Molded surface fastener
a synthetic resin and surface fastener technology, applied in the direction of snap fasteners, press-button fasteners, buckles, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to secure a predetermined degree of engaging strength, difficult to remove the hook from the hook, and the density of engaging elements on the substrate sheet surface is necessarily limited to a considerable low degree, so as to achieve the effect of convenient removal of the hook
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
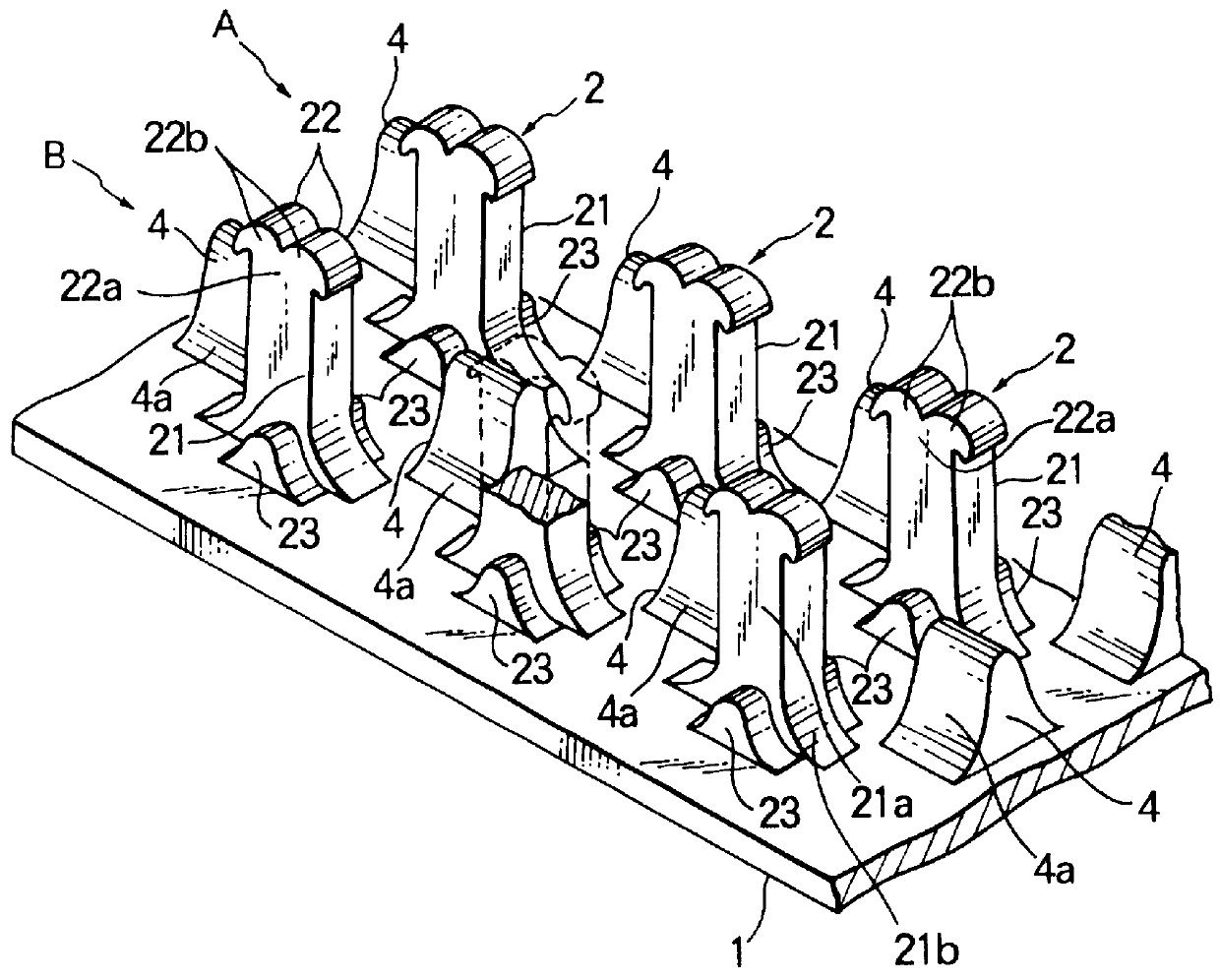
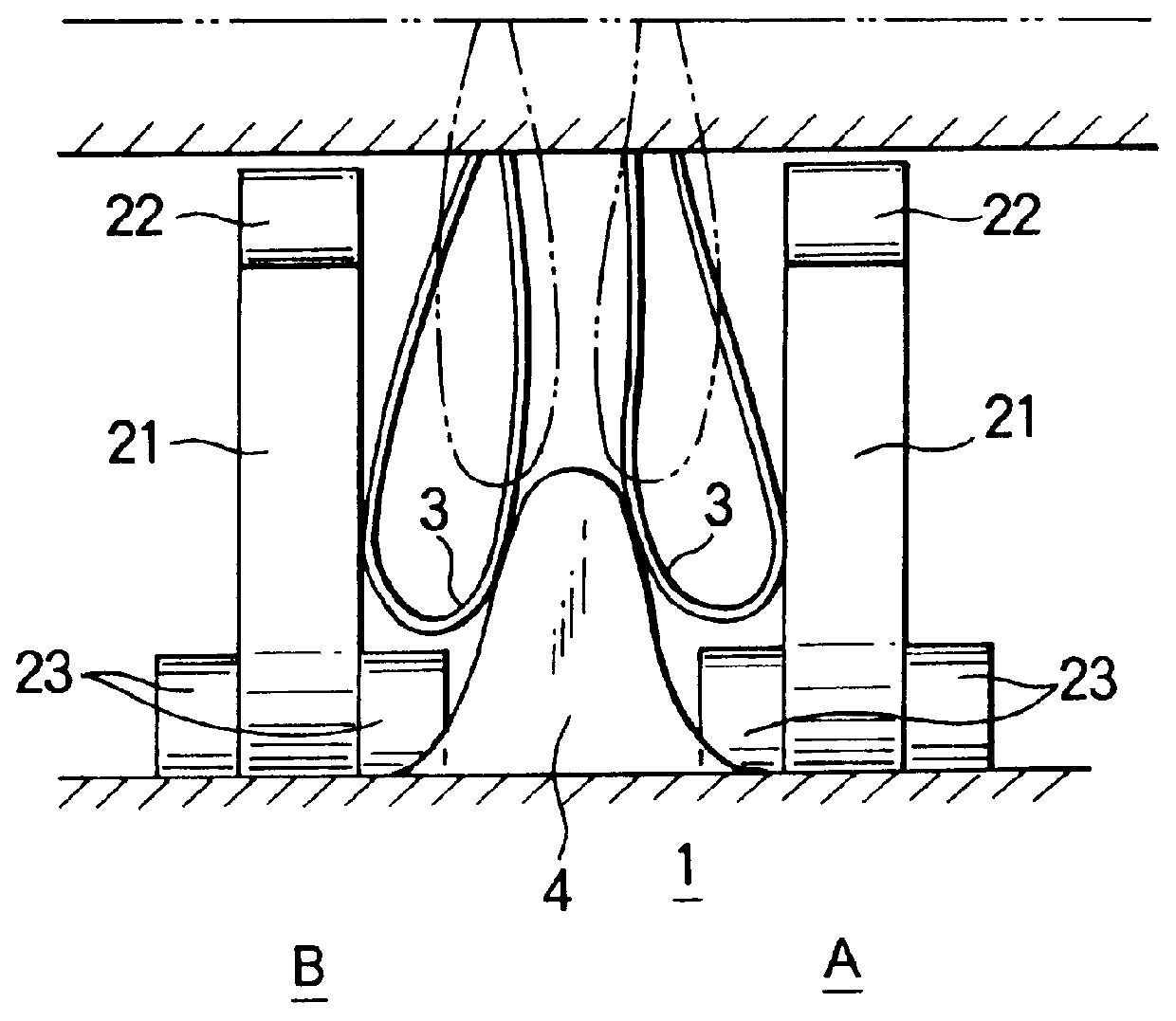
According to the molded surface fastener of the first embodiment, since the loops 3 entering at random between a multiplicity of the engaging elements 2 are parted toward the adjacent engaging elements 2 by the parting guide member 4 as shown in FIG. 2, the loopes 3 entering between the engaging element rows A, B are parted toward any of the right and left engaging element rows A, B to increase the rate of catching the loops 3 by the engaging elements 2, thus increasing the rate of engagement remarkably to obtain a predetermined engaging force. Further, contrary to the conventional surface fasteners which are easy to be torn between rows of the engaging elements, it is possible to prevent the molded surface fastener from being torn during the ejecting of the molded surface fastener from the mold or during the sewing of the molded surface fastener
or in use since the parting guide members 4 are integrally formed on the substrate sheet 1 at positions between the engaging element rows a...
