Optimized non-canonical zinc finger protein
A technology of zinc finger protein and zinc finger, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, peptides, desipeptides, etc., and can solve problems such as reduced ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0322] Embodiment 1: ZFN expression vector
[0323] A ZFN comprising encoding 4 fingers described in Examples 2 and 14 (referred to as "5 -8" and "5-9") sequence expression vector. Briefly, the 5-8 and 5-9 ZFNs (which comprise the nuclease domain of the type IIS restriction enzyme Fok I via a 4 amino acid ZC linker (Wah et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 : 384-579 amino acids of the sequence of 10564-10569) fused four zinc finger domains) modified to CCHC structure. Additional modifications (substitutions and insertions) were also made to the residues between the C-terminal His and Cys zinc coordination structures and / or the C-terminal residues of the C-terminal Cys of Finger 2 and / or Finger 4.
Embodiment 2
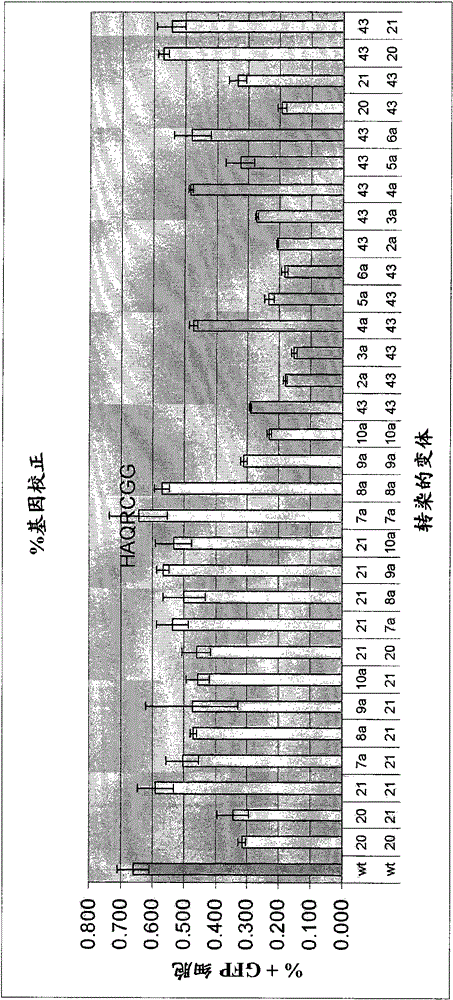
[0324] Example 2: Gene Correction of eGFP in Reporter Cell Lines
[0325] ZFNs comprising CCHC zinc fingers described herein were tested for their ability to promote homologous recombination in the GFP system described in Urnov (2005) Nature 435(7042): 646-51 and U.S. Patent Publication No. 20050064474 (eg, Examples 6-11). ability. Briefly, 50 ng of each ZFN and 500 ng of the promoterless GFP donor (Urnov (2005) Nature) were transfected into 500,000 reporter cells using 2 μL Lipofectamine 2000 per sample according to the Invitrogen Lipofectamine 2000 protocol.
[0326] Vinblastine at a final concentration of 0.2 μM was added 24 hours after transfection and removed 72 hours after transfection.
[0327] Cells were assayed for GFP expression 5 days after transfection by measuring 40,000 cells per transfection on a Guava benchtop FACS analyzer.
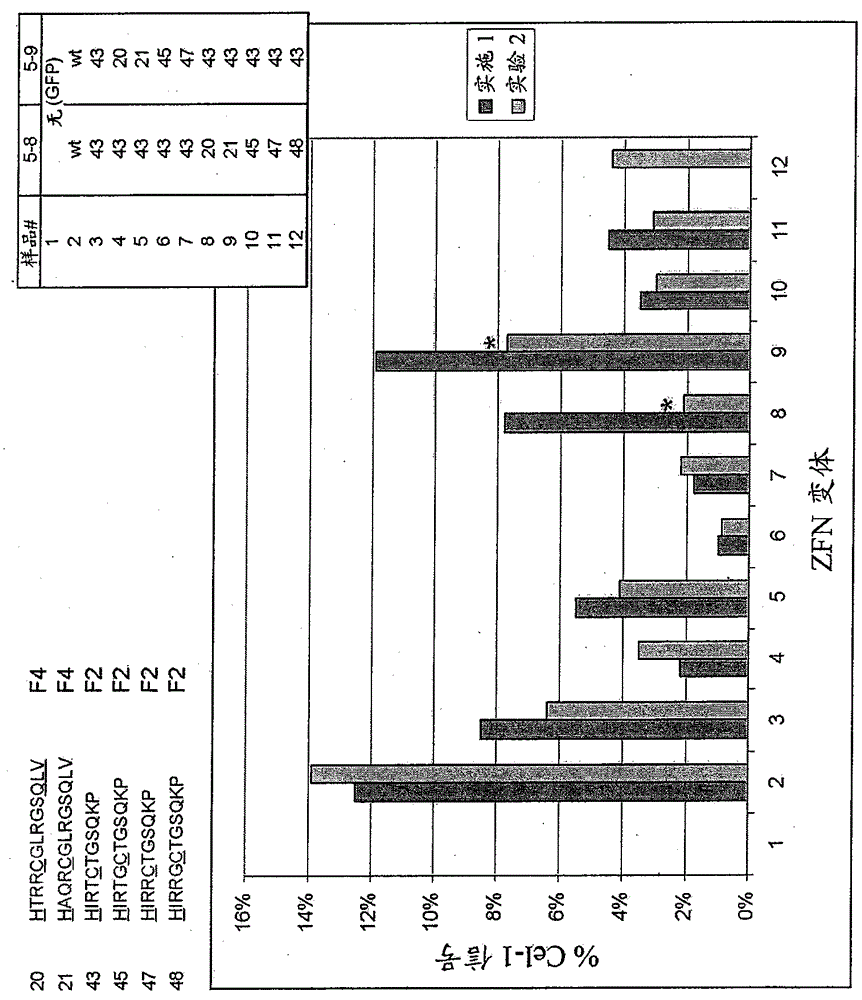
[0328] Such as figure 1 As shown, most ZFNs comprising the altered CCHC zinc fingers shown in Tables 1 and 2 above promote homologous...
Embodiment 3
[0329] Example 3: Editing of the chromosomal IL2Rγ gene by targeted recombination
[0330] The ZFNs described herein were also assayed in Urnov (2005) Nature 435(7042):646-51 and the endogenous IL2Rγ assay described in Example 2 of US Patent Publication No. 20050064474. Briefly, 2.5 μg of each ZFN expression construct was transfected into 500,000 K562 cells using Nucleofector (Amaxa). Genomic DNA was harvested and assayed for gene disruption at the endogenous IL2Rγ locus using the Surveyor Endonuclease Kit.
[0331] figure 2 ZFNs are shown on the upper left of . Specifically, altered zinc finger 20 refers to a CCHC zinc finger comprising the sequence HTRRCGLRGSQLV; zinc finger 21 comprises the sequence HAQRCGLRGSQLV (SEQ ID NO: 53); zinc finger 43 comprises the sequence HIRTCTGSQKP (SEQ ID NO: 75); zinc finger 45 comprises The sequence HIRTGCTGSQKP; zinc finger 47 comprises the sequence HIRRCTGSQKP; and zinc finger 48 comprises the sequence HIRRGCTGSQKP. Zinc fingers 20 a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com