Integrative compressing method and device of image
A compression method and image technology, applied in image communication, television, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] H.264 with fixed quantization factor is used to perform lossy encoding, lossless compression uses dictionary compression gzip, Hextile encoding in remote frame buffer RFB (remote frame buffer) protocol; ZRLE encoding in remote frame buffer RFB (remote frame buffer) protocol Some encoding methods in , specifically refer to all encoding methods that appear before the zlib encoding step, we call it RLE (Run-Length Encoding) encoding; and four filtering methods in PNG (Portable Network Graphics). Each pixel uses n-bits R, G, B (red, green, blue) for a total of 3n-bit RGB representation.
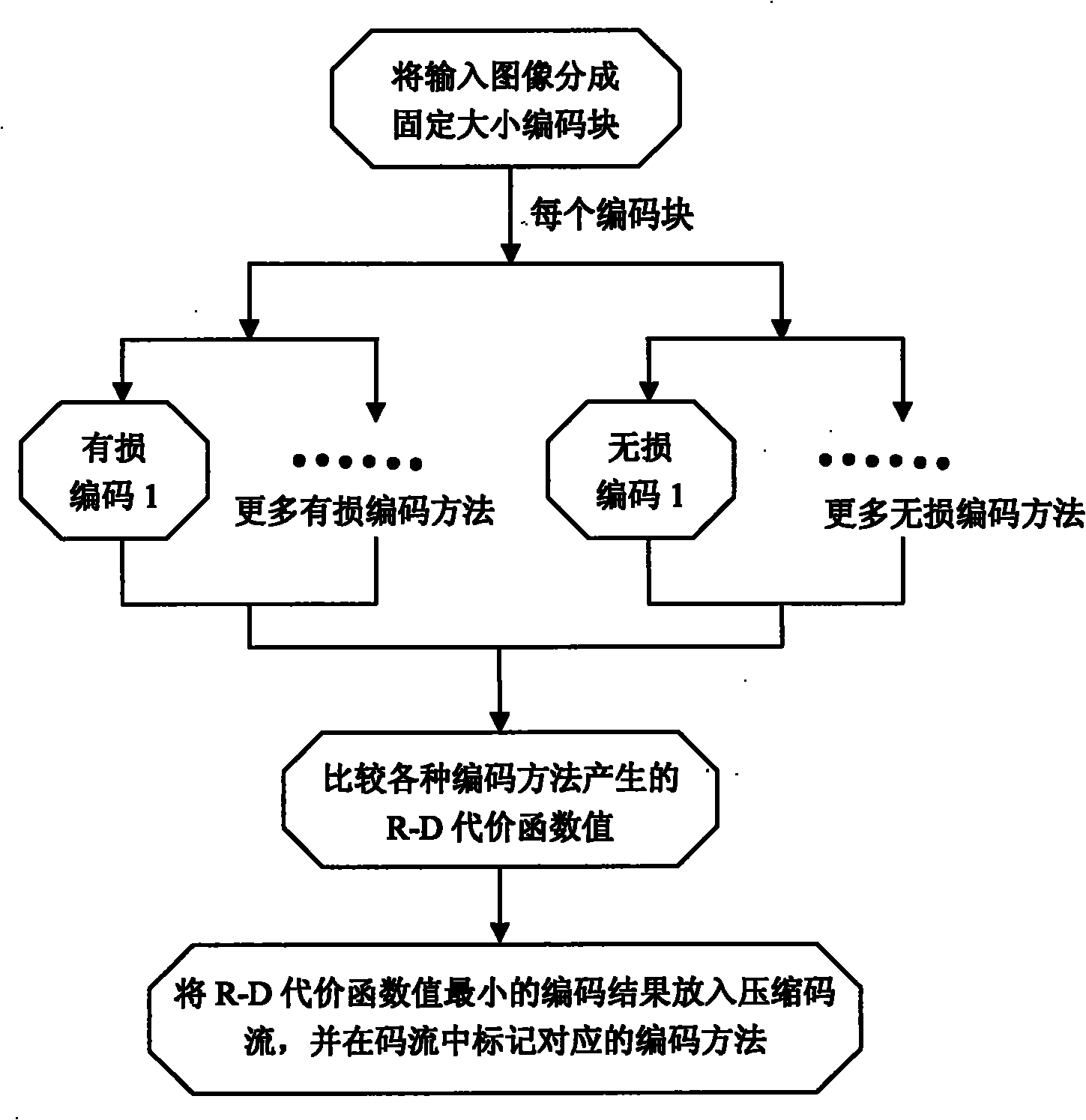
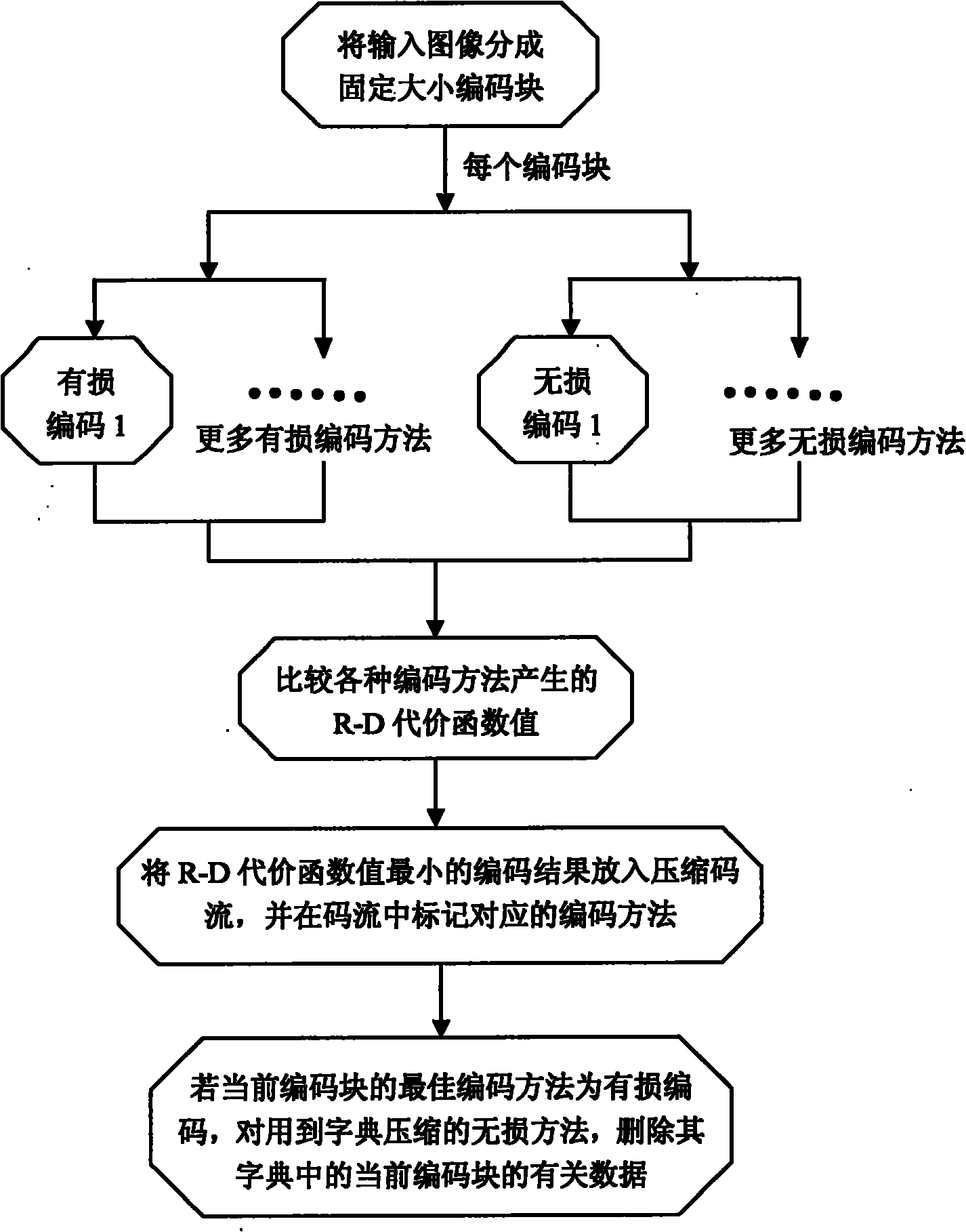
[0098] An integrated encoding method for images, the process is as follows Figure 7 shown, including:
[0099] 1. Divide the input image into 16×16 non-overlapping macroblocks, and then repeat steps 2 to 5 for these macroblocks until the last macroblock in the image.
[0100] 2. H.264 and four lossless methods are used for encoding, and each method is encoded once.
[0101] In the spec...
Embodiment 2
[0139] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: H.264 with a fixed target bit rate and variable quantization factor is used to perform lossy encoding, and lossless compression uses two methods in Embodiment 1: gzip encoding and PRLEG, The encoding process and