Mineral exploration method adopting rotaary and crossed type mineral exploration network
A mineral, counterclockwise rotating technology, applied in mining equipment, mining equipment, earthwork drilling, etc., can solve the problems of lag, low accuracy of geological maps, low control degree of ore body and structure control, etc. ability, improve the accuracy, and the effect of high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
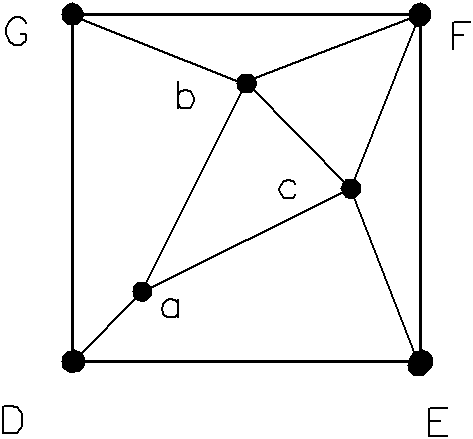
[0009] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 6 This embodiment will be specifically described. This embodiment includes the following steps: 1. Taking twice the side length of the square survey network grid determined according to the ore body stability and structural complexity, geostatistics or fractal geometry method as the side length of the basic square, for coalfield exploration Generally speaking, the exploration grid is determined according to the degree of stability of the coal seam and the degree of structural complexity. The state has stipulated the network degree standards for various types of coal fields. The basic line distance of the proven reserves is 250-500m, the common one is 500m, its double is 1000m; 2. One control point is arranged at each of the four vertices of the basic square, and three control points are scattered in the basic square, see diagram figure 1 , D(0,0), E(1000,0), F(1000,1000), G(0,1000), a(200,2...
specific Embodiment approach 2
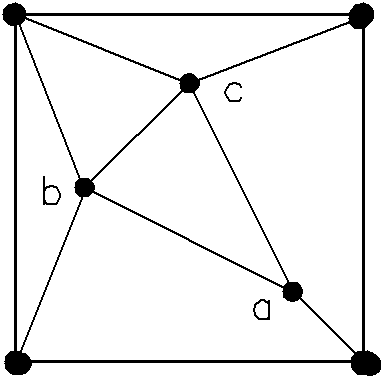
[0033] Specific implementation mode two; see illustration Figure 8 to indicate Figure 13 , the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in step 2, the three control points distributed in the basic square are a(300,300), b(400,750), c(800, 400); other steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0034] Compared with Embodiment 1, this embodiment has better dispersibility along the trend and inclination of exploration wells or boreholes in the basic unit in Embodiment 1; in this embodiment, the dispersion of exploratory wells or boreholes along the direction and inclination in supporting units 2. The length between two adjacent control points in the survey network is reduced compared with Embodiment 1, within the range of 0.43 to 0.67 times the side length of the basic square.
specific Embodiment approach 3
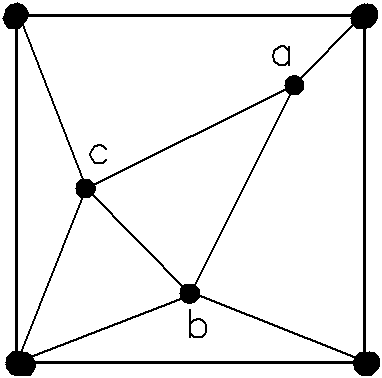
[0035] Specific implementation mode three: see Figure 14 to Figure 19 , the present embodiment comprises the following steps: 1. Take twice the side length of the square survey network grid as the side length of the basic square; 2. Arrange one control point at each of the four vertices of the basic square, and distribute three The above-mentioned internal three points are connected to form a triangle, and then a control point is arranged at the midpoint on the right side of the basic square, which is added to the control points on the four vertices of the basic square and the three control points scattered in the basic square. A total of eight control points, connect the control point at the right midpoint of the square with the two control points of the nearby triangle inside, and connect the two square vertices on the same straight line as the control point at the right midpoint of the square with the interior A control point of the nearest triangle is connected respective...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com