Ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) method having excitation noise add parameter option function
A technology that integrates empirical modes and noises. It is applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc. It can solve the problems of high calculation volume, nonlinear and non-stationary signals that cannot achieve decomposition accuracy at the same time, and achieve high decomposition accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
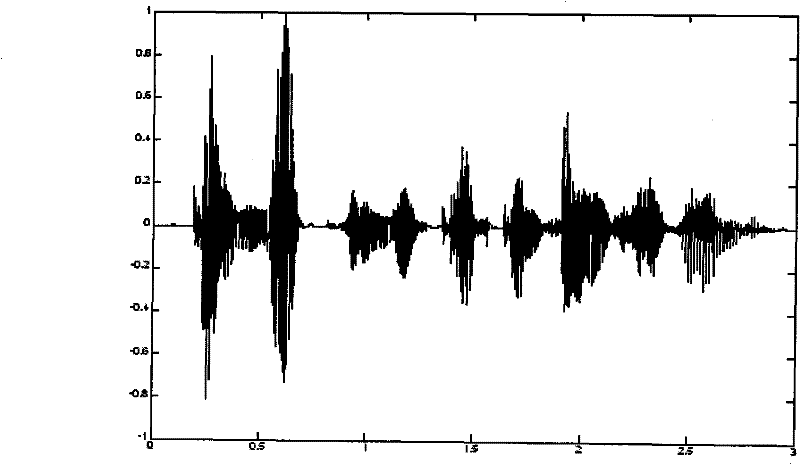
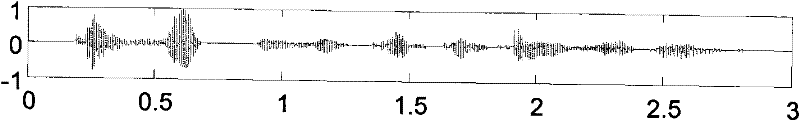
[0012] Specific implementation mode one: according to the instructions attached figure 1 Specifically explain this embodiment, a kind of ensemble empirical mode decomposition method with excitation noise addition parameter selection function described in this embodiment, the decomposition method is:
[0013] Step 1: Set the initial value for the ensemble empirical mode decomposition, the preset difference of the decomposition error and the maximum difference of the decomposition error, the initial value includes the initial value P of the set number 0 and the initial noise amplitude a 0 , and use the initial value to calculate the initial value P of the set number 0 The initial value of the decomposition error e 0,0 ;
[0014] Step 2: Add noise with amplitude a to the signal to be decomposed u The white noise of the signal to be decomposed, the set number P v The set empirical mode decomposition under the following method is used to obtain the internal solid mode function...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0018] Specific embodiment two: This embodiment is a further description of the set empirical mode decomposition method with excitation noise addition parameter selection function described in specific embodiment one. The set number described in step one of specific embodiment one Initial value P 0 Selected as 2, the initial value of the noise amplitude a 0 It is selected as 1 / 2 of the maximum amplitude of the signal to be decomposed.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0019] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is a further description of the method for ensemble empirical mode decomposition with excitation noise addition parameter selection function described in specific embodiment one. The number of signal sets P v The set empirical mode decomposition under the following method is used to obtain the internal solid mode function matrix, and the previous decomposition error e is obtained according to the internal solid mode function matrix u,v and this decomposition error e u+1,v The specific process is:
[0020] Set the number P of the signal to be decomposed v The empirical mode decomposition of the set under, obtains P v Sequence of solid mode functions within the group c ij (t k ) and a set of final internal solid mode function sequences c i (t k ), i=1, Λ, n, j=1, Λ, P v , k=1, Λ, L, L is the length of the decomposed data, and the previous decomposition error e is calculated by formula 1 u,v :
[0021] formula one ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com