Error detection device and control method for laser communication link beams
A laser communication and detection device technology, applied in measuring devices, optical devices, transmission monitoring/testing/fault measurement systems, etc., can solve poor control stability, high-frequency vibration of satellite platforms cannot be effectively compensated, rough aiming and fine aiming The control is prone to problems such as mutual coupling, so as to avoid mutual coupling problems, realize system miniaturization, stable high-precision control, and high-frequency stable beam control.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
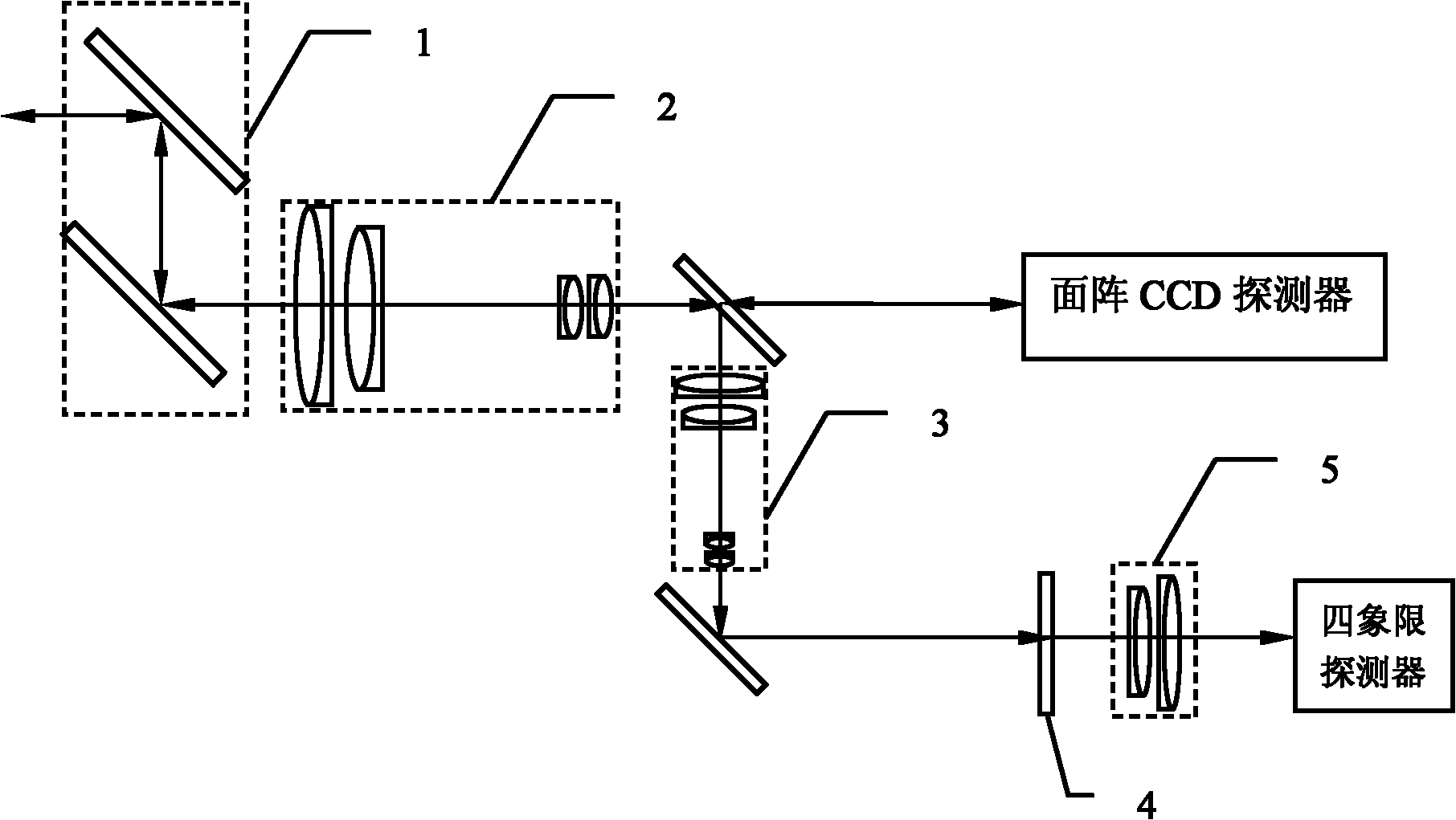
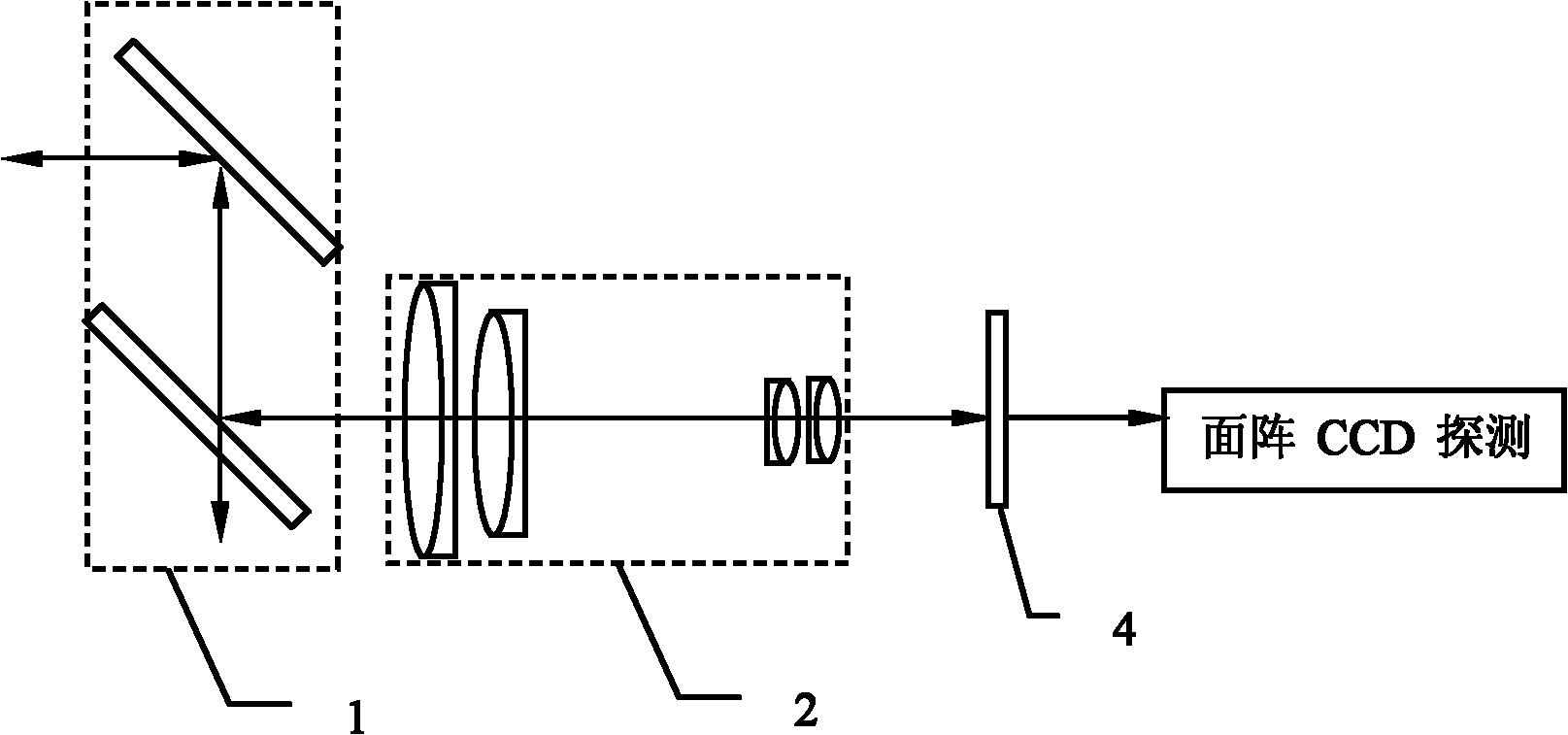
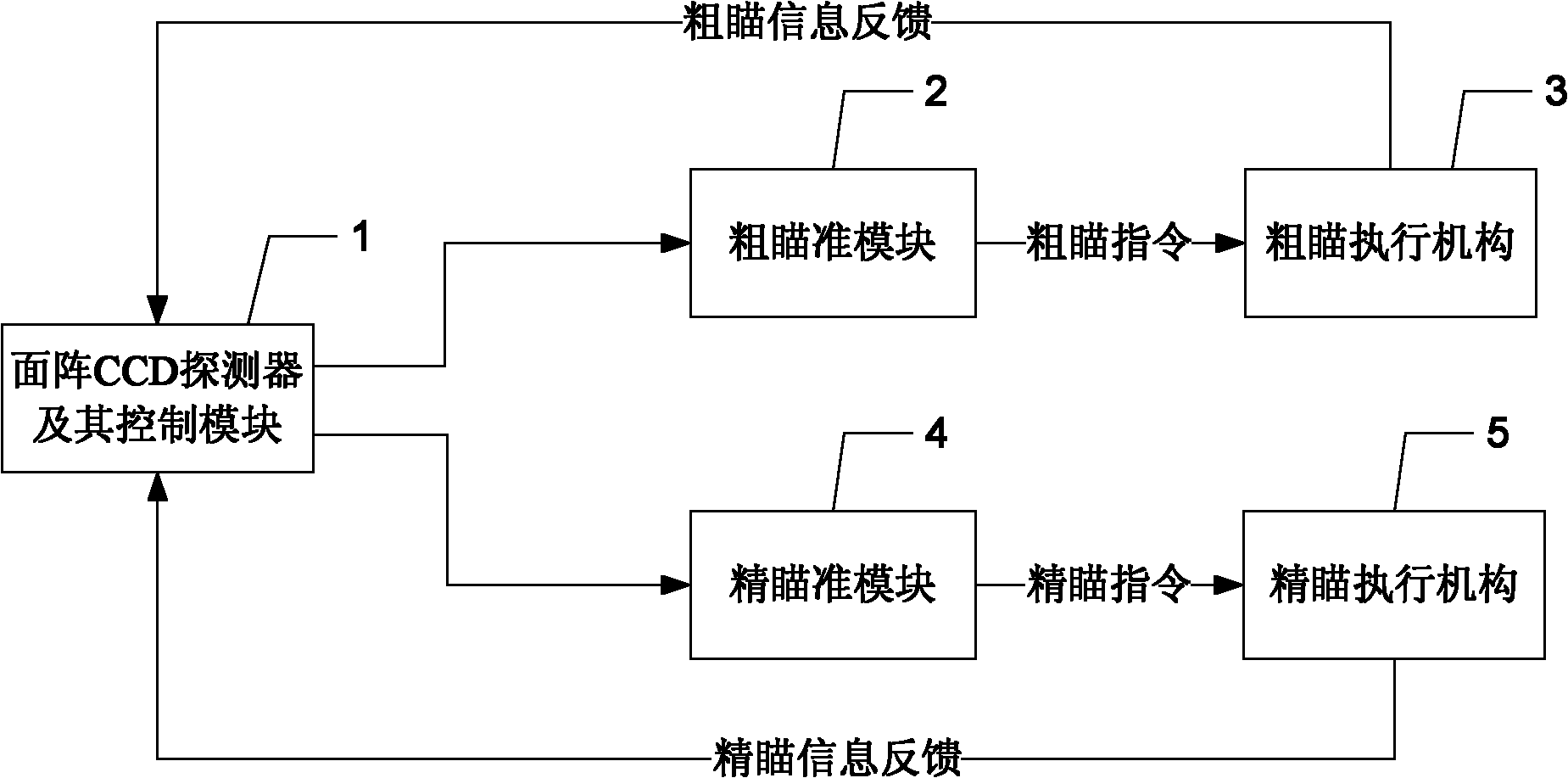
[0035] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this embodiment, the error detection device of the laser communication link beam described in this embodiment includes a rough aiming module 2, a rough aiming actuator 3, a fine aiming module 4 and a fine aiming actuator 