Perceptually-based compensation of unintended light pollution of images for display systems
An image and display technology, applied in the field of optical systems, can solve the problems of pollution quality, degradation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
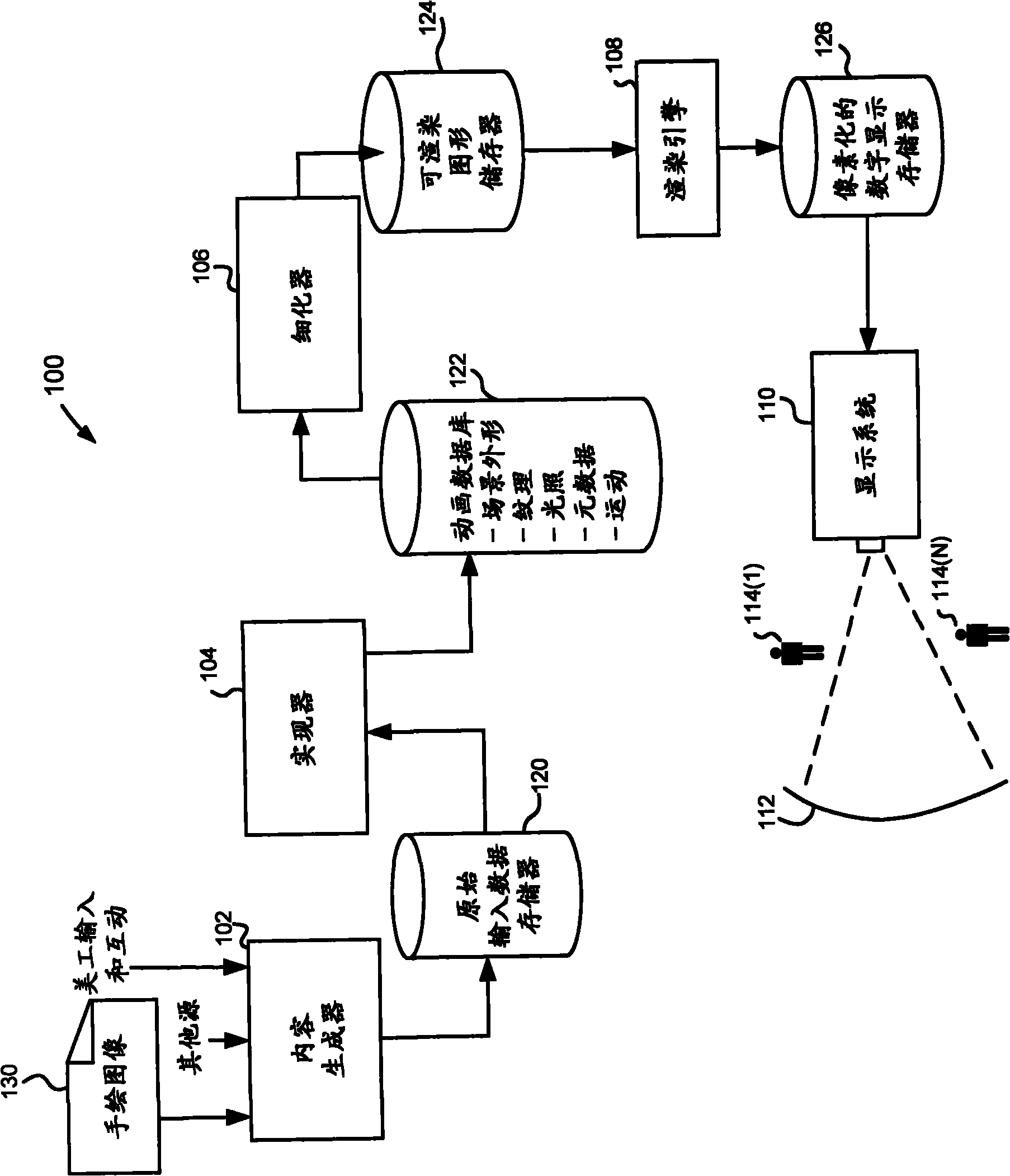
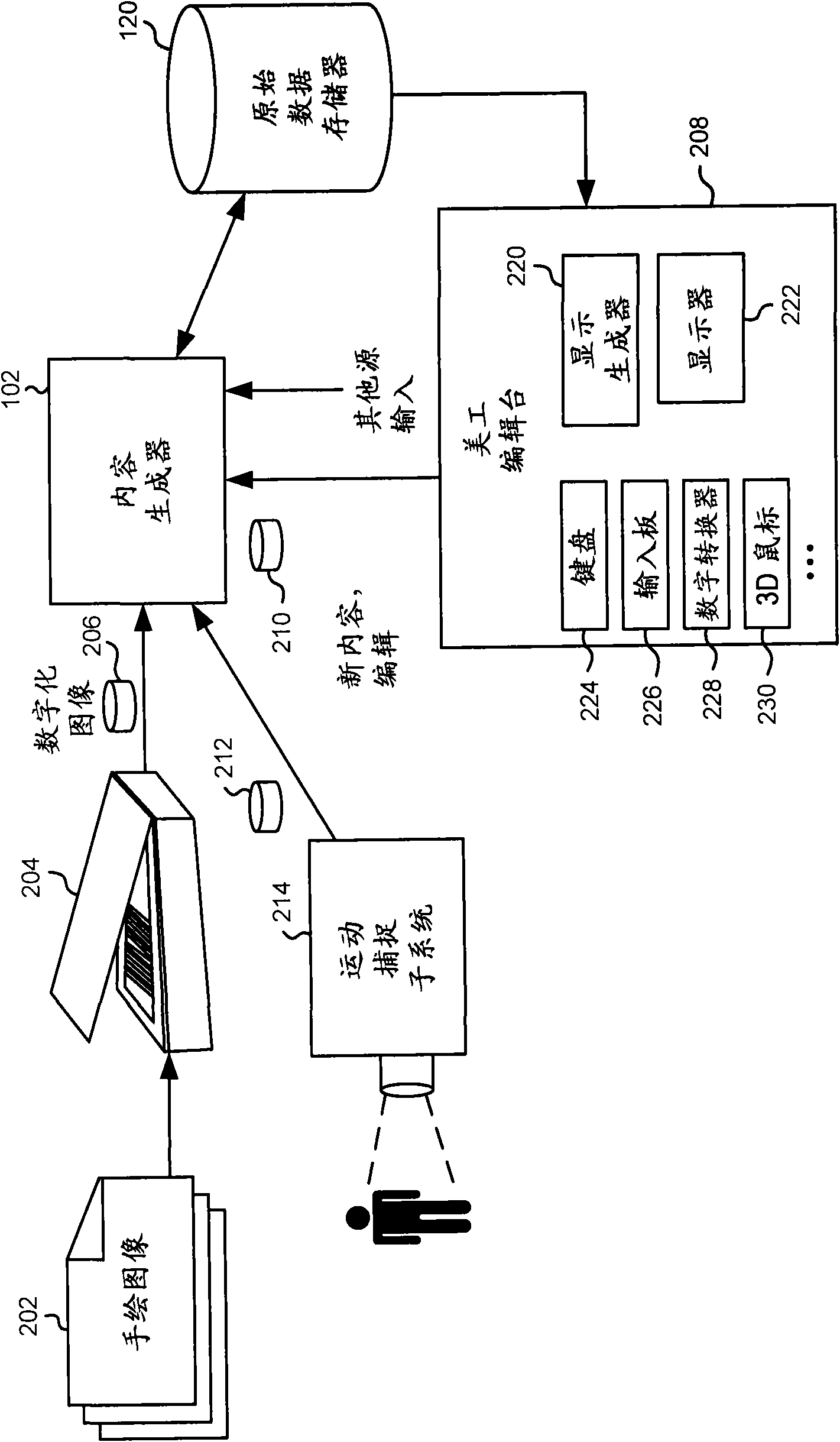