second embodiment
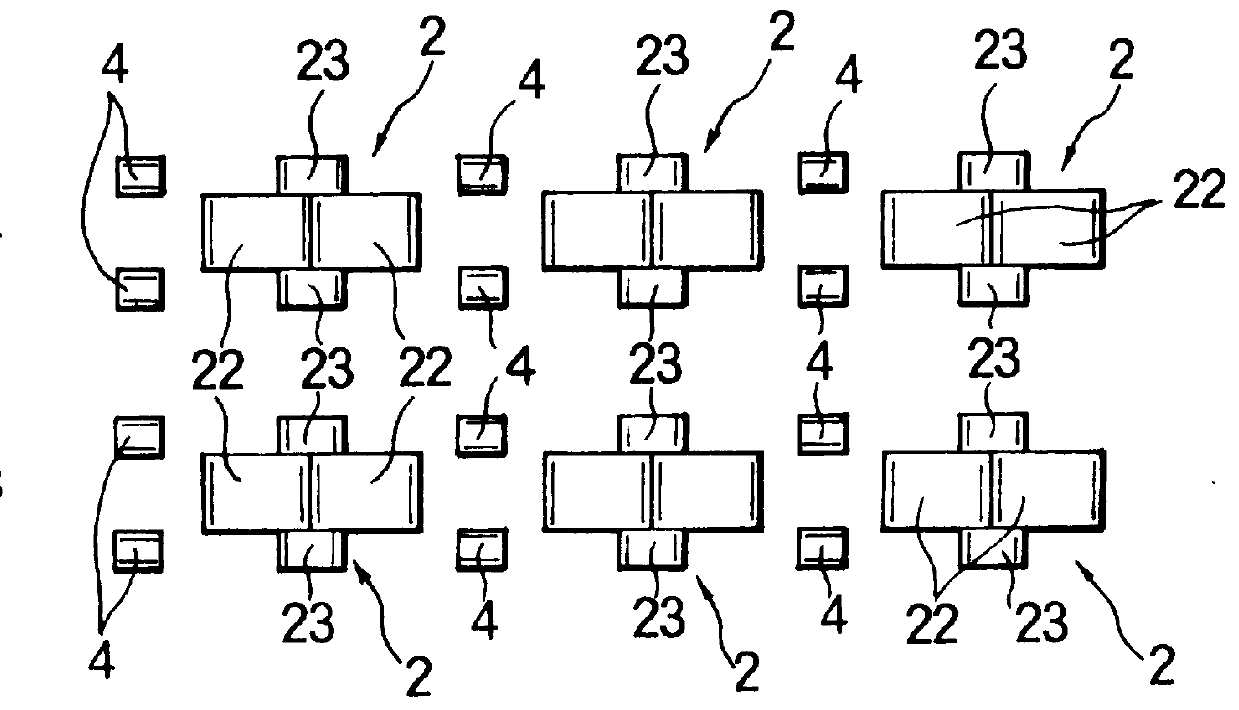
In the second embodiment, the engaging element 2 is composed of a pair of members 2-1, 2-2. Each member 2-1, 2-2 comprises a stem portions 21-1, 21-2 each having a rear surface 21c rising along a gentle curve from the upper surface of the substrate sheet 1 and a front surface 21d rising initially in a predetermined curvature and then perpendicularly from the upper surface of the substrate sheet 1 and composing a stem 21, and a hook 22 extending from the stem 21 and terminating in a downwardly directed end. The two engaging members 2-1, 2-2 are integrally joined partly at their respective hooks 22, 22 and at their respective stem portions 21-1, 21-2, as indicated by diagonal dotted lines in FIG. 7, with the hooks 22, 22 extending from the respective stem portions 21-1, 21-2 in opposite directions. In the illustrated example, each stem 21 has on its lower outside surfaces reinforcing ribs 23. A multiplicity of such engaging elements 2 are formed on the upper surface of the substrate s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| durability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com