Memory OLAP What-if analytical method based on a difference table
An analysis method and a technology of difference tables, which are applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as exponential changes in data volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] In order to understand the present invention and its advantages more fully, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. In the drawings, the same reference numerals are used to denote the same elements.
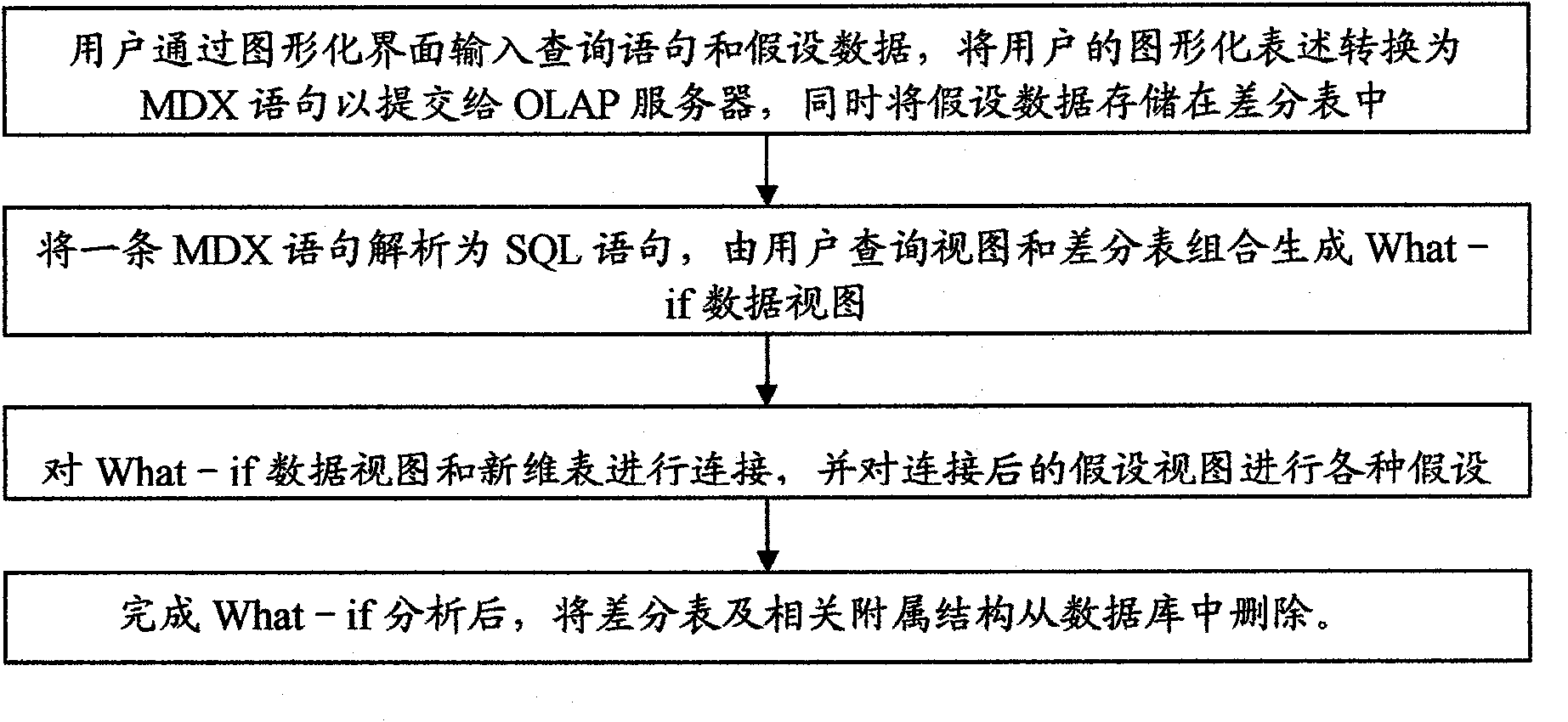
[0035] First, refer to figure 1 , to illustrate the difference table-based memory OLAP What-if analysis method according to the present invention.
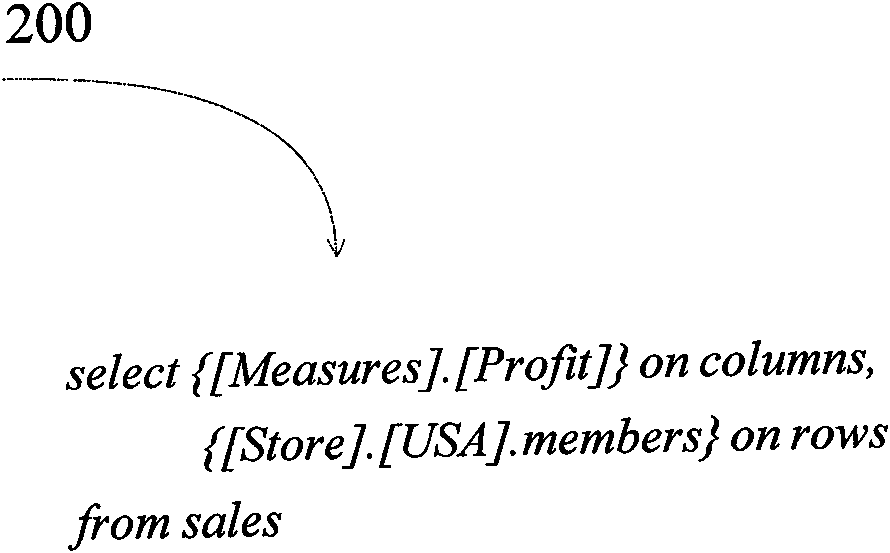
[0036] In step A, the user obtains the data he is interested in by directly inputting MDX statements or a graphical interface for subsequent What-if analysis, and converts the user's graphical representation into MDX statements and submits them to the OLAP server. That is to say, the user inputs the user query statement and hypothetical data through the graphical interface, and at the same time stores the above hypothetical data in the difference table. Thereafter, the server parses and executes the MDX statement, and returns the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com