Information recording medium and method for producing the same
A technology of information recording and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the fields of optical record carrier manufacturing, temperature recording method, data recording, etc. It can solve the problems of inability to ensure the stability of the amorphous phase, the inability to realize the medium, and the drop in the crystallization temperature, so as to achieve record preservation Excellent performance, excellent record retention, and high erasing performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
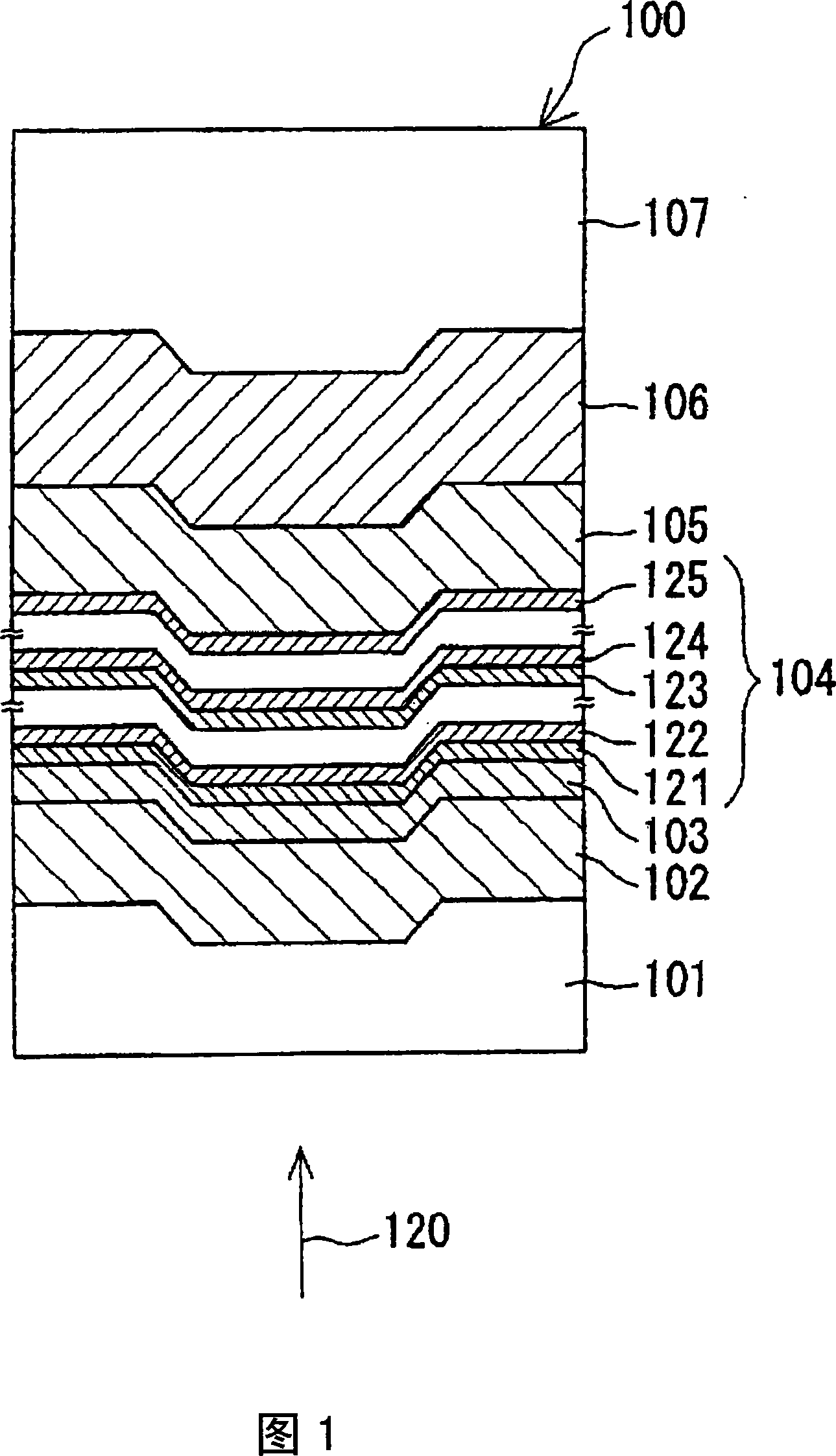
[0047] As the first embodiment of the present invention, an example of an optical information recording medium that performs recording and reproduction of information using laser light will be described. Fig. 1 shows a partial cross section of the information recording medium.
[0048] The information recording medium 100 shown in FIG. 1 has a structure in which a reflective layer 106 is formed on the surface of one side of the substrate 107, a dielectric layer 105 is formed on the surface of the reflective layer 106, and a dielectric layer 105 is formed on the surface of the dielectric layer 105. The recording layer 104 is formed on the surface, the interface layer 103 is formed on the surface of the recording layer 104, the dielectric layer 102 is formed on the surface of the interface layer 103, and the cover layer 101 is formed. Here, the recording layer 104 includes structural layers from the first to the M-th, starting from the dielectric layer 125 side, an M-th structure la...
