Method and device for computing service transmission path in optical transport network
A technology of business transmission and calculation method, which is applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as rising business blocking rate, network resource bottleneck, and reducing network resource utilization, so as to achieve the effect of reducing blocking rate and improving utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
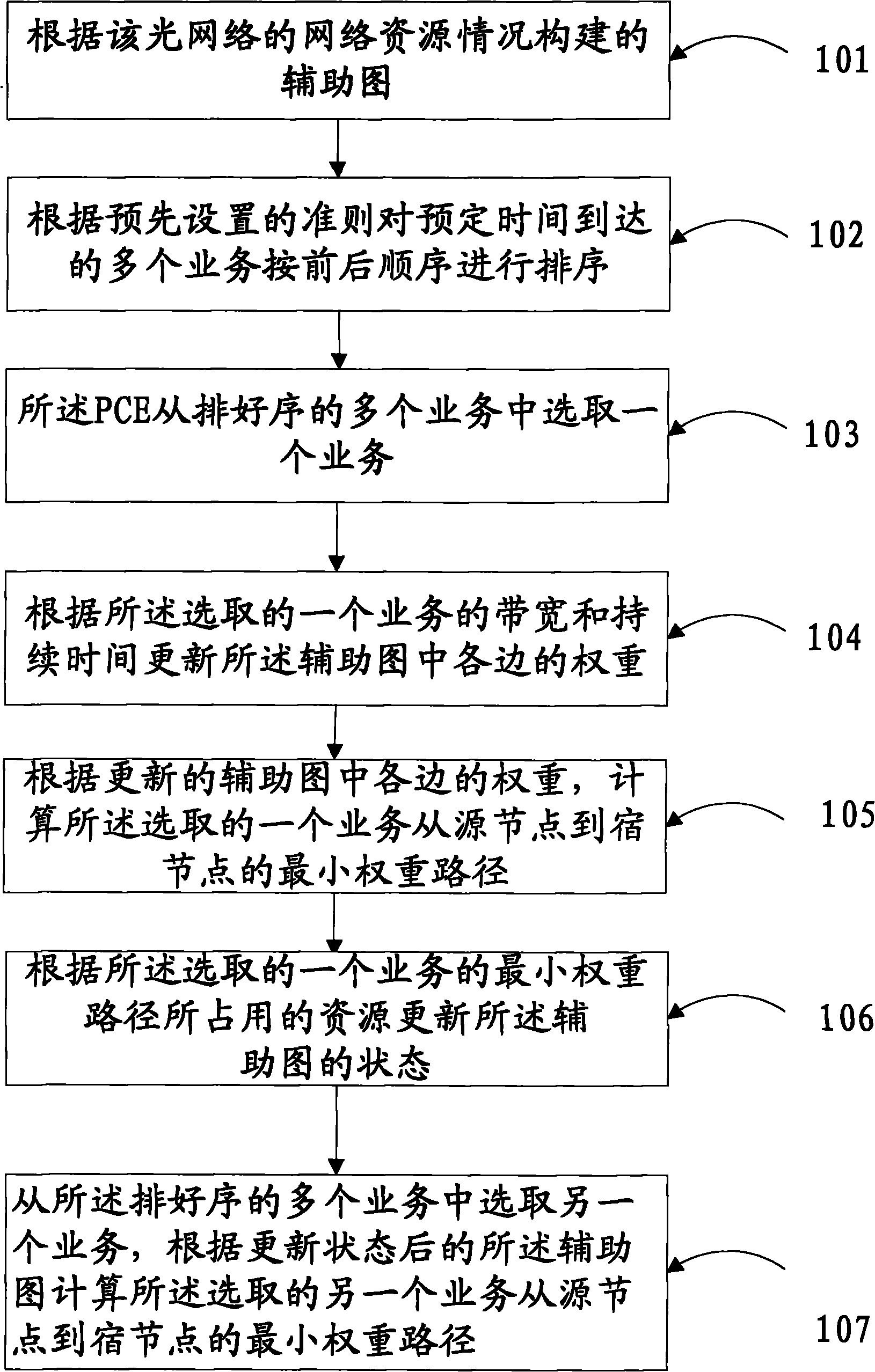
[0033] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for calculating a service transmission path in an optical transport network, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0034] 101. In the optical transport network, the optical network corresponds to an auxiliary graph constructed according to the network resources of the optical network, wherein the auxiliary graph is an optical transceiver in the node device in the optical network, and upper-layer traffic Network equipment constraints such as grooming capability, wavelength conversion capability, and link wavelength are transformed into edges (Edges) in the graph, which are integrated into a unique graph in the entire network; each edge in the auxiliary graph corresponds to a corresponding weight, indicating that the service passes The route selection and resource allocation of the upper-layer business at the cost of this edge are calculated once on the auxiliary graph.
