Prevention of nuclear, solar, and other radiation-induced tissue damage
A technology of ionizing radiation and ionizing radiation exposure, applied in the directions of X-ray/γ-ray/particle irradiation therapy, drug combination, active ingredients of phosphorus compounds, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0121] Enhanced cell viability by administering myo-inositol / IP-6 compound following standard procedures of irradiation:
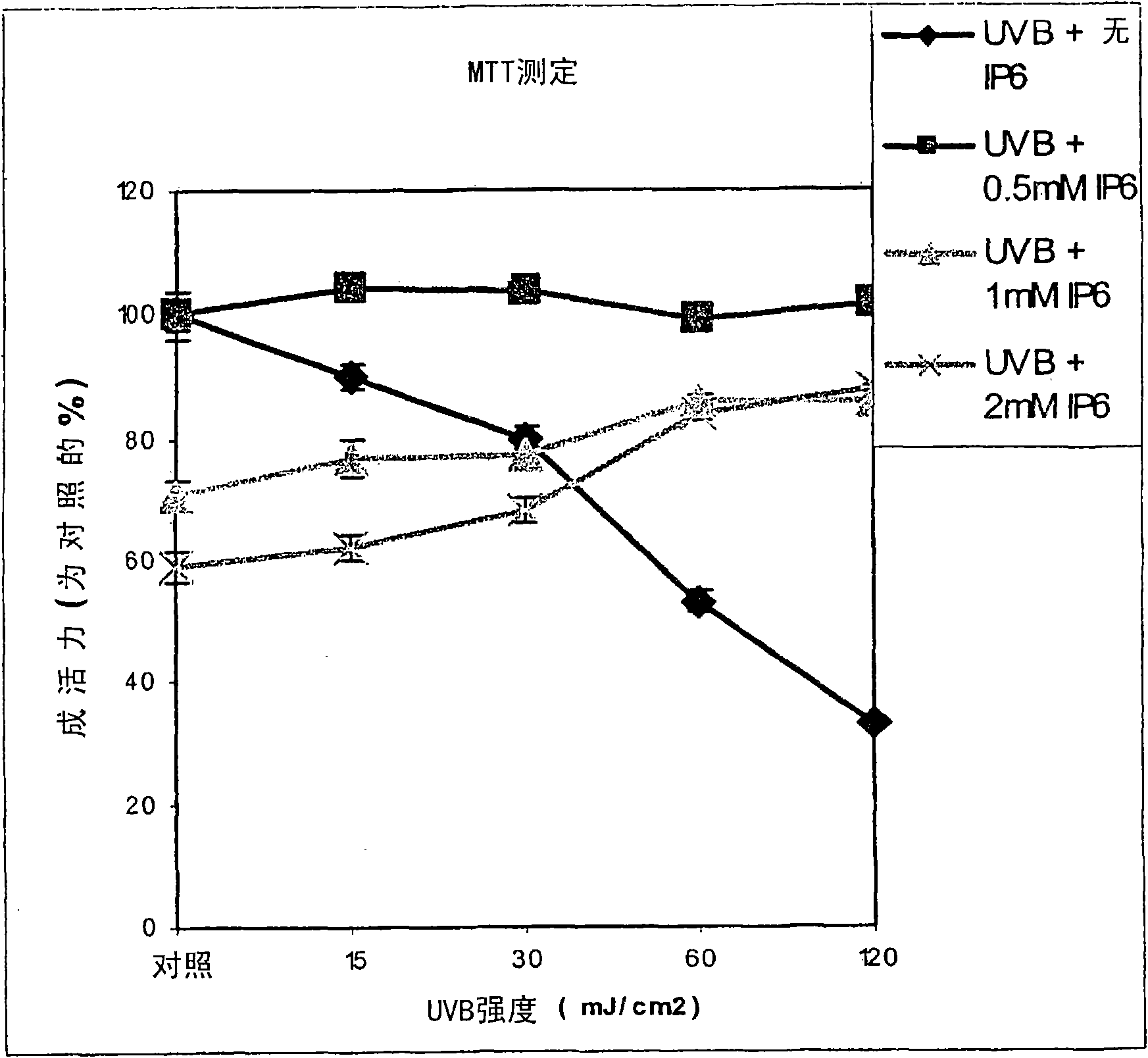
[0122] Human keratinocytes (HaCaT) were cultured in Dulbecco's solution containing 7 mg / L inositol (38.8 μM) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 1% L-glutamine, and 1% antibiotics (penicillin, streptomycin). Grow in modified Eagle's medium. Keep cells at 37 °C and 5% CO 2 . Na-IP-6 was diluted from a 100 mM stock solution to the desired concentration (0.05-2.0 mM) using cell culture medium as a diluent. Use 15, 30, 60 and 120mJ / cm 2 The UVB intensity obtained by varying the exposure time of the cells to UVB light (80% of the light output is in the 290-320 nm UVB range).
