Methods for treating live plants or live plant parts or mushrooms with UV-C light
A UV-C and plant technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, plant preservation, gardening methods, etc., can solve the problems of not specifying UV-C, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
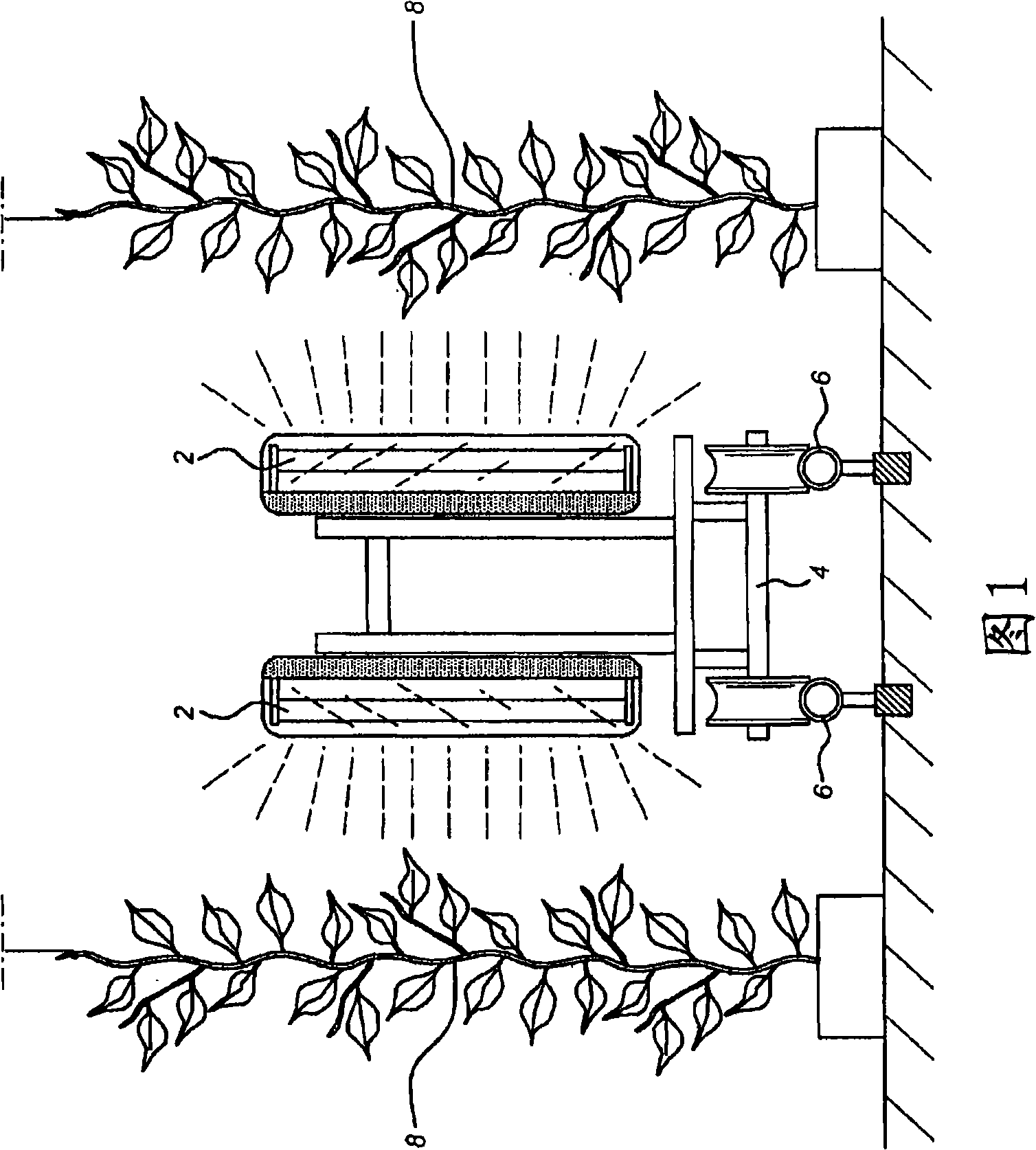
[0123] Example 1 - Controlling Botrytis on Tomato Plants
[0124] Tomato plants grow in rows in a greenhouse. On the rails (eg heating tubes) between some rows were placed fixtures comprising two UV-C lamps, one at the front end on either side of the fixture, placed at a height such that the UV-C light contacted approximately 2 / 3 of the stem.
[0125] The amount of Botrytis cinerea mycelium on the stem surface of UV-C treated plants and control plants was assessed periodically. This estimation enables finding the optimal UV-C dosage that damages the botrytis and increases the yield of the treated plants.
[0126] By periodically treating the tomatoes, botrytis growth is reduced, which delays or prevents the botrytis from completely surrounding the tomato stem, and thus increases tomato lifespan and yield.
