Electronic tag applied to Internet of things and system using same
An electronic tag and Internet of Things technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, can solve the problems of lack of diversified information identification capabilities and inability to identify information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
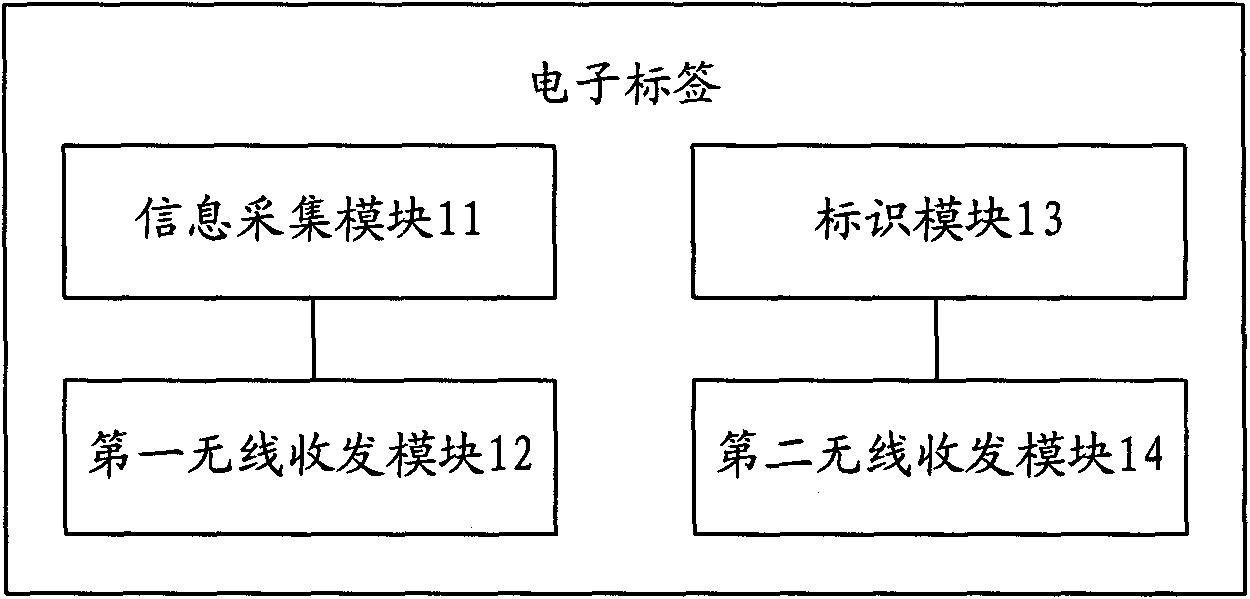
[0044] refer to figure 1 , is a structural diagram of an electronic tag applied to the Internet of Things described in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0045] The electronic tags can include:
[0046] Information collection module 11, is used for collecting the dynamic attribute information of tag attachment;
[0047] The first wireless transceiver module 12 is configured to receive radio wave energy, and transmit the dynamic attribute information collected by the information collection module 11 according to the trigger of the radio wave energy.
[0048] Wherein, the label attachment includes but not limited to the above-mentioned articles (commodities).
[0049] The information collection module 11 can use sensor technology to collect dynamic attribute information such as temperature and humidity of the label attachment. The sensor is a physical device that can detect and feel external signals, physical conditions (such as light, heat, humidity) or chemical compon...
Embodiment 2
[0084] This embodiment provides another implementation solution of an electronic tag and a tag data reading device.
[0085] In the electronic tag and the tag data reading device, the respective first wireless transceiver module and the second wireless transceiver module can also be implemented using the same frequency. In this case, there is no need for two wireless transceiver modules, only need One.
