High speed zero DC power programmable logic device (PLD) architecture
A technology for programming logic and devices, applied in logic circuits, logic circuits using basic logic circuit components, and electro-solid devices, etc., and can solve problems such as sense amplifier consumption, high power, and incorrect PLD reading.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
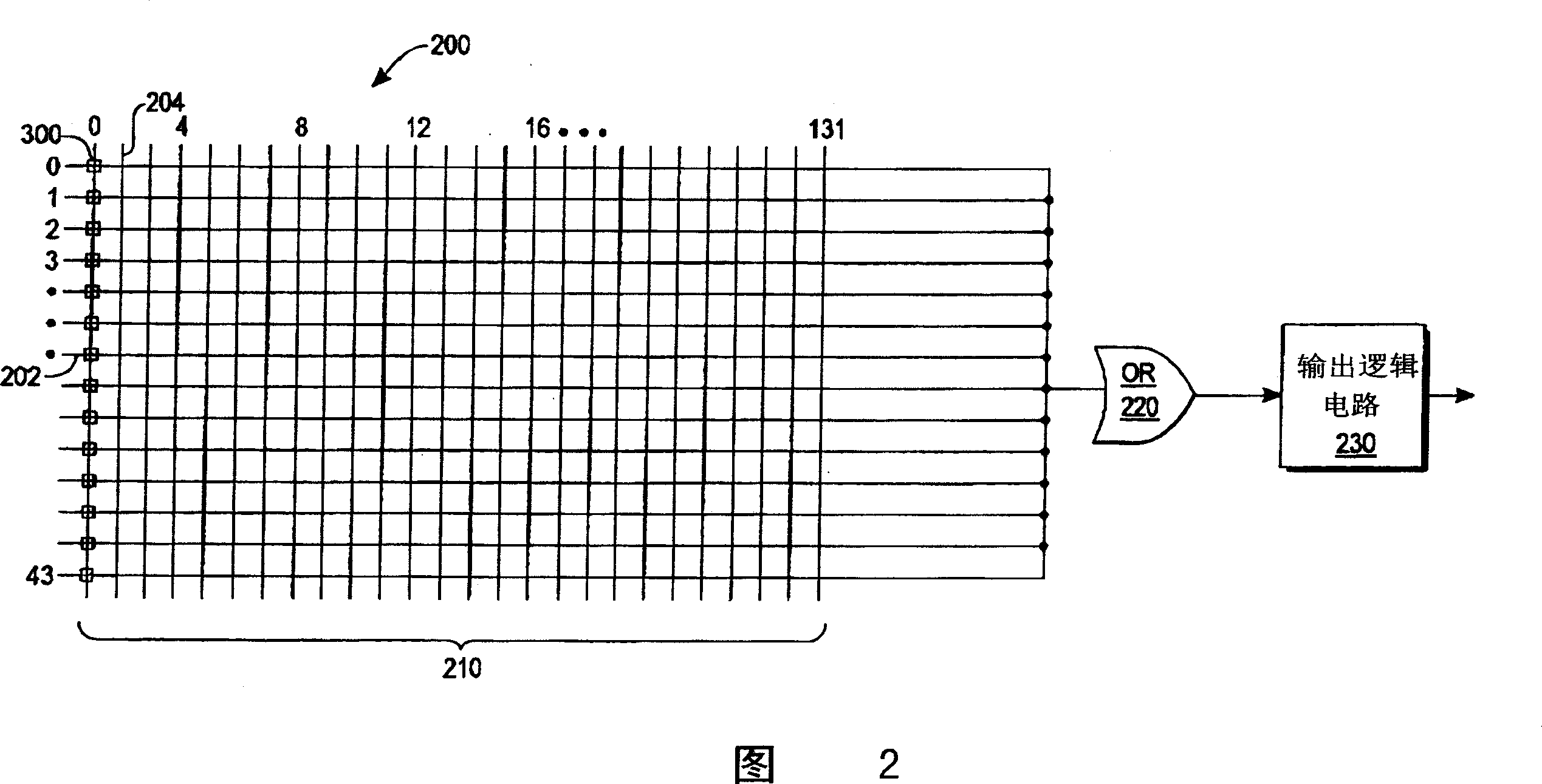
[0023] Referring to FIG. 2 , a new PLD structure 200 is implemented by using PLD unit cells as basic building blocks to construct a programmable array. The PLD structure 200 has a programmable array 210 , an array of OR gates 220 and an output logic circuit 230 like any prior art PLD. However, the programmable array 210 of the PLD 200 is configured by using a plurality of PLD unit cells 300 . The PLD unit cell 300 will be described in detail later with reference to FIG. 3 . In a preferred embodiment, the PLD structure 200 has 44 rows and 132 columns.
[0024]In FIG. 2 , each PLD unit cell 300 is represented by a square located at the intersection of each row 202 and each column 204 . The total number of rows 202 and columns 204 of PLD unit cells 300 in a PLD device is a matter of design choice and may vary according to user needs. The PLD structure 200 in FIG. 2 is an example with 5808 cells arranged in a programmable array 210 having 44 rows and 132 columns. Each column 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com