Target tracking method for wireless multimedia sensor network
A multimedia sensor and target tracking technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, advanced technology, etc., can solve the problems of communication energy consumption, and achieve the effect of ensuring service life, extending network life, and saving energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
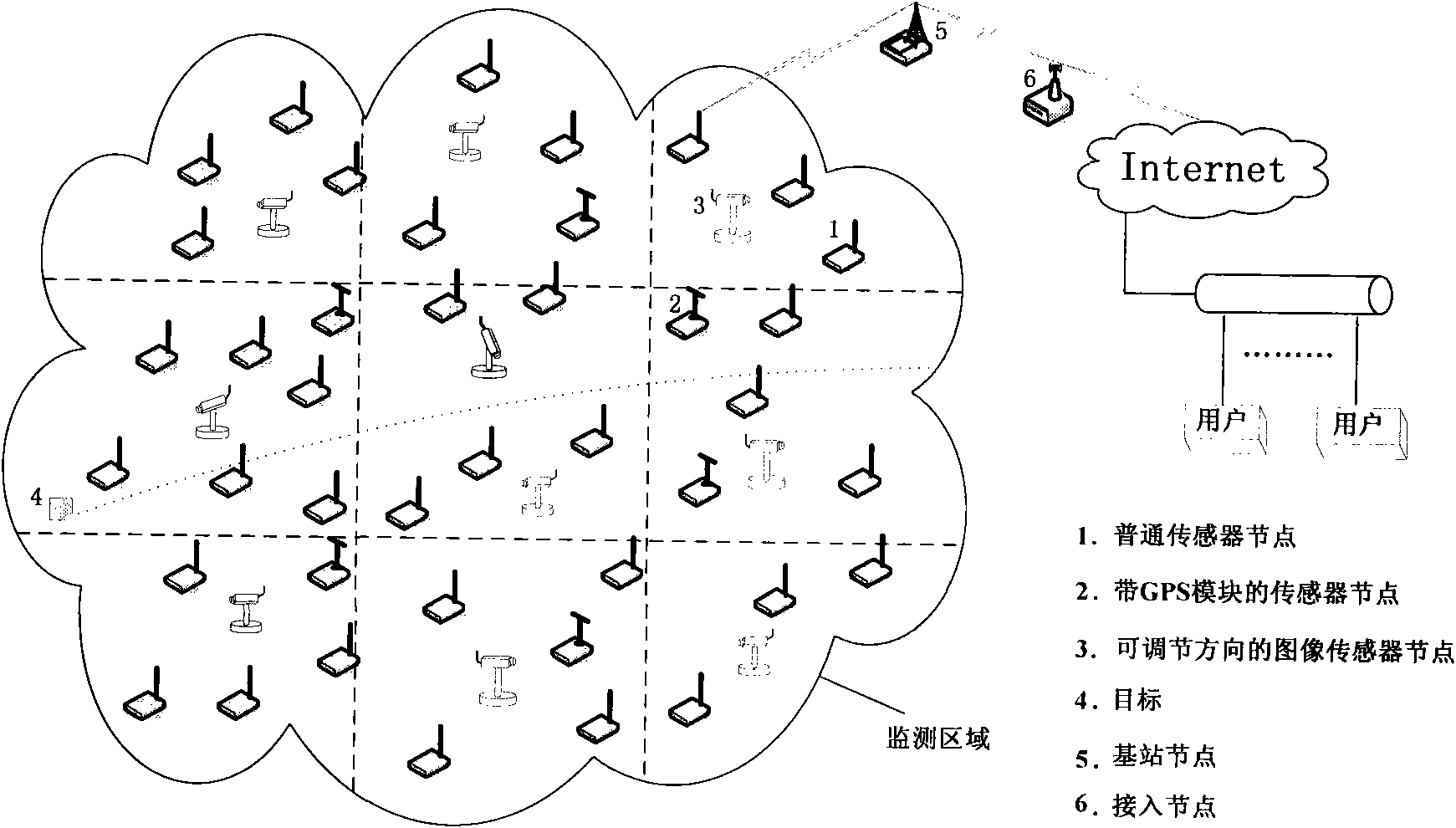
[0038] The invention adopts common sensor nodes, sensor nodes equipped with GPS modules and image sensor nodes with adjustable direction to cooperate with each other to complete target tracking. Each node in the network can play its own advantages, thereby saving costs and prolonging the life of the network, and can complete the tracking of the target in real time.