5, and it also includes an area array CCD The detector and its control module 1, the output end of the rough aiming command of the area array CCD detector and its control module 1 is connected to the input end of the rough aiming module 2, the output end of the rough aiming module 2 is connected to the input end of the rough aiming actuator 3 Connected, the output end of the rough aiming actuator 3 is connected with the beam coarse aiming correction input end of the area array CCD detector and its control module 1;
[0036] The fine aiming command output end of the area array CCD detector and its control module 1 is connected with the input end of the fine aimin...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination Figure 3 to Figure 6 This embodiment is described. This embodiment is based on the beam control method of the laser communication link beam error detection device described in Embodiment 1. The method includes the following steps:
[0042] Step 1. Initialize the area array CCD detector 1-1, determine the aiming center point, and set multiple concentric windows nested sequentially from outside to inside on the area array CCD detector 1-1 with the aiming center point as the reference center: thick Tracking window, fine tracking window and alignment window, the coarse tracking window is a square window with a length of 280 pixels to 350 pixels, the fine tracking window is a square window with a length of 25 pixels to 35 pixels, and the alignment window is a square window with a length of 3 pixels to 6 pixels square window,
[0043] Step 2, judging whether the target imaging spot appears on the area array CCD det...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0078] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that the coarse tracking window in step 1 is a square window with a length of 300 pixels, the fine tracking window is a square window with a length of 30 pixels, and the alignment window is a square window with a length of 4 Pixel square window. Others are the same as the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com