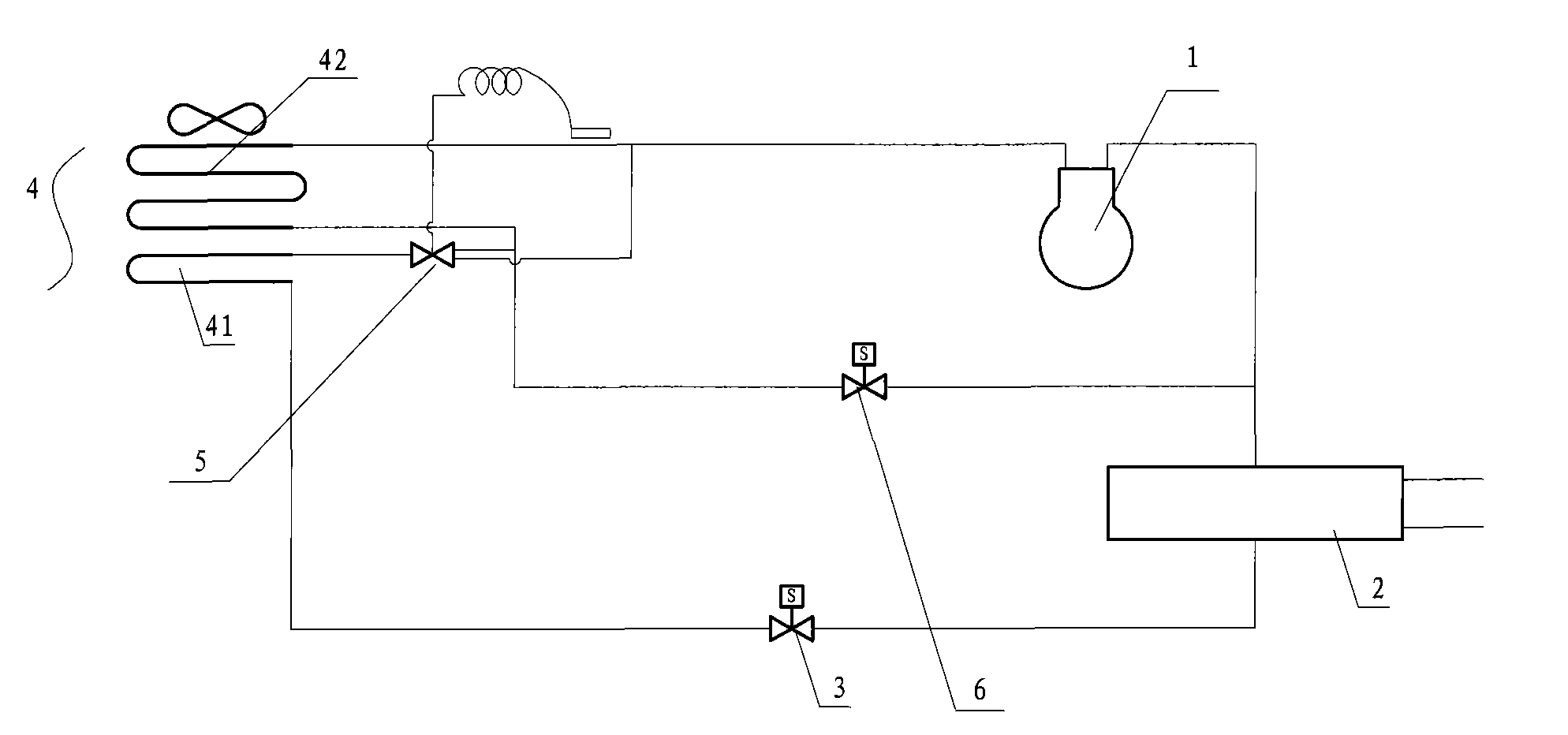
Hot-gas bypass and surface cooler supercooling defrosting device
A hot gas bypass and surface cooler technology, applied in refrigerators, refrigeration components, refrigeration and liquefaction, etc., can solve the problems of long defrosting operation time, low system energy efficiency, high energy consumption, and achieve fast and effective results and reduce economical costs. cost, and the effect of improving the system energy efficiency ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] When in use, the refrigerant vapor is charged in the refrigeration cycle system. The refrigerant vapor enters the first heat exchanger 2 through the pipeline after the pressure is increased by the compressor 1, condenses the refrigerant vapor into a high-pressure liquid, and then enters the process at the bottom of the heat exchange tube in the second heat exchanger 4 through the solenoid valve 3. The heat exchange tube 41 in the cold section, because the refrigerant in the heat exchange tube 41 in the subcooling section is a medium-temperature and high-pressure liquid, the temperature of the subcooling tube is relatively high. When the ambient temperature is low and the relative humidity is high, it is effectively prevented. The condensed water produced by the heat exchange tubes in the second heat exchanger 4, especially in winter, a large amount of water droplets gather in the lower part of the evaporator to form frost on the heat exchange tubes at the bottom of the s...
Embodiment 2
[0020] When the environment needs to take heat, the electromagnetic valve 3 can be de-energized, the electromagnetic valve 6 is energized, and the heat exchange tube 42 in the upper part of the heat exchange tube in the compressor 1, the electromagnetic valve 6 and the second heat exchanger 4 is connected by a pipeline and A circuit is formed. After the refrigerant vapor is boosted by the compressor 1, the solenoid valve 6 directly enters the heat exchange tube 42 in the middle and upper part of the second heat exchanger 4 along the pipeline, and exchanges heat with the external low-temperature medium. At this time, the heat exchange tube The refrigerant in the compressor condenses into a medium-temperature liquid or a mixture of medium-temperature steam and liquid, and then returns to the compressor 1 for circulation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com