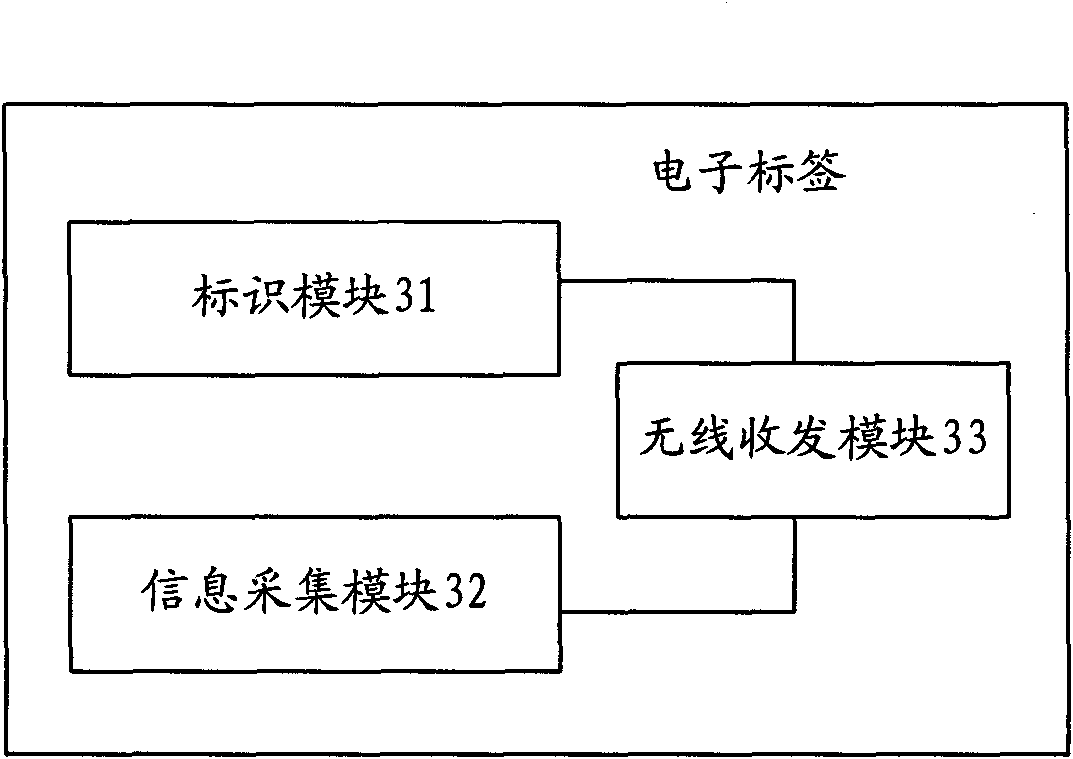
[0086] refer to image 3 , is a structural diagram of an electronic tag applied to the Internet of Things described in Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0087] The electronic tags can include:
[0088] Identification module 31, for storing the static attribute information of the tag attachment;
[0089] Information collection module 32, is used for collecting the dynamic attribute information of tag attachment;
[0090] The wireless transceiver module 33 is configured to receive radio wave energy, and transmit the static attribute information stored by the identific...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Combining the first and second embodiments above, this embodiment provides an electronic tag system (RFID) system applied to the Internet of Things.
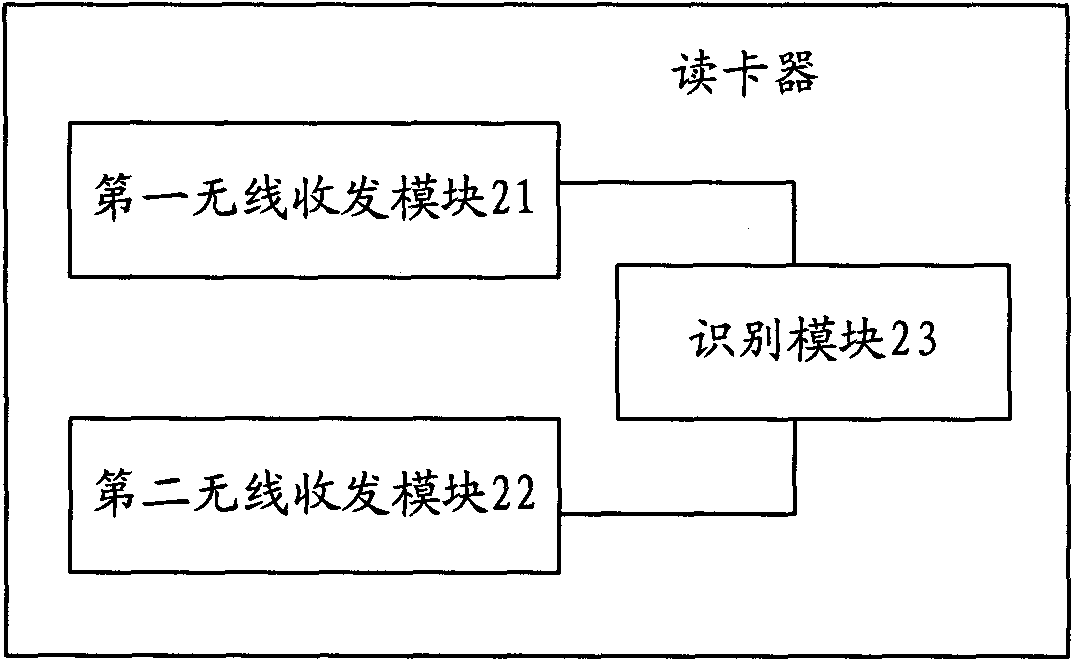
[0107] refer to Figure 5 , is a structural diagram of an RFID system applied to the Internet of Things described in Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0108] The RFID system mainly includes:
[0109] The electronic tag 51 includes an information collection module 511 and a first wireless transceiver module 512, the information collection module 511 is used to collect dynamic attribute information of the label attachment; the first wireless transceiver module 512 is used to receive radio wave energy, and According to the triggering of the radio wave energy, send the dynamic attribute information collected by the information collection module 511;
[0110] The reading device 52 is configured to send radio wave energy to the electronic tag 51 and receive dynamic attribute information sent by the electronic tag 51 . ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com