A pad retention device
A technology for retaining devices, pads, applied in the direction of axial brakes, brake types, brake components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
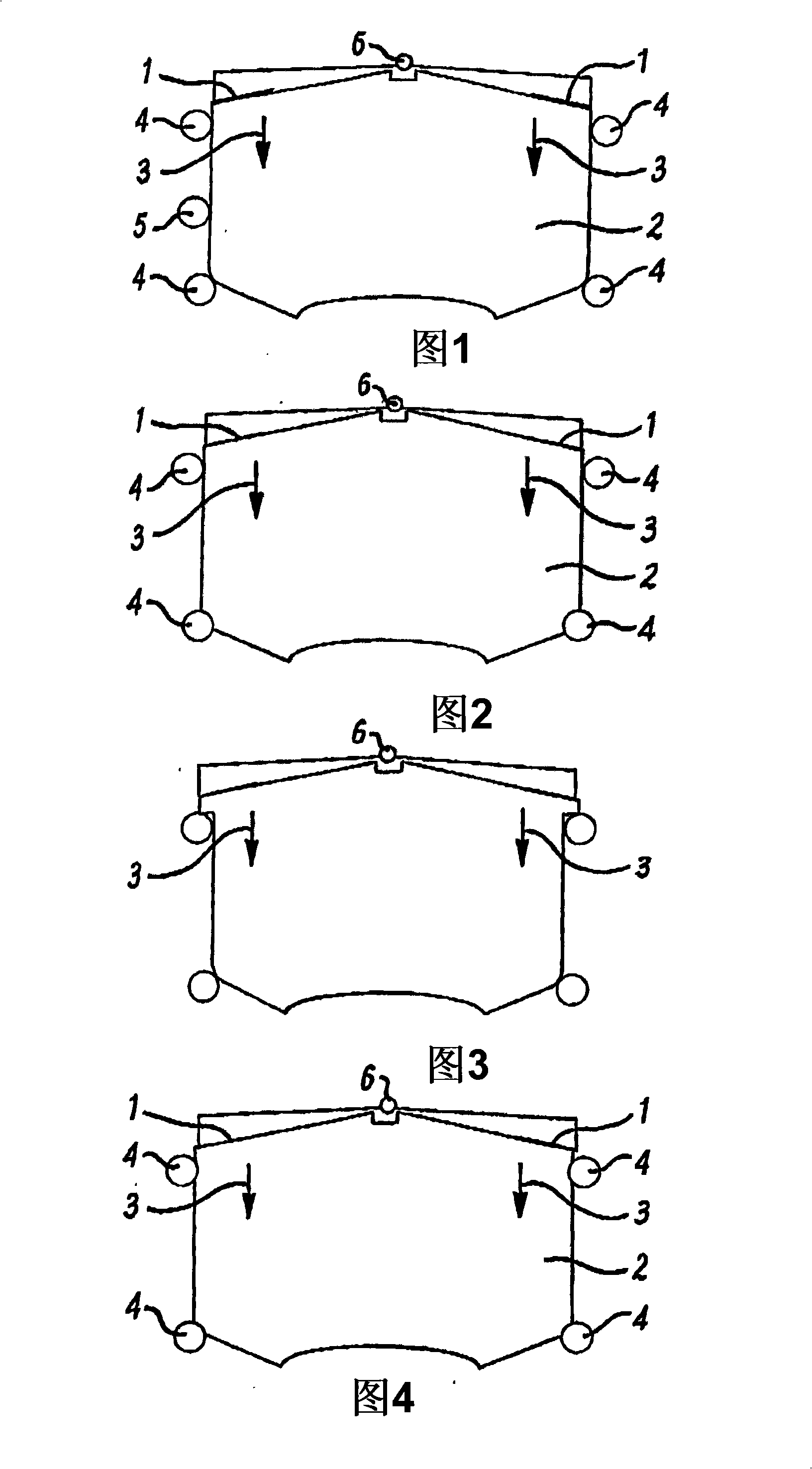
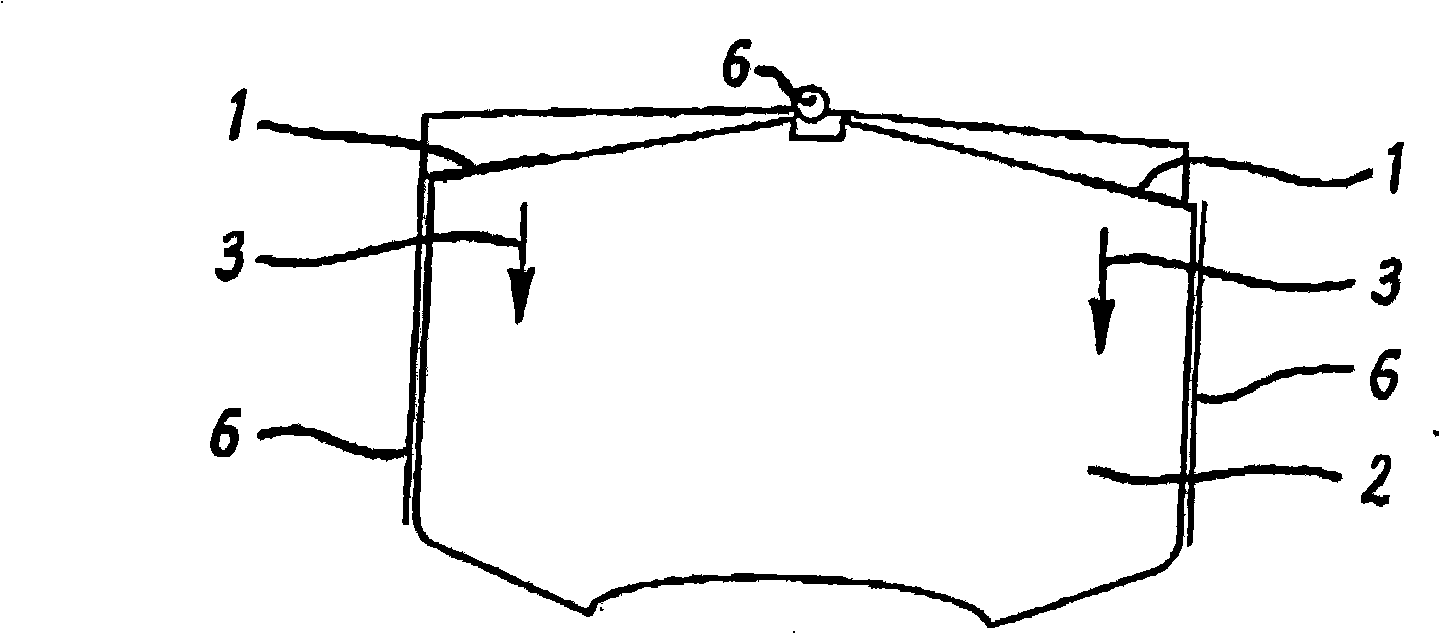
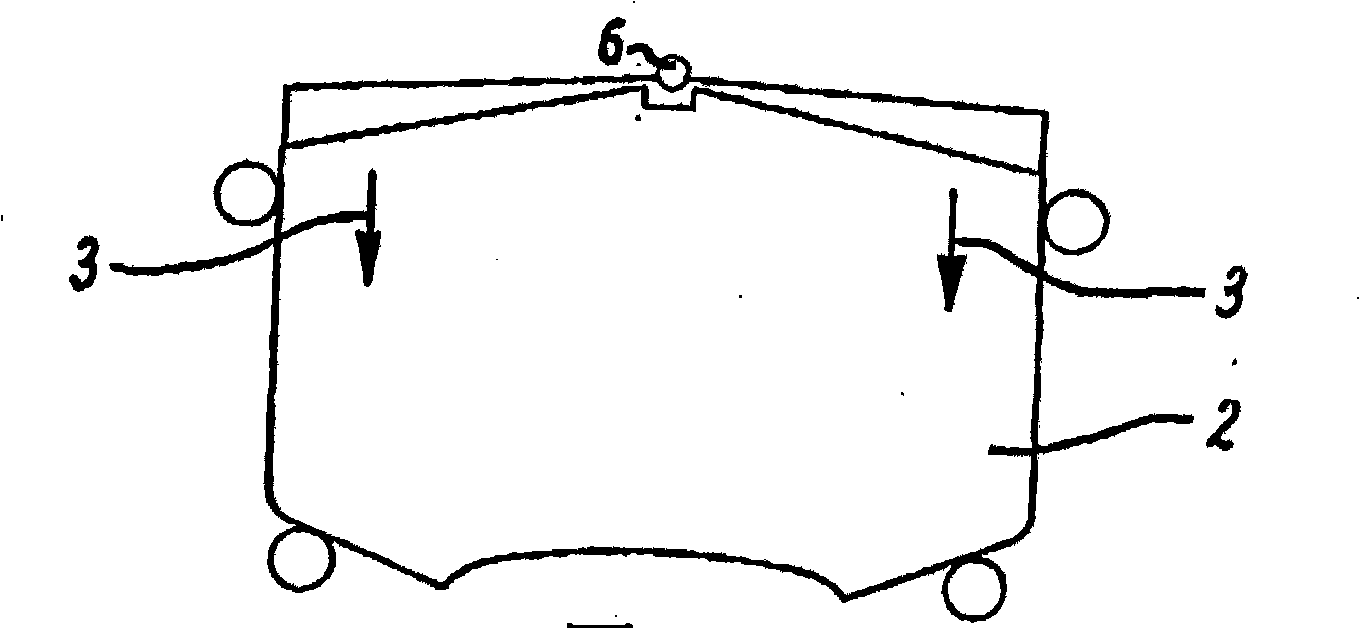
[0009] 1-8 illustrate various known pad retaining arrangements for a caliper of a disc brake of a vehicle. In all cases, a conventional push spring urges the liner in a downward direction identified in each case as arrow 3, wherein the conventional push spring is identified as 1 throughout Figures 1-8 and the liner is throughout Figures 1-8. 8 is identified as 2. Springs mounted on the centrally located pivot 6 act in each case on the front and rear ends of the pads in the same downward direction. Other known devices use conventional lift springs which act in an upward rather than downward direction in the same way as push springs. In Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 and 8, elongated cylindrical pins extending at an angle perpendicular to the plane of the pad and its backing plate are arranged at spaced intervals around the perimeter of the pad . exist Figure 5 In the arrangement of , the plate abutment extends alongside the liner, yet is slightly spaced from the liner.
[0010]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com