Needle nailing force self-adjusting energy-storage clamp-shaped stapler
An energy storage type, stapler technology, applied in binding and other directions, can solve the problems of limited space for human hands, increased force arm, limited structure space, etc., to achieve obvious labor-saving effect, prolong working life, and high binding efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
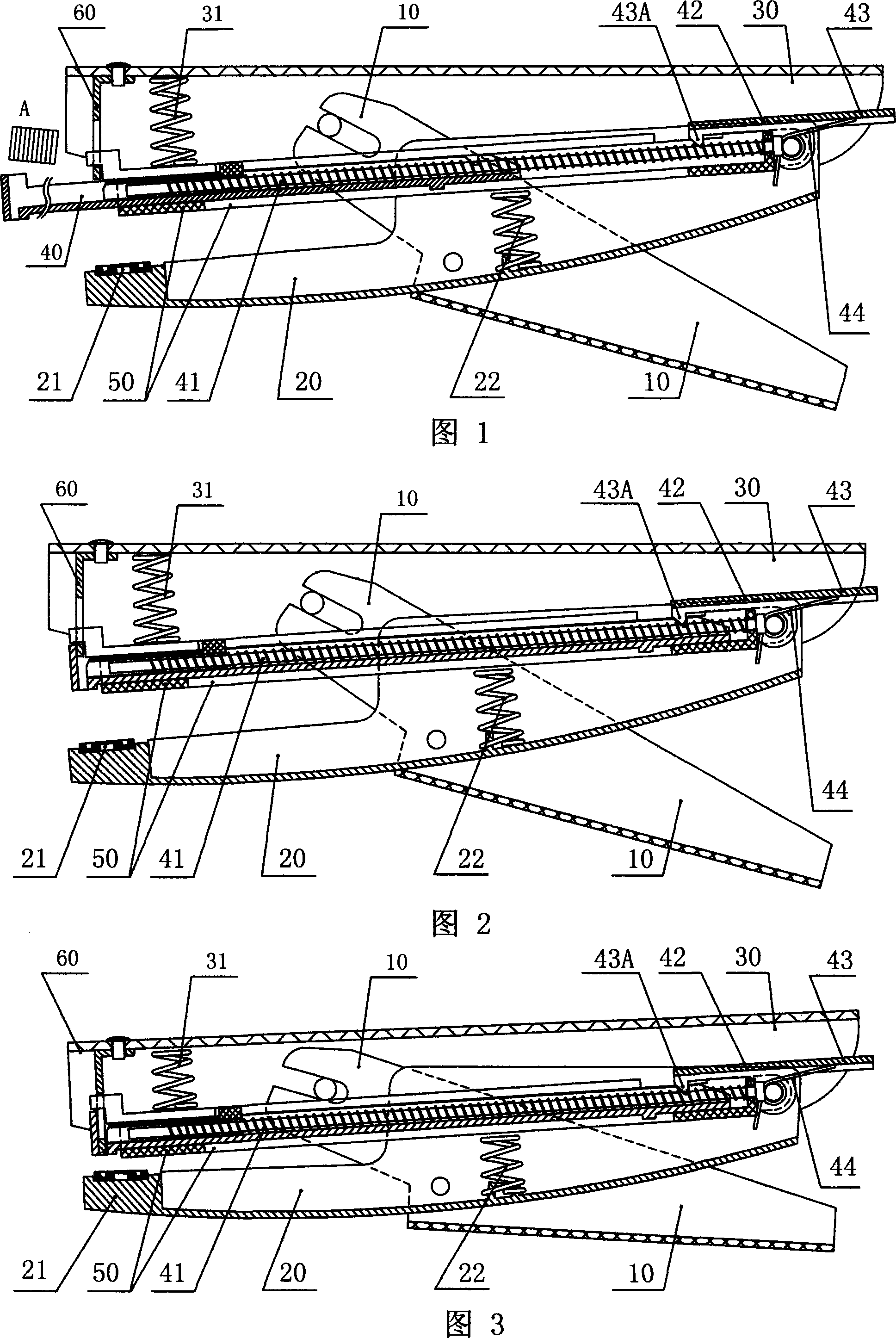
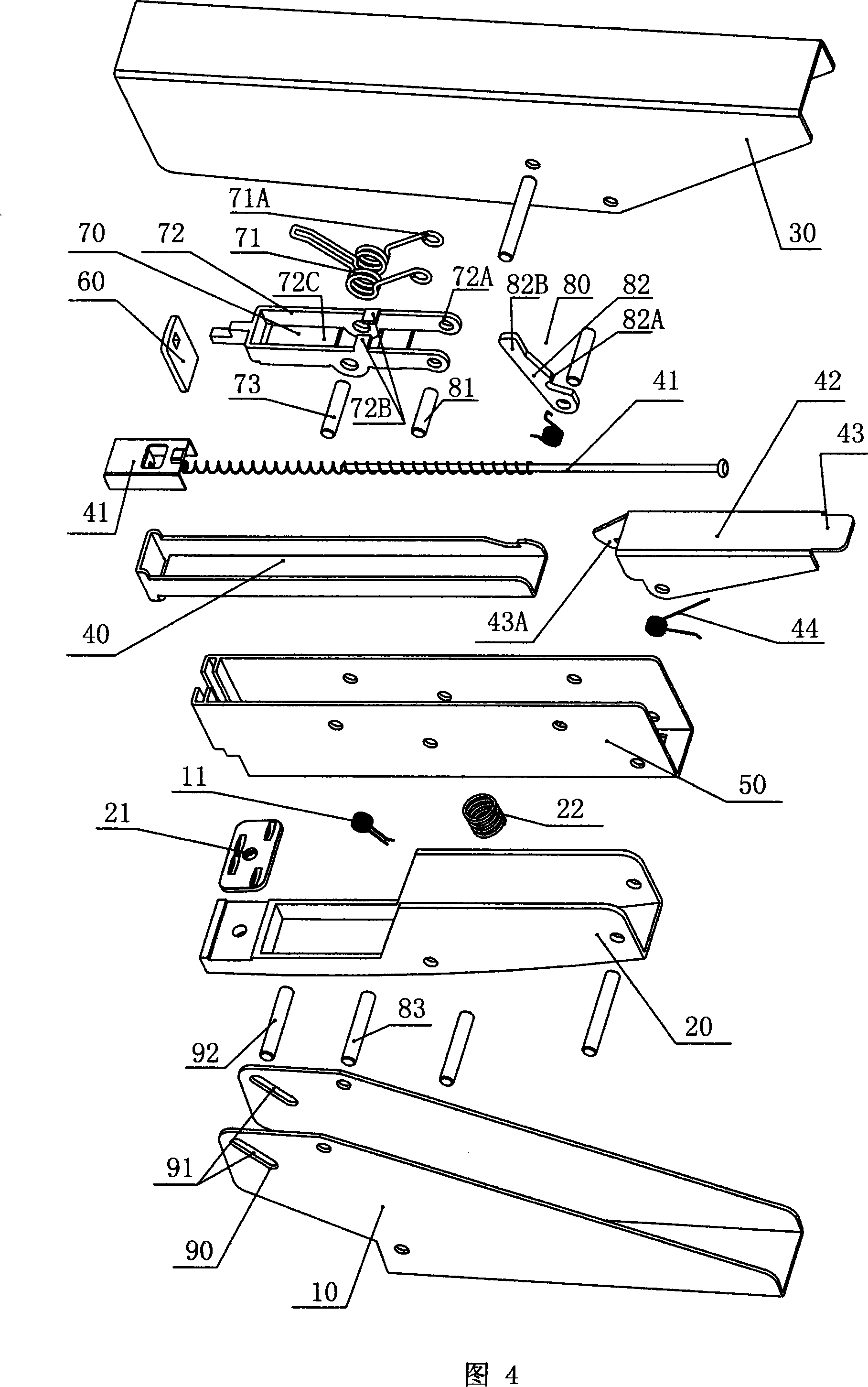
[0047] Figures 4 to 8 show the three-dimensional schematic diagram of the dismantled structure of Embodiment 1 of the energy storage type pliers-type stapler of the present invention, and the cross-sectional view of the assembly structure when the thick paper and thin paper are pressed tightly and the nails are operated. schematic diagram. Embodiment 1 includes a handle 10, a base 20, an upper cover 30, a box 50 with an elastic needle pusher 41 or a book needle slot 40 slidably fitted therein, and a staple sheet for pressing the book needle A on the end of the elastic needle pusher 41 60, on the base 20, a needle plate 21 is provided at the position where the corresponding nail sheet 60 falls, and a bottom spring 22 is also provided on the base 20; the box 50 is hinged at the rear of the base 20, The upper cover 30 is on the box 50, the upper cover 30 and the box 50 are coaxially hinged on the base 20, the middle part of the handle 10 is hinged on the middle part of the base 2...