[0035] 102. PCE (Path Computati...
Embodiment 2
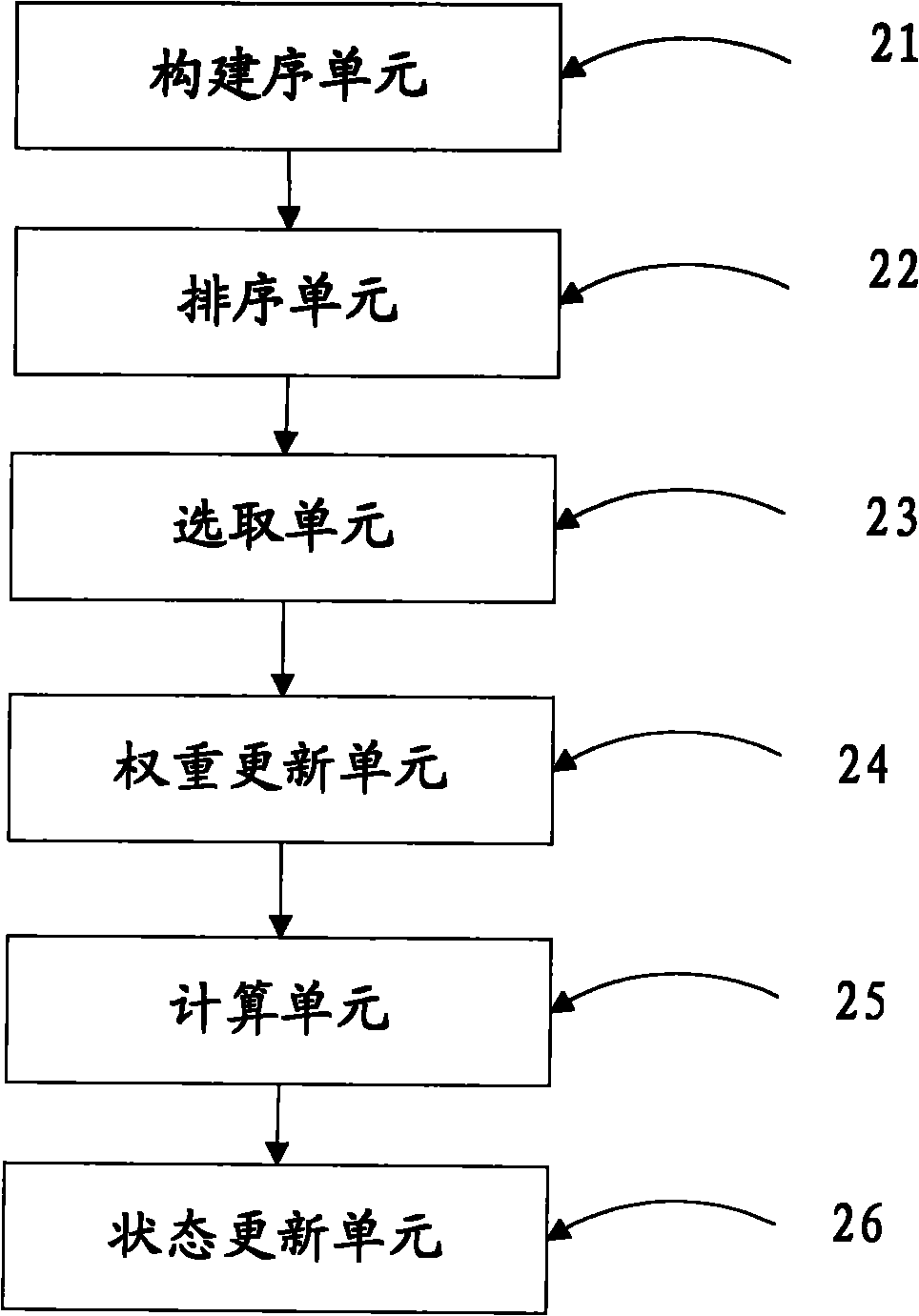
[0053] An embodiment of the present invention provides a device for calculating a service transmission path in an optical transport network. The device is specifically a PCE (Path Computation Element, Path Computation Element), such as figure 2 As shown, the device includes: a construction unit 21 , a sorting unit 22 , a selection unit 23 , a weight update unit 24 , a calculation unit 25 and a state update unit 26 .
[0054] When calculating the service transmission path in the optical transport network, the PCE first constructs an auxiliary graph according to the network resource conditions of the optical network through the construction unit 21, wherein the auxiliary graph is a node device in the optical network Network equipment constraints such as optical transceivers, upper-layer traffic grooming capabilities, wavelength conversion capabilities, and link wavelengths are transformed into edges (Edges) in the graph, and integrated into a unique graph of the entire network; ...