decoding process of the PRLEG method are as follows Figure 10 and Figure 13 shown. Each pixel uses n-bit Y, Cb, Cr for a total of 3n-bit YUV444 representation. Similar to Embodiment 1, for each coding block, H.264 and two lossless methods are used for coding, and the one with the smallest R-D cost function value is selected as the best coding method. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that for H.264 encoding, after the encoding of the current macroblock is completed, the quantization factor used for the next macroblock needs to be determined according to the preset target number of bits instead of using a fixed quantization factor.
Embodiment 3
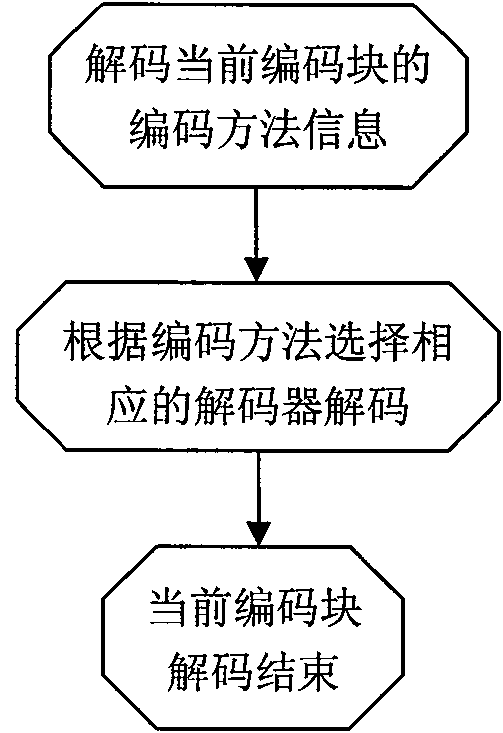
[0141] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: VC-1 with a fixed quantization factor is used to perform lossy encoding, and lossless compression uses gzip encoding. Each pixel uses an average 16-bit YUV422 representation. Similar to Embodiment 1, for each coding block, VC-1 and gzip coding are used, and the one with the smallest R-D cost function value is selected as the best coding method. Different from Embodiment 1, since only one lossless method is used, in the decoding process, there is no need to determine whether the best encoding method of the current encoding block is a lossless method, and to update the dictionary of other lossless methods; similarly Reasonably, the dictionary data update module is not needed in the decoding device.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com