Liquid crystal device, method of controlling liquid crystal device, and electronic apparatus
A liquid crystal device and control circuit technology, applied in the direction of cathode ray tube indicators, instruments, static indicators, etc., can solve the problem of continuing and achieve the effect of suppressing flickering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
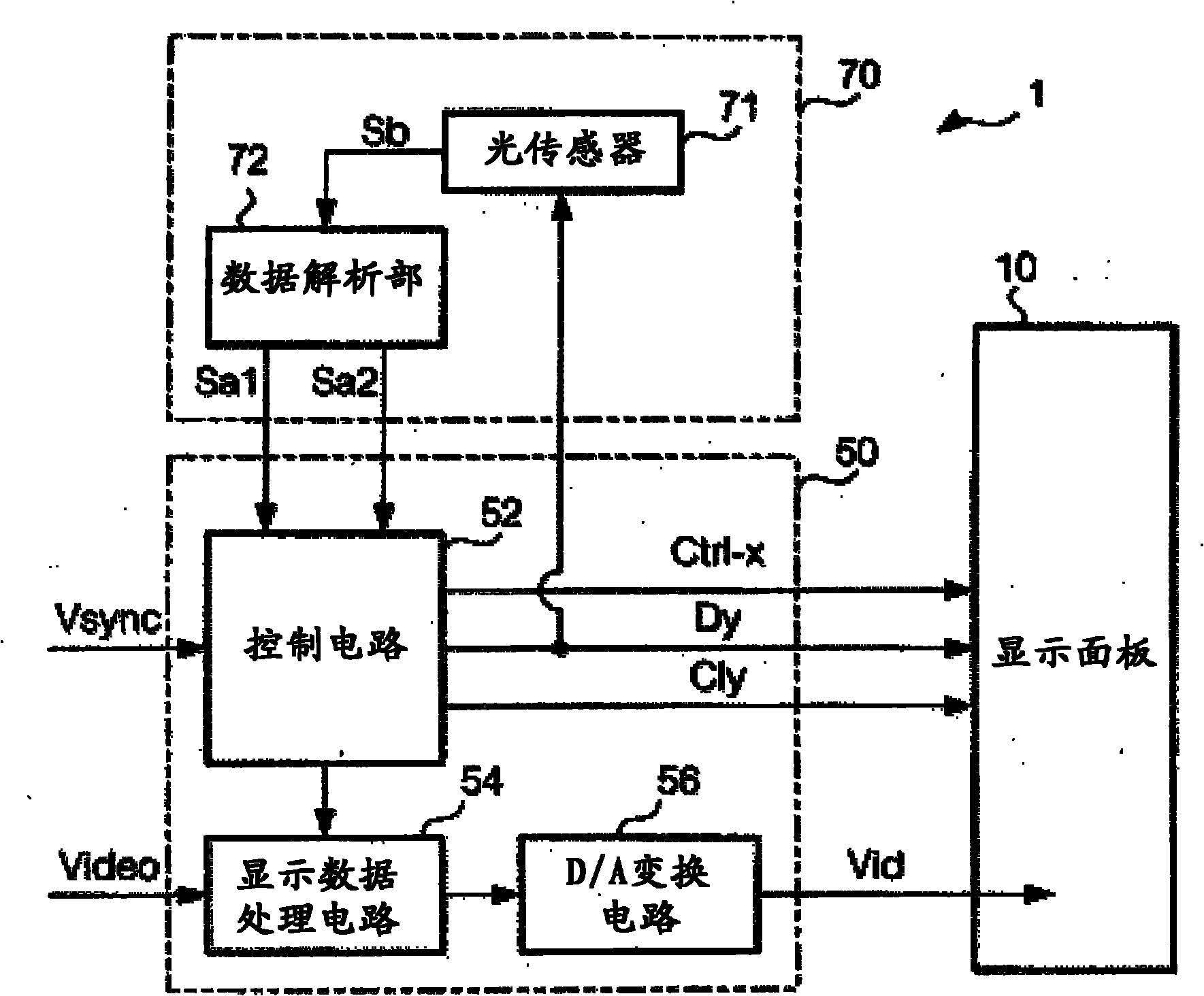
[0041] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the electro-optical device 1 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
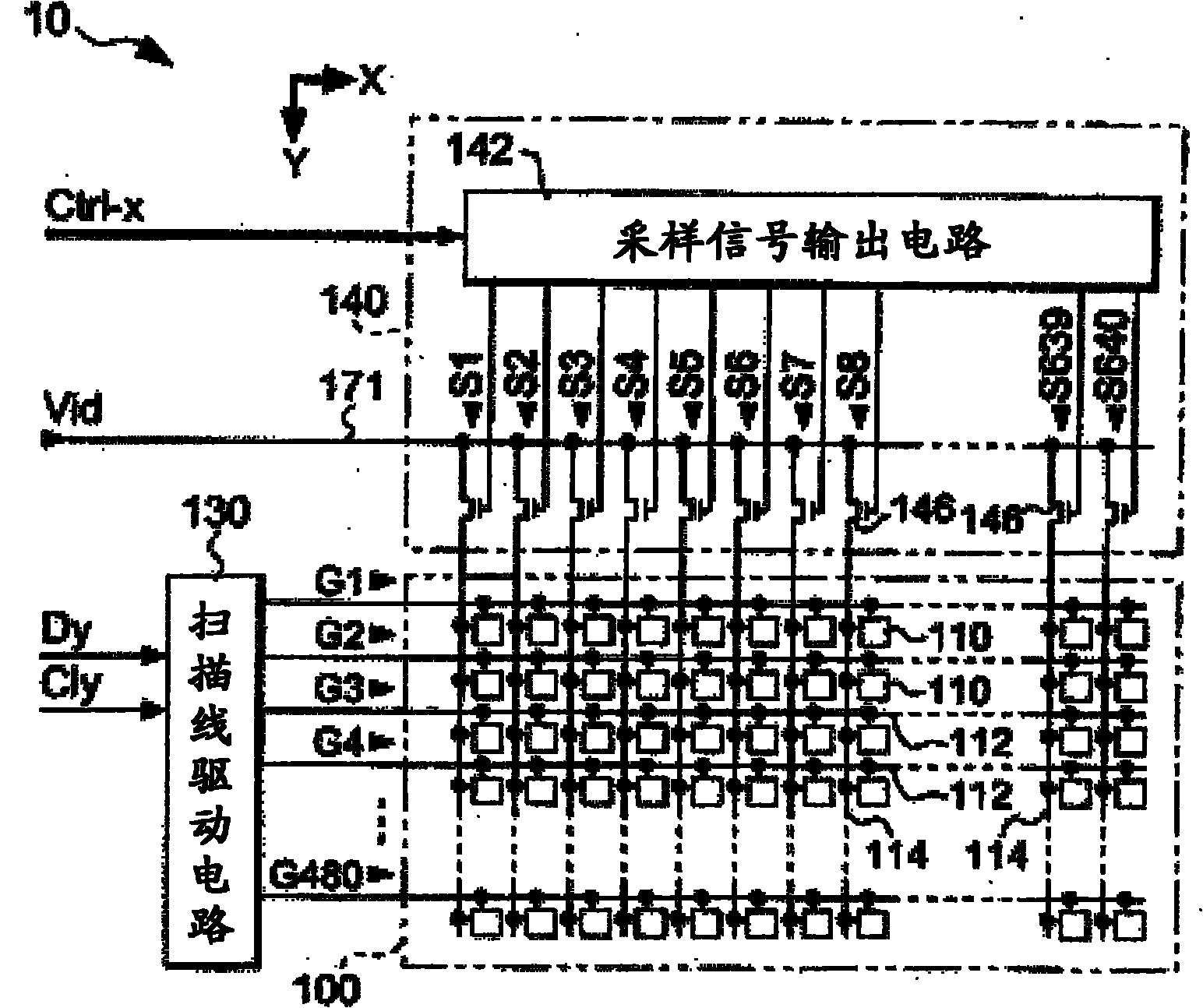
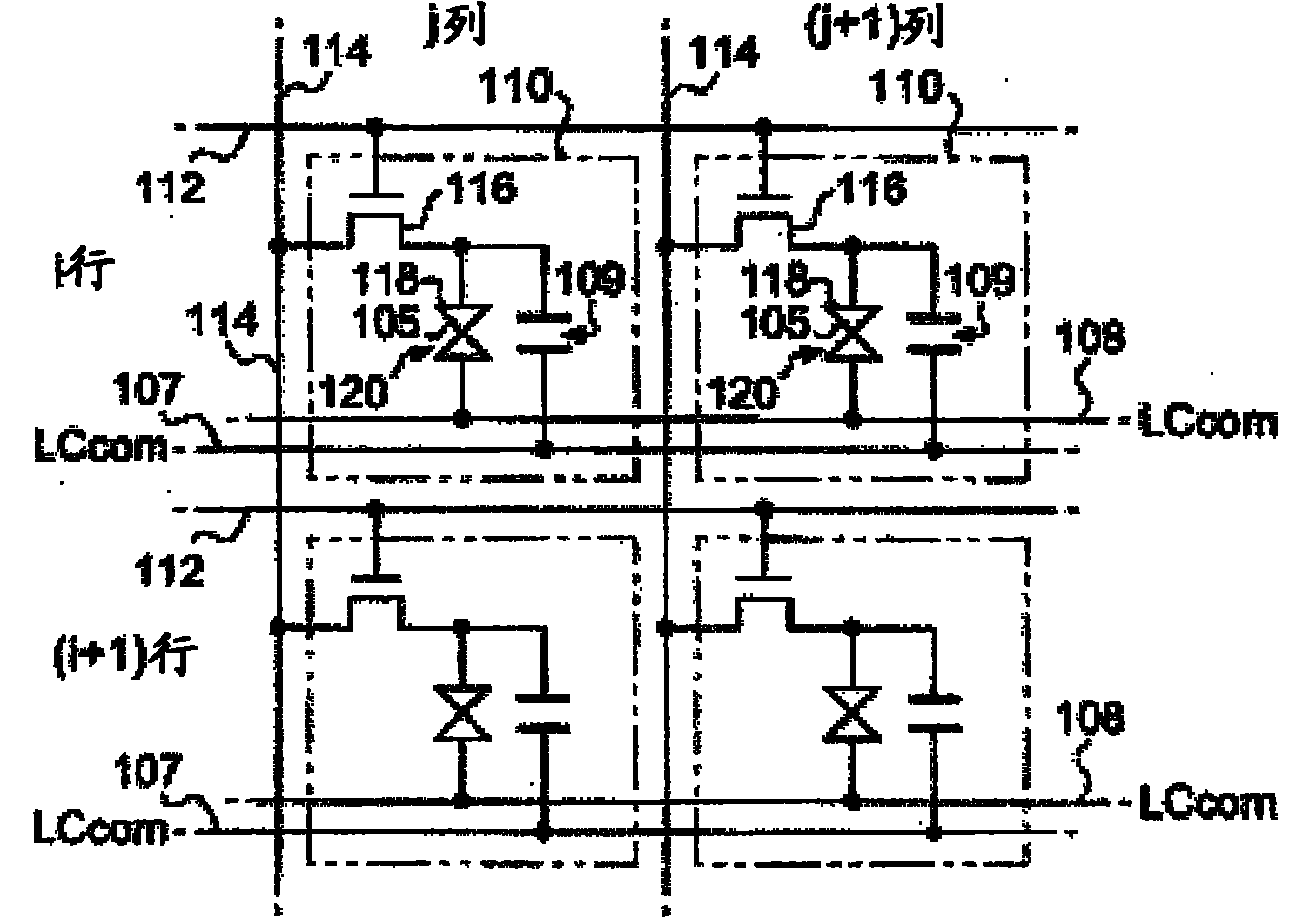
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the electro-optical device 1 is roughly divided into a display panel 10 , a processing circuit 50 , and a detection circuit 70 . Among them, the processing circuit 50 as a circuit module for controlling the operation of the display panel 10 includes: a control circuit 52, a display data processing circuit 54, and a D / A conversion circuit 56, and is connected to the display panel 10 through, for example, an FPC (flexible printed circuit) substrate. connect. In addition, the detection circuit 70 