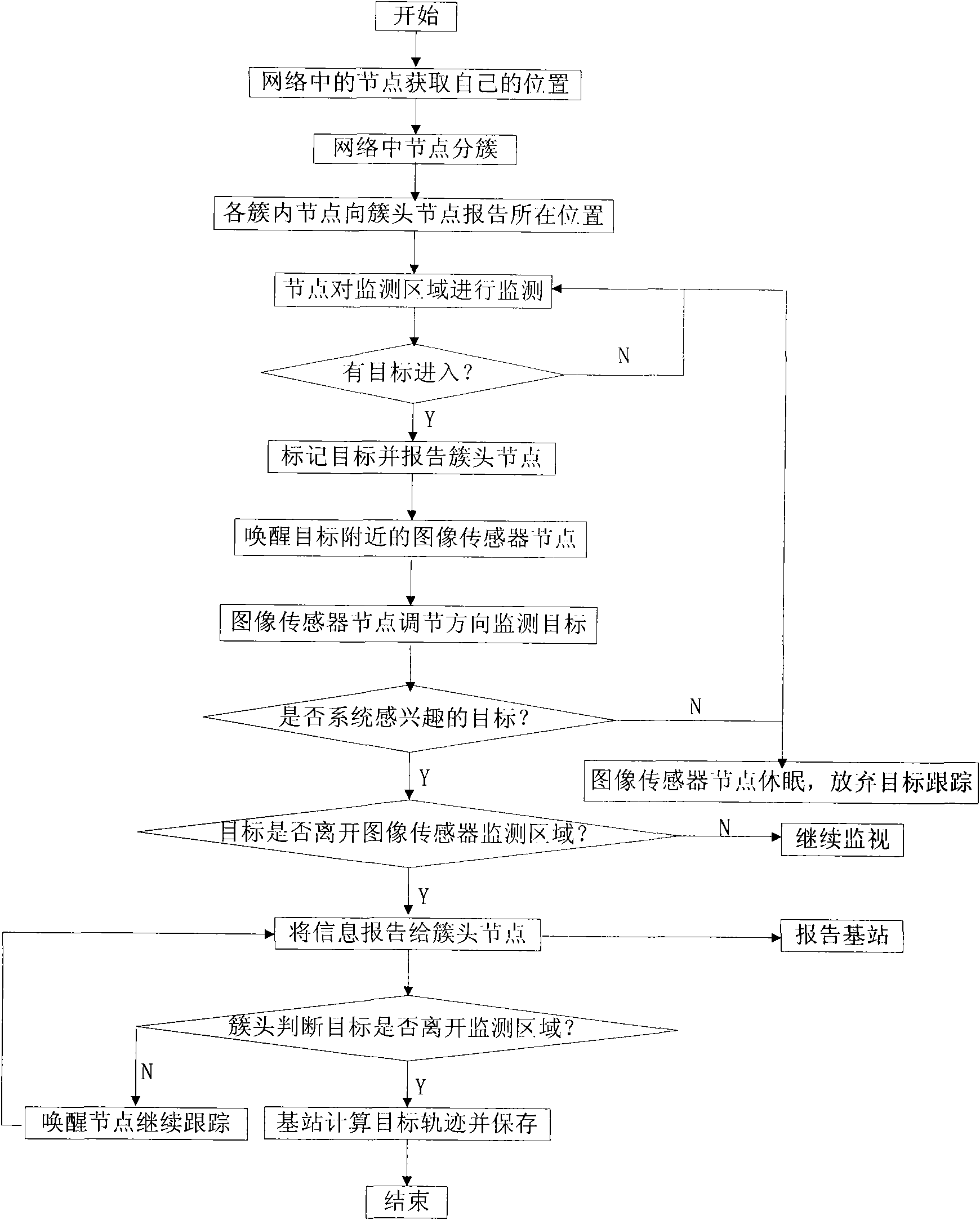
[0039] The target tracking method in the wireless multimedia sensor network that the present invention proposes has the following steps:
[0040] Step 1) Node types and their functions in the network. In the network, there are mainly three types of nodes: ordinary sensor nodes, sensor nodes equipped with GPS modules, and image sensor nodes with adjustable directions. The main functions of ordinary sensor nodes are abnormal detection, Target positioning and data transmission; the main function of the sensor node equipped with the GPS module is to obtain the position of the node itself and the function of the ordina...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com