[0123] HaCaT cells were grown to approximately 80-90% confluency. 100 μL of 1 x 10 4 cells / mL HaCaT cells were seeded in each well of four 96-well plates. Treat cells with IP-6 (0-2.0 mM) and add 100 μL of 1 mg / mL aqueous MTT dissolved in DMEM medium to each ...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Effects of IP-6 and UVB radiation on attached cells
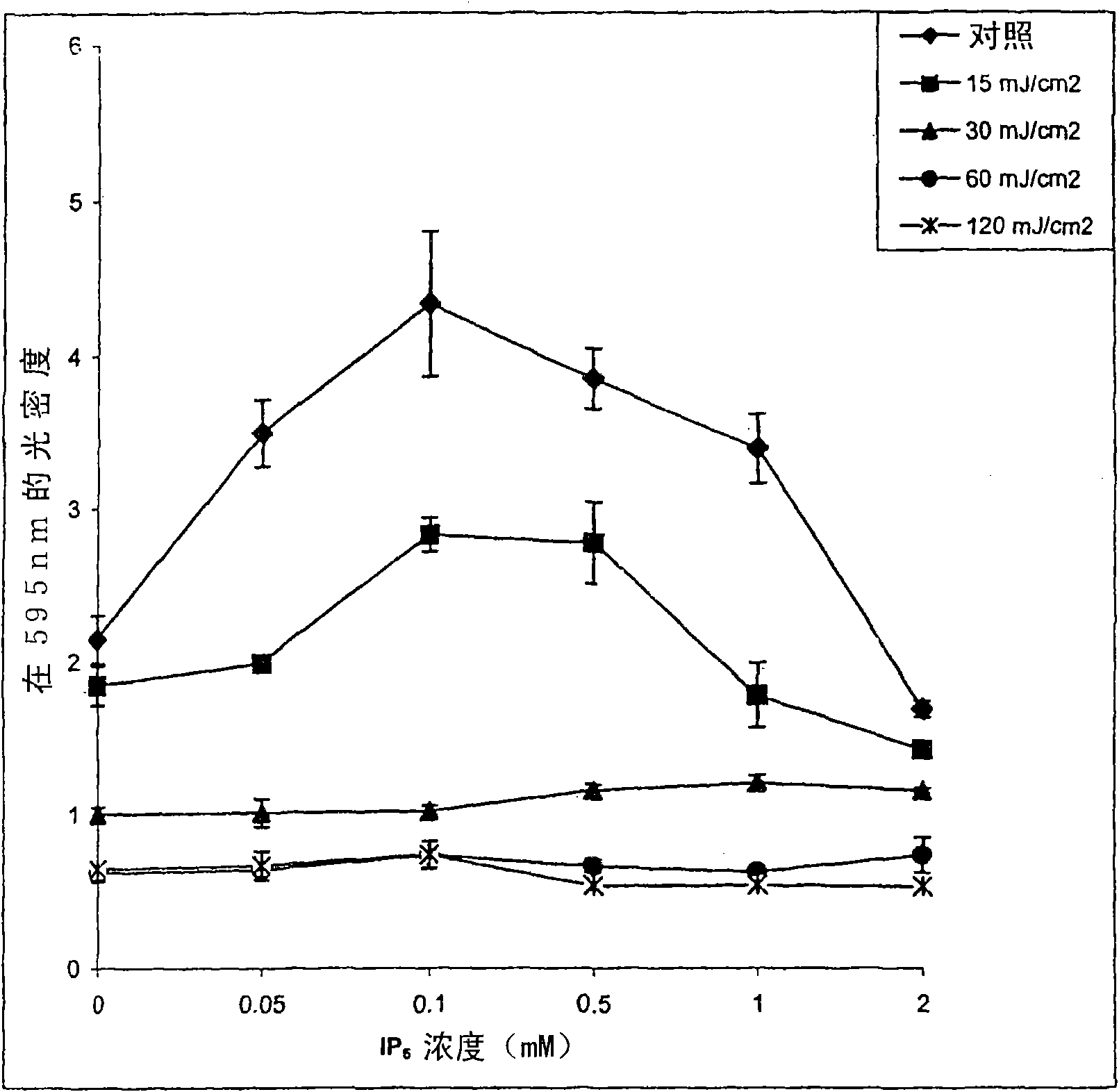
[0129] will be 5×10 4 HaCaT cells were seeded into each well of four 6-well tissue culture plates and incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO 2 Incubate for 24 hours. One hour before UVB irradiation, two plates were treated with IP-6 (0 and 0.1 mM), one for IP-6 pretreatment and the other for IP-6 pretreatment and posttreatment. All four plates were then washed twice with PBS 1X, and a small amount of PBS 1X was added to the wells at 30 mJ / cm 2 irradiated. After UVB exposure, PBS was removed from the wells, and DMEM medium was added to each well. IP-6 (0.05 and 0.1 mM) was then added to non-UVB exposed, IP-6 post-treated, and pre- and post-treated labeled plates. The cells were then incubated (37°C and 5% CO 2) for 18 hours. After incubation, cells were washed 4 times with PBS 1X (pH 7.4), then fixed with 4.0% formaldehyde for 15 minutes, and stained with 0.5% aqueous crystal violet for at least 5 minutes. Excess crysta...
