Solids passivation
A technology of solid and composition, applied in the field of solid passivation, which can solve the problems of increasing the amount of waste and expensive methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Passivation of solid materials by direct method
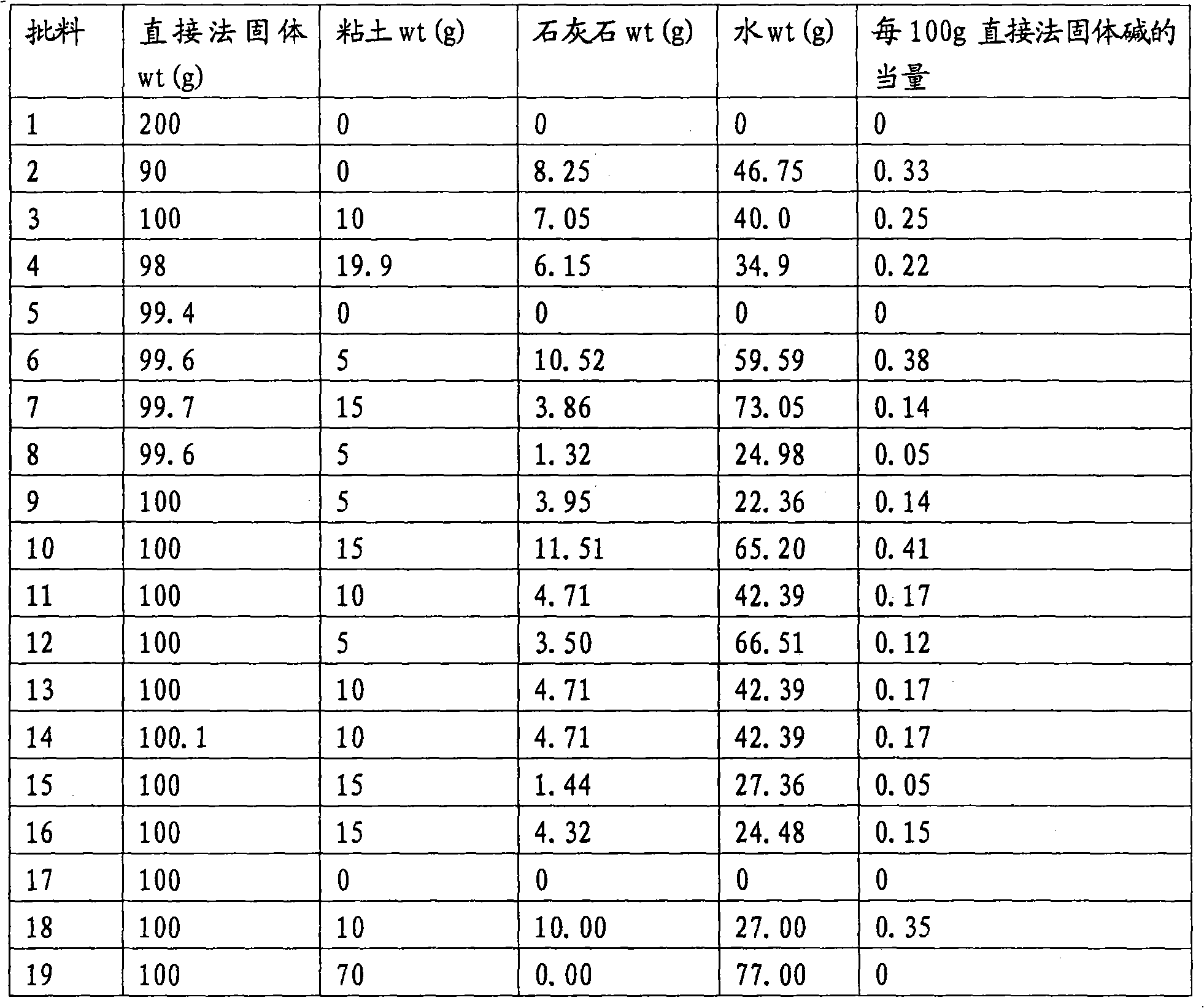
[0051] Batches of direct process solids and passivating compositions were prepared varying the amounts of clay, alkali and water. Batches were prepared as described below. The clay (kaolin), direct process solids, water and base were measured into a beaker and mixed by hand with a metal stirrer until well combined. The base used in the examples is first dissolved and / or diluted with water, or made into a water slurry. In the following examples, this water constituted the final water listed in each batch. Then according to "Recommendation on the transport of Dangerous Goods, Manual of Test and Criteria" (1995), United Nations, New York and Geneva, ISBN 92-1-139049-4, by forming into 4 inch cubes, at 140°C Bake the cubes in an oven