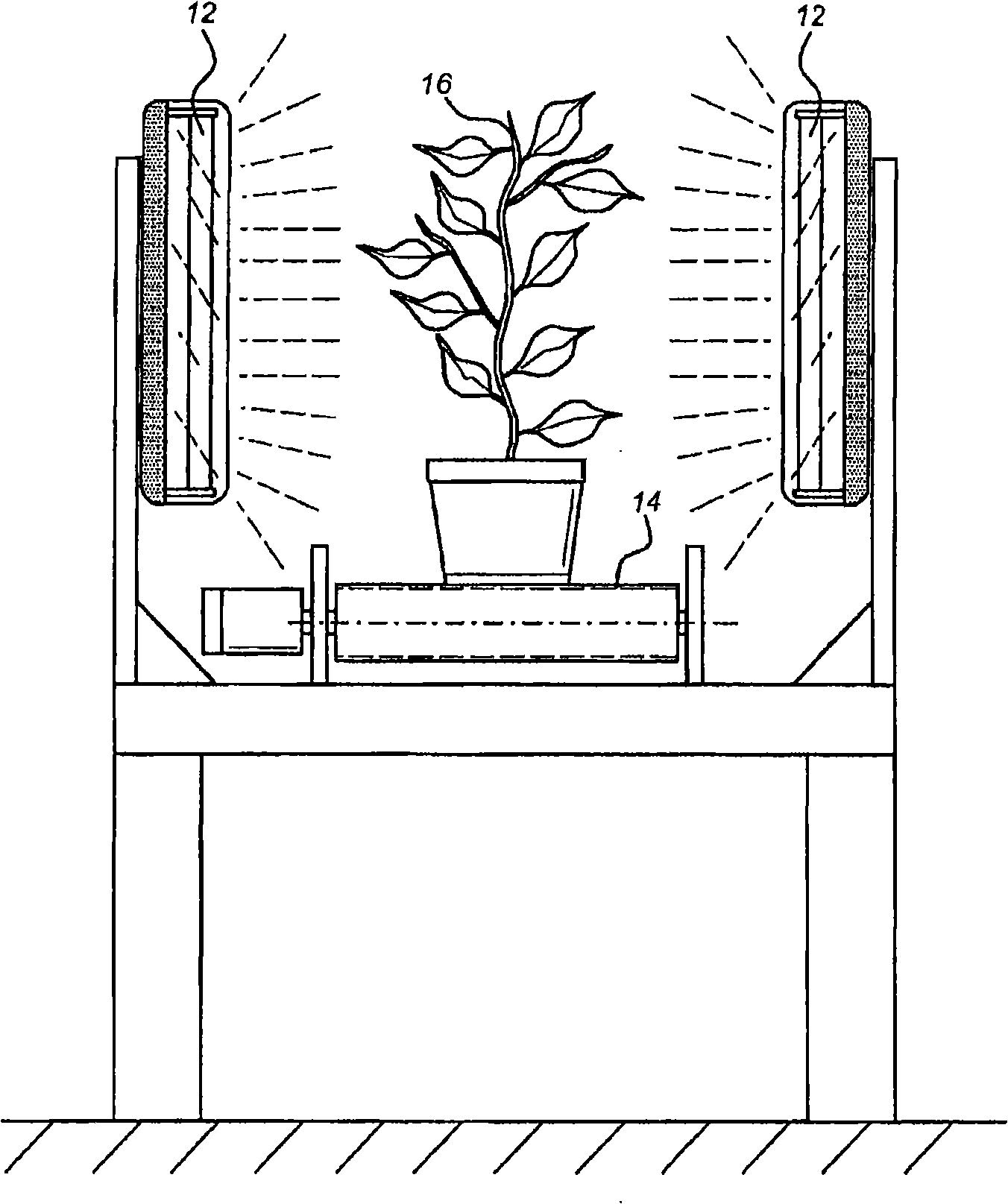
Embodiment 2
[0127] Example 2 - Reduction of sporangia germination of Phytophthora infestans
[0128] Estimation of the effect of UV-C dose rate on sporangia of Phytophthora infestans on water agar. Phytophthora infestans sporangia were plated on 1% water agar and exposed to different doses of UV-C. Germination of 100 sporangia per plate was assayed. Each dose rate includes four replicas.
[0129] image 3 The result is shown. Data points represent the mean of four replicate plates. Repeat the experiment. Solid points represent data from Experiment 1 and open points represent data from Experiment 2. Error bars represent standard deviation.
[0130] The results showed that the viability of P. infestans reproductive structures was significantly reduced using UV-C light. Use about 6-10mJ / cm 2 UV-C, the percent germination was reduced by at least 80%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com