Embodiment 3
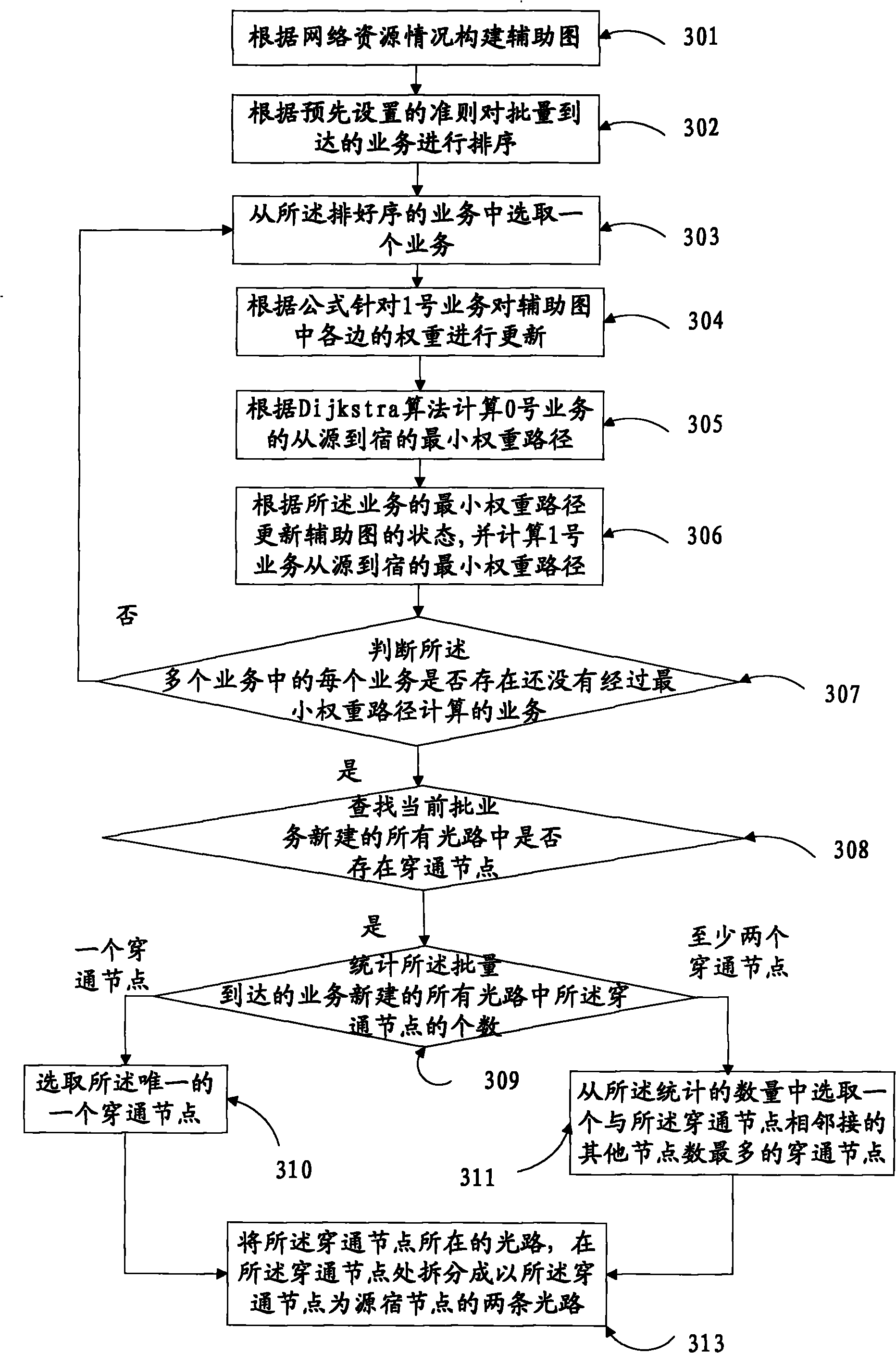
[0068] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for calculating a service transmission path in an optical transport network, such as image 3 As shown, the method includes:
[0069] 301. An auxiliary graph constructed according to the network resource situation of the optical network, each edge in the auxiliary graph corresponds to a corresponding weight, indicating the cost when the service passes through the edge; the network resource situation refers to the number of wavelengths in the optical fiber and the upper-layer business grooming capabilities of each node in the network.
[0070] The embodiment of the present invention takes six nodes in the network and the number of optical fiber wavelengths as W as an example to construct an auxiliary graph. For the convenience of service route selection, the auxiliary graph is abstracted into a virtual topology graph, as shown in Figure 4 As shown in , there is only one wavelength on each side of the virtual topo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com