and monitor the temperature of the cubes for 24 hours to test the self-heating of the batch. In this test, a temperature rise of the cube composition above 200°C is considered self-heating. ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] In a large-scale continuous process plant test, kaolin clay and direct process solids were fed from a hopper to a mixer by means of a screw conveyor. The direct process solids are fed into the screw conveyor by means of a rotary valve to control the ratio of clay to direct process solids entering the mixer. Limestone slurry was pumped into the mixer from a large tote through the inlet of the mixer with a 2 inch double diaphragm pump. The amount of limestone slurry added to the mixer is adjusted to achieve the desired consistency of the product leaving the mixer. Six different ratios of clay to direct process solids were tested and individually tested for self-heating and monitoring time for product to return to ambient temperature. Table 4 gives the test results for days from heating and product return to ambient temperature. Combine Test Trials 25 and 26 to test the time to self-heat and return to ambient temperature.
[0065] Table 4: Test results for self-heating ...
Embodiment 3
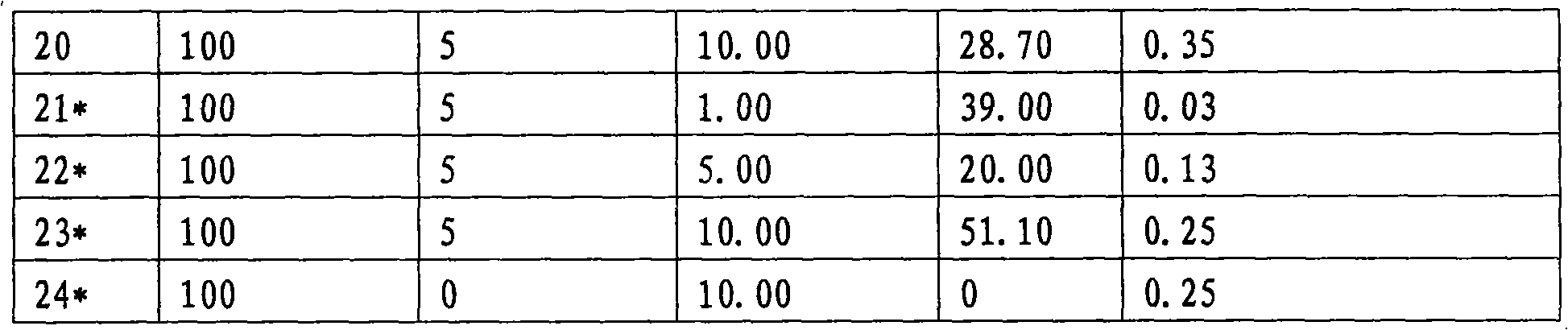
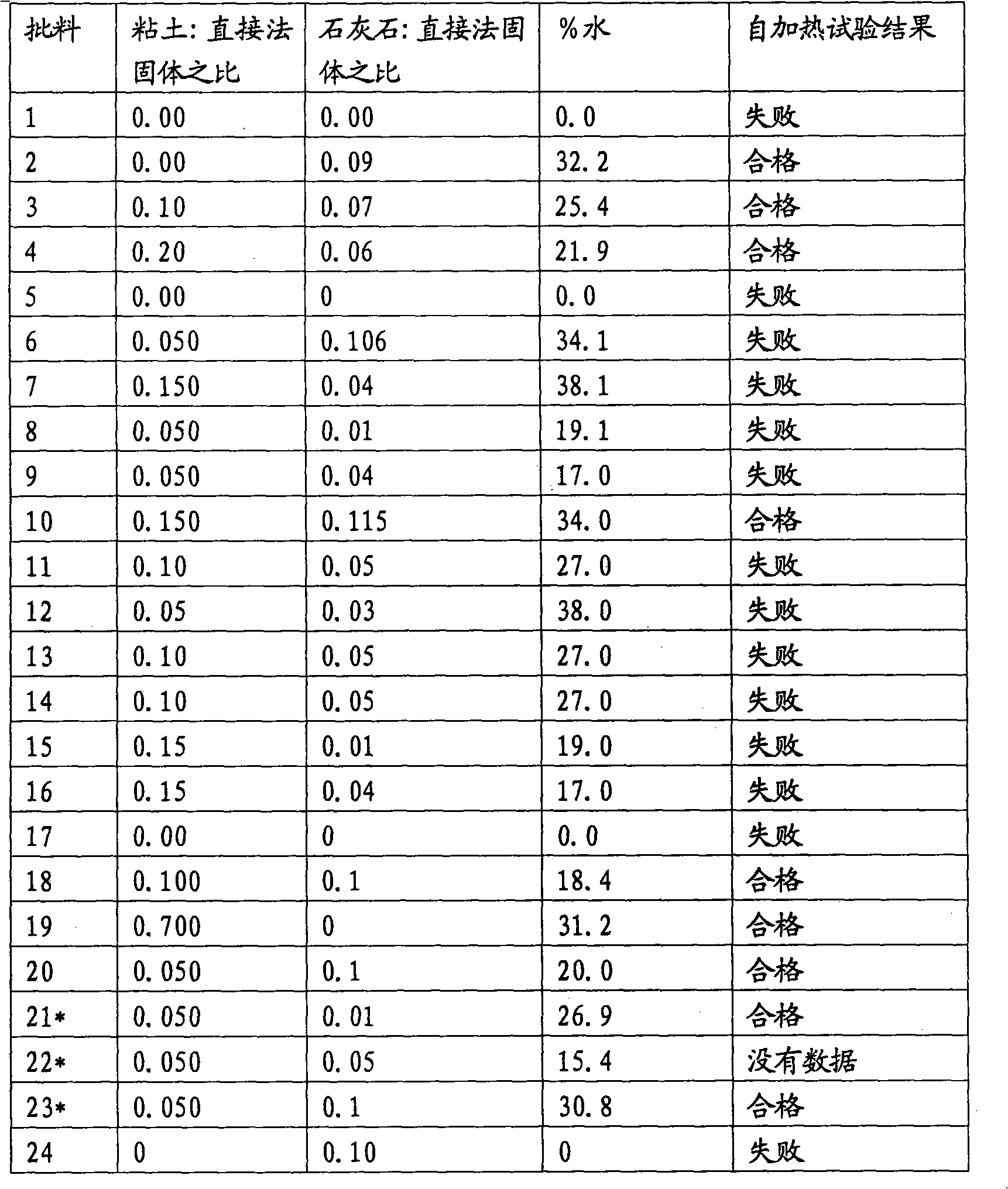
[0069] Batches of the compositions of the invention were prepared in the laboratory on a small scale, varying the ratio of clay to waste. Limestone slurry was used as base and added with direct process solids at varying ratios. The resulting compositions were evaluated for self-heating and % water. The results are summarized in Table 4 below.
[0070] Table 5: Compositions of the invention and their results for self-heating and water content
[0071]
[0072] The results in Table 5 show that the ratio of clay to direct process solids can be reduced to 0.05:1, and the ratio of limestone to direct process solids to 0.1:1, while producing compositions without self-heating. Furthermore, the percentage of water in the final product can be as low as 18.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com