Method for coordinating interferences among HSUPA substricts in TD - SCDMA system
A TD-SCDMA, inter-cell interference technology, applied in transmission systems, wireless communications, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing mutual interference, unable to reduce transmission power, and difficult to control the level of interference in adjacent cells The effect of throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
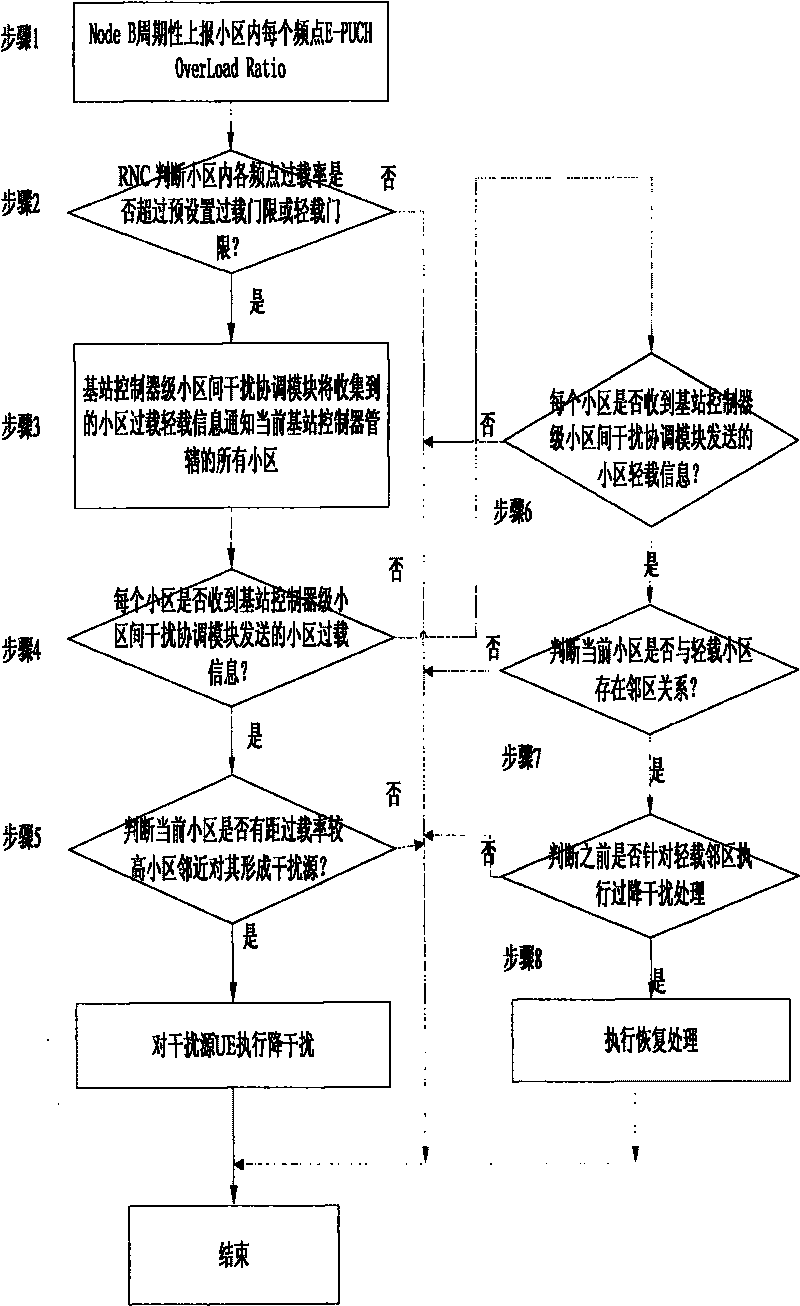
[0032] This technical solution introduces a new public measurement E-PUCH overload rate, which is defined as follows:
[0033] E-PUCH Overload Ratio (E-PUCH OverLoad Ratio): base station (Node B) within a specified period counts the ratio of the average interference of time slots carrying E-PUCH resources in each 5ms TTI exceeding the ROT threshold to the total number of TTIs within a specified period ratio. The measurement can support periodic reporting.
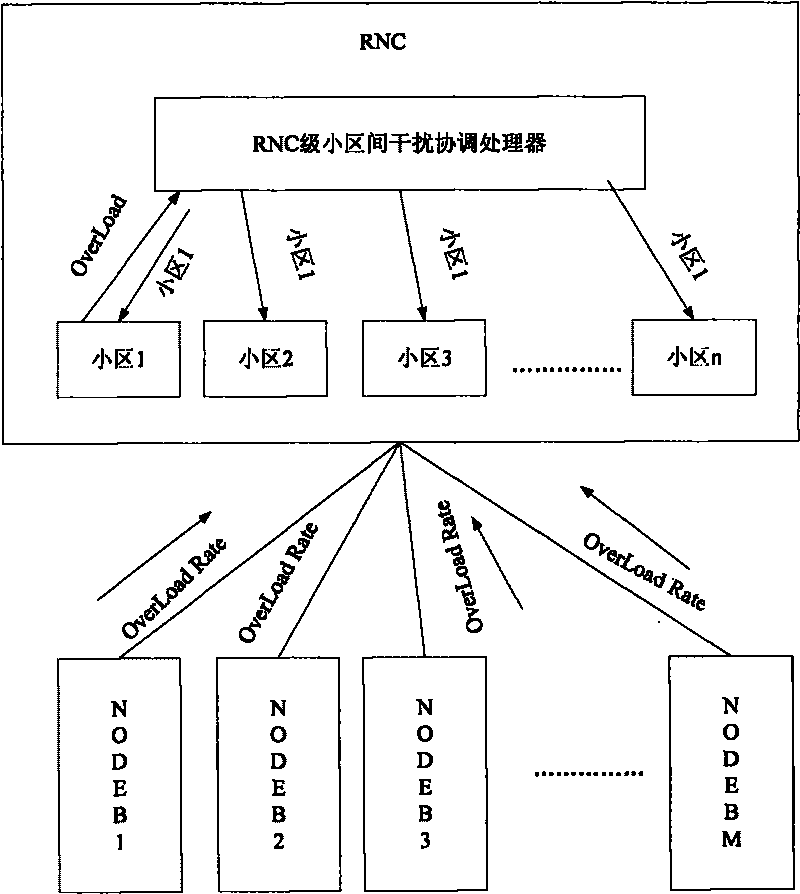
[0034] If the overload rate reported by the base station (Node B) is at a high level for a sustained period of time, it is considered that the base station (Node B) has been unable to control the interference level of this frequency point within a reasonable range through the power authorization method in the cell Inside. Inter-cell interference coordination strategies at the base station controller (RNC) level need to be activated
[0035] Step 101: The base station (Node B) periodically reports the E-PUCH OverLoad Rati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com