Embodiment approach 2
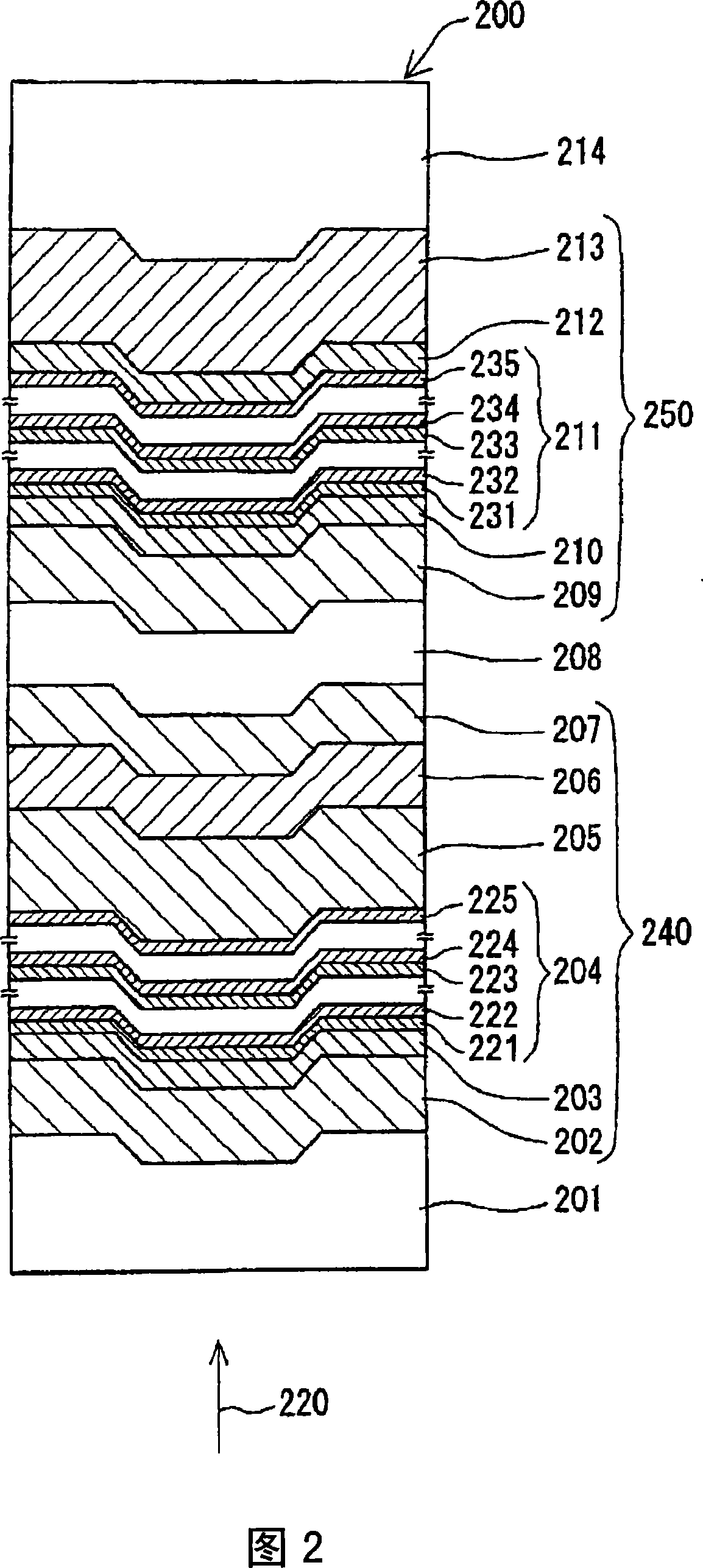
[0161] As the second embodiment of the present invention, an example of an information recording medium will be described. Fig. 2 shows a partial cross-section of the information recording medium.
[0162] The information recording medium 200 shown in FIG. 2 has a structure in which a substrate 214, an intermediate layer 208, a first information layer 240, and a cover layer 201 are arranged in this order. In order to distinguish the two information layers and the recording layer contained therein in relation to the medium 204 of the structure shown in FIG. 2, the layer closer to the incident light is referred to as "first" and the layer farther away is referred to as " 2nd".
[0163] More specifically, the second information layer 250 is formed by sequentially arranging a reflective layer 213, a dielectric layer 212, a second recording layer 211, an interface layer 210, and a dielectric layer 209 on one surface of the substrate 214. Among them, the second recording layer 211 inclu...
Embodiment approach 3
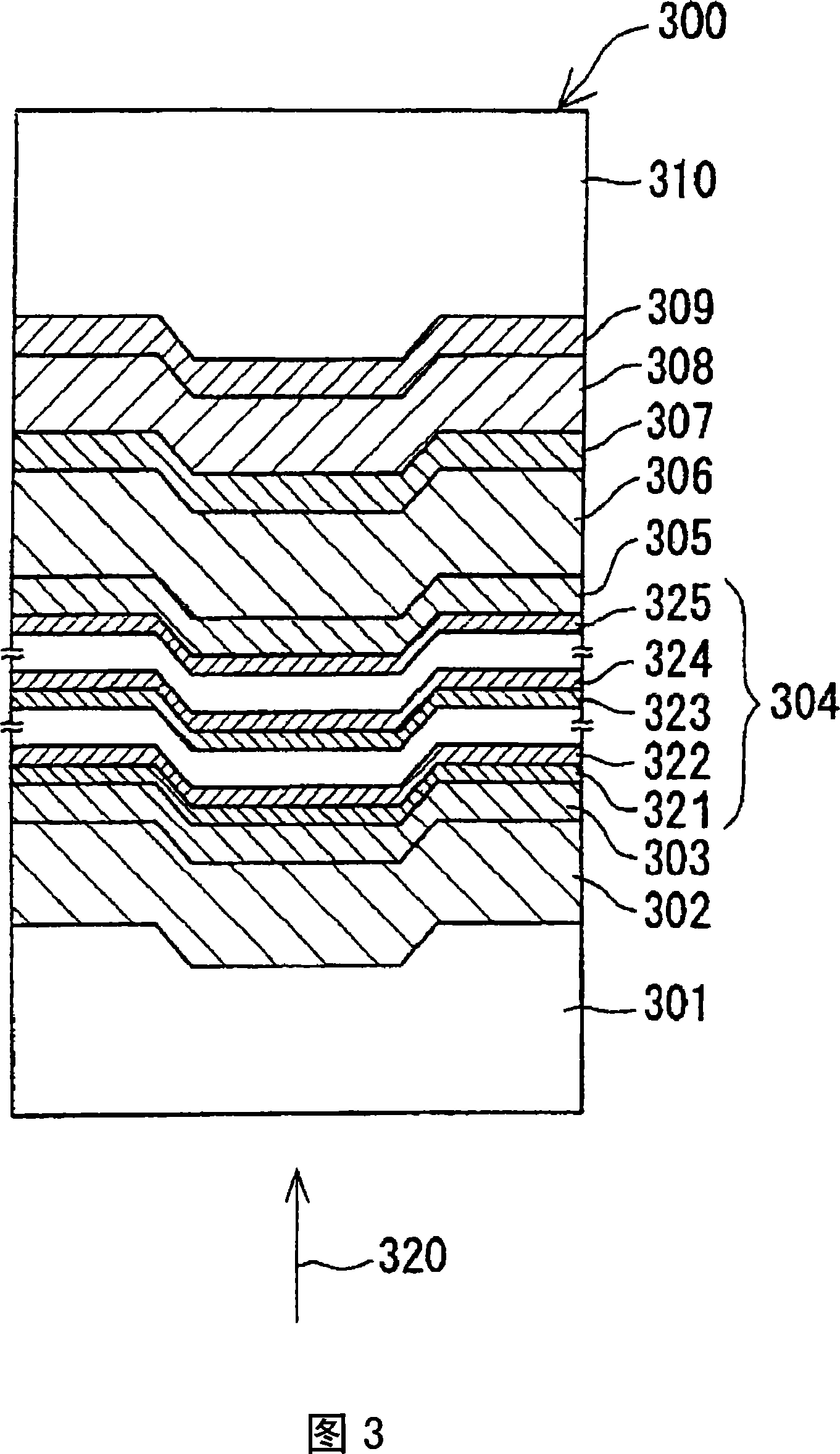
[0218] As the third embodiment of the present invention, an example of an information recording medium will be described. Fig. 3 shows a partial cross-section of the information recording medium.
[0219] The information recording medium 300 shown in FIG. 3 has a dielectric layer 302 formed on one surface of a substrate 301, an interface layer 303 is formed on the surface of the dielectric layer 302, and a recording layer 304 is formed on the surface of the interface layer 303. The interface layer 305 is formed on the surface of the recording layer 304, the dielectric layer 306 is formed on the surface of the interface layer 305, the light absorption correction layer 307 is formed on the surface of the dielectric layer 306, and the light absorption correction layer 307 The reflective layer 308 is formed on the surface, and the dummy substrate 310 is bonded by the adhesive layer 309. The recording layer 304 includes the first to the Mth structural layers, and the first structural l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com