includes an optical sensor 71 and a data analysis unit 72 . In addition, the electro-optical device 1 is an example of a liquid crystal device that displays images using liquid crystals.
[0043] The control circuit 52 generates various control signals for controlling the display panel 10 in syn...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0121] Next, an electro-optical device 1 according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. The electro-optical device 1 according to the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment in terms of hardware configuration. The electro-optical device 1 according to the second embodiment is different from the electro-optical device 1 according to the first embodiment in that the process performed by the control circuit 52 is different. Therefore, the following description will focus on this point of difference.
[0122] Figure 15 It is a flowchart showing the flow of processing performed by the control circuit 52 according to the second embodiment. In addition, in the control circuit 52 , the processing from the start of the drive of the display panel 10 to step SB1 is the same as that of the first embodiment.
[0123] First, the control circuit 52 acquires the signal Sa1 and the signal Sa2 supplied from the data analysis unit 72 (step ...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0135]Next, an electro-optical device 1 according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described. The electro-optical device 1 according to the third embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment in terms of hardware configuration. The electro-optical device 1 according to the third embodiment is different from the electro-optical devices 1 according to the first and second embodiments in that the processing performed by the control circuit 52 is different. Therefore, the following description will focus on this point of difference.
[0136] Figure 17 It is a flowchart showing the flow of processing performed by the control circuit 52 according to the third embodiment. The third embodiment differs from the second embodiment in that it has step SB2a.
[0137] Figure 18 It is a flowchart showing the flow of the set value setting process performed in step SB2a.
[0138] First, the control circuit 52 acquires the signal Sa1 and the signal Sa2 (ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com