Embodiment 3
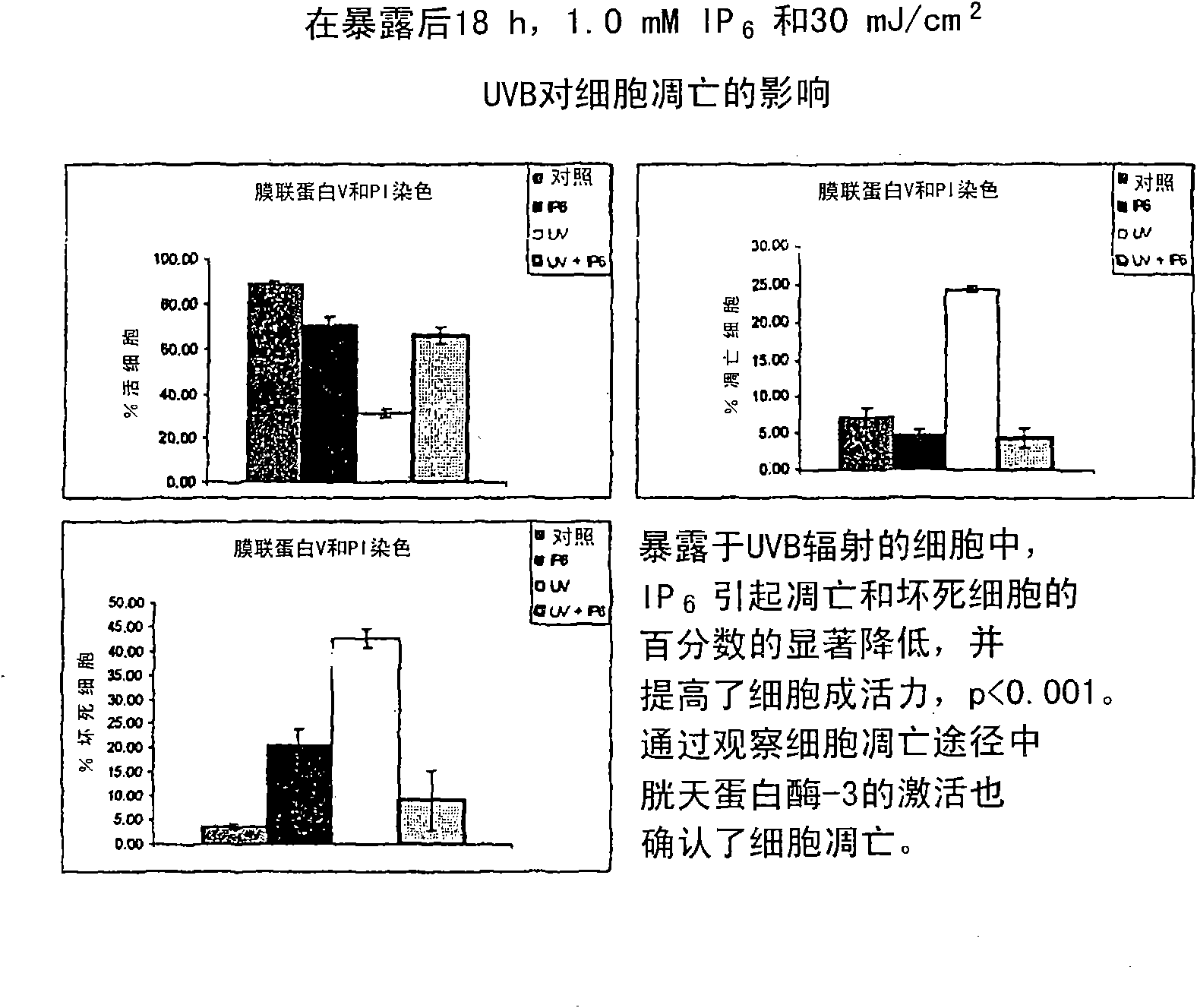
[0133] Effects of IP-6 and UVB radiation on the apoptosis of HaCaT cells
[0134] HaCaT cells were plated onto 60mm tissue culture dishes for 24 hours. Cells were then left unexposed or exposed to 30mJ / cm 2 UVB irradiation and immediate treatment with 0, 0.5 mM or 1.0 mM IP-6. Cells were harvested 6 and 18 hours after UVB exposure. Add 5 μL RNase (DNase-free) to 10 6 cells / mL. The cell suspension was incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes. The suspension was then frozen on ice (2-8°C). 100 μL of PI was added to the cell suspension (Cellular DNA Flow Cytometry Analysis Kit, Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN). DNA quantification was performed on the same day by flow cytometry using FACS.
[0135] Compared with the non-UVB exposure control group, at 30mJ / cm 2 Six hours after UVB irradiation, the G1 phase was significantly increased while the S phase was significantly decreased, p<0.001. However, G2M phase was not significantly different between exposed and non-exposed groups...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com