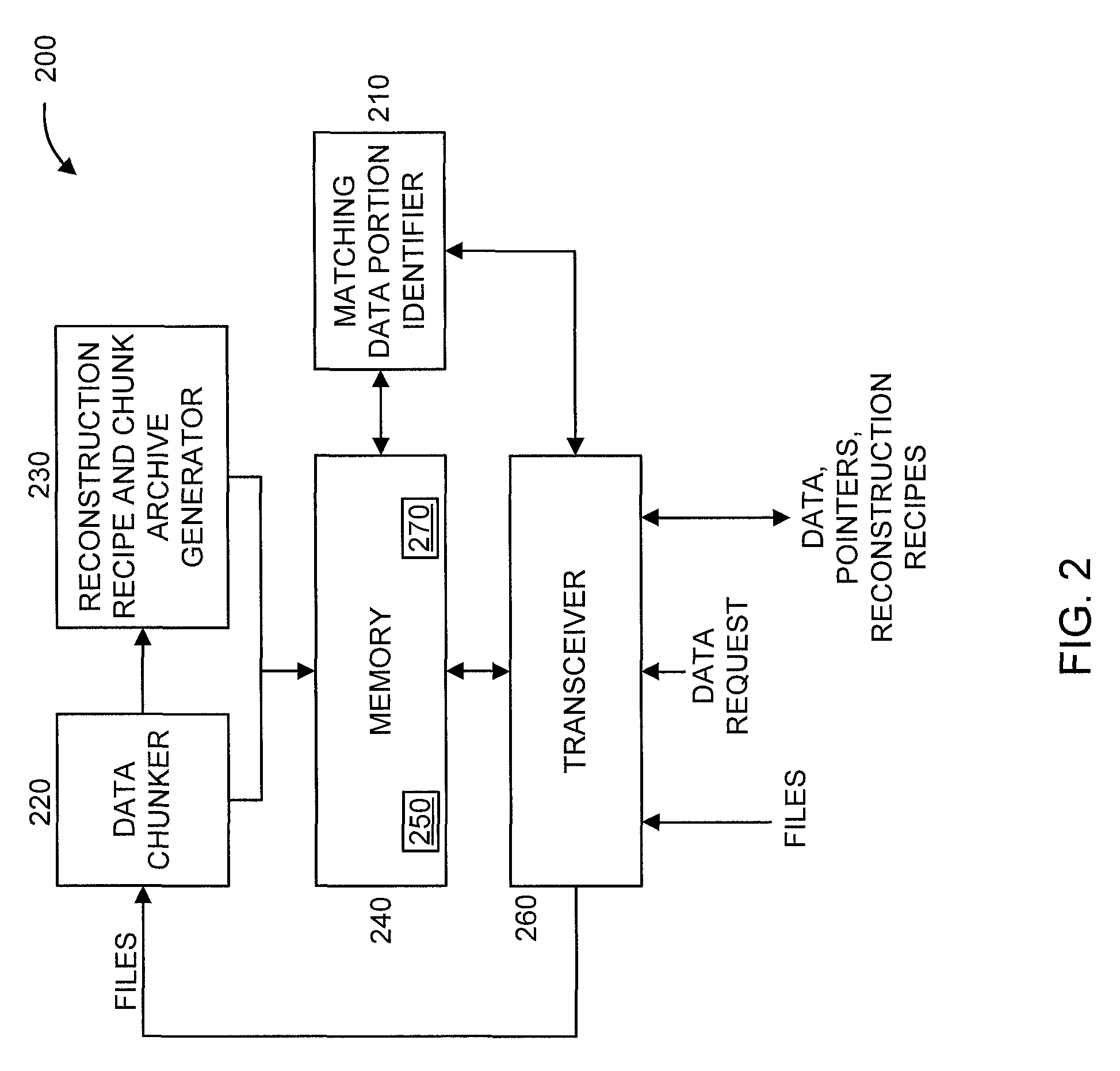
[0016]The present principles are directed to data transfer optimization through destination analytics and data de-duplication. The present principles reduce data re-transmission by strategically maintaining data warehouses at intermediate nodes. When a user wishes to transfer data between two nodes, we check to see if some or all of that data already exists at a node closer to the recipient. In an embodiment, we then only send the following: (1) the data not existing on suitable intermediate nodes; and (2) the instructions required to assemble the original data. Such a policy will increase transfer speeds and reduce transmission costs. It should be noted that the preferred embodiment obviates the need to synchronize databases between nodes.
[0017]In an embodiment, the present principles use a chained de-duplication strategy that incorporates dynamic chunking optimization to reduce the size of data transmission. As used herein, the term “chained de-duplication strategy” refers to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com