Embodiment 2
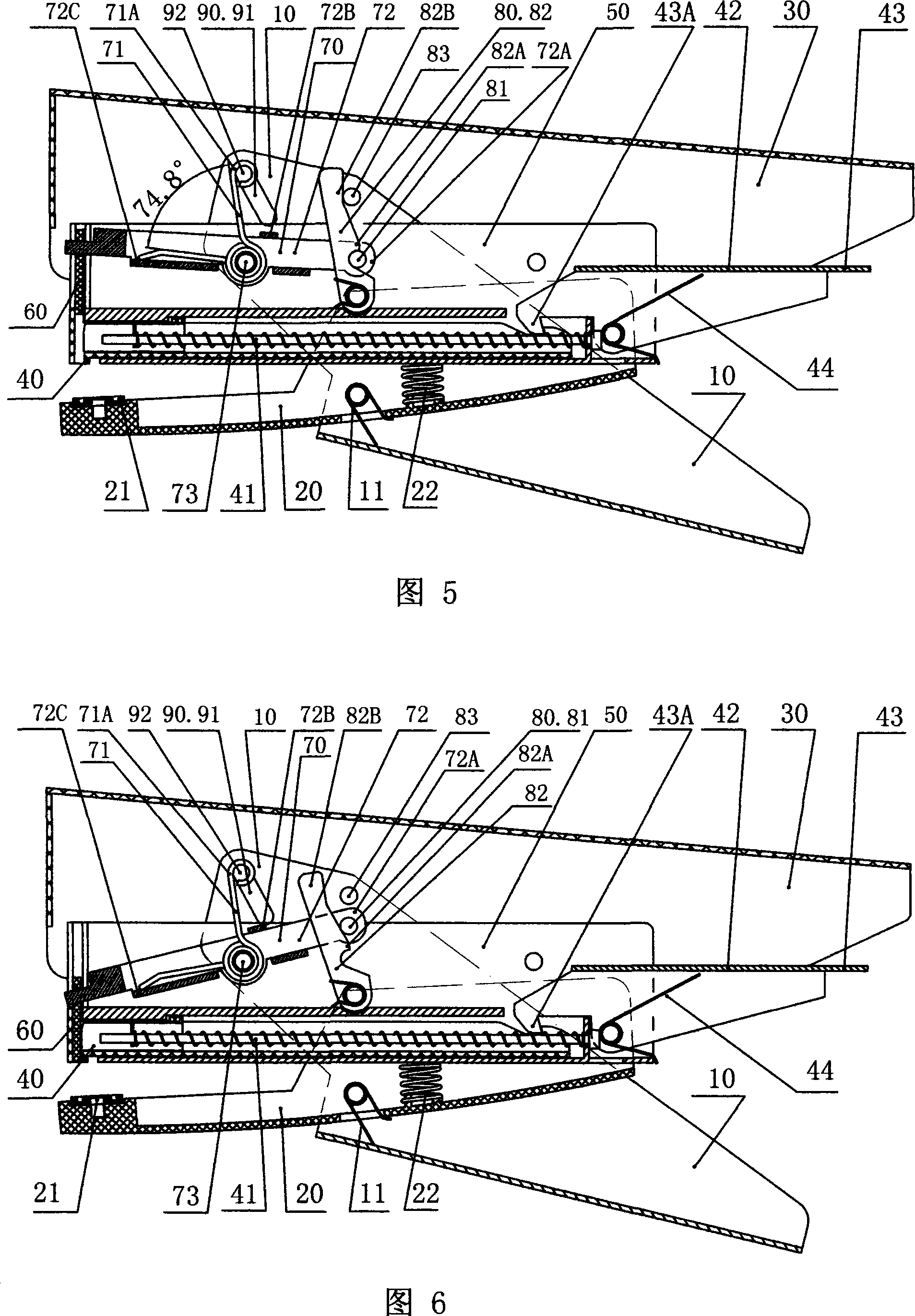
[0056] Figures 9 to 13 are the three-dimensional schematic diagrams of the disassembled structure of Embodiment 2 of the energy storage type pliers-type stapler of the present invention, and the cross-sectional schematic diagrams of the assembled structure when pressing thick paper and thin paper and performing staple operations. The structure of embodiment 2 is basically the same as that of embodiment 1, but the following structure is different from embodiment 1: that is, the lock head 81 is arranged on the outer section of the limit lever 72 that deviates from the hinge axis 73 .
[0057] Figures 10 and 11 are respectively schematic cross-sectional views of the assembled structure in Embodiment 2 when the thick paper is pressed tightly and the staples are operated. It can be seen from the figure that due to the support of thick paper, the driving lever 83 on the top of the handle 10 is at the lower position of the switch paddle 82B, and the power transmission shaft 92 on the ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Figures 14 to 18 are the three-dimensional schematic diagrams of the disassembled structure of Embodiment 3 of the energy-storage pliers-type stapler of the present invention, and the cross-sectional schematic diagrams of the assembled structure when pressing thick paper and thin paper and performing staple operations. The structure of embodiment 3 is basically the same as that of embodiment 2, but the following structure is different from that of embodiment 2: that is, the firing outer end of the torsion spring 71 is directly hooked on the nail plate 60 .
[0061] Figures 15 and 16 are respectively schematic cross-sectional views of the assembly structure in embodiment 3 when the thick paper is pressed tightly and the nails are operated. It can be seen from the figure that due to the support of thick paper, the driving lever 83 on the top of the handle 10 is at the lower position of the switch paddle 82B, and the power transmission shaft 92 on the top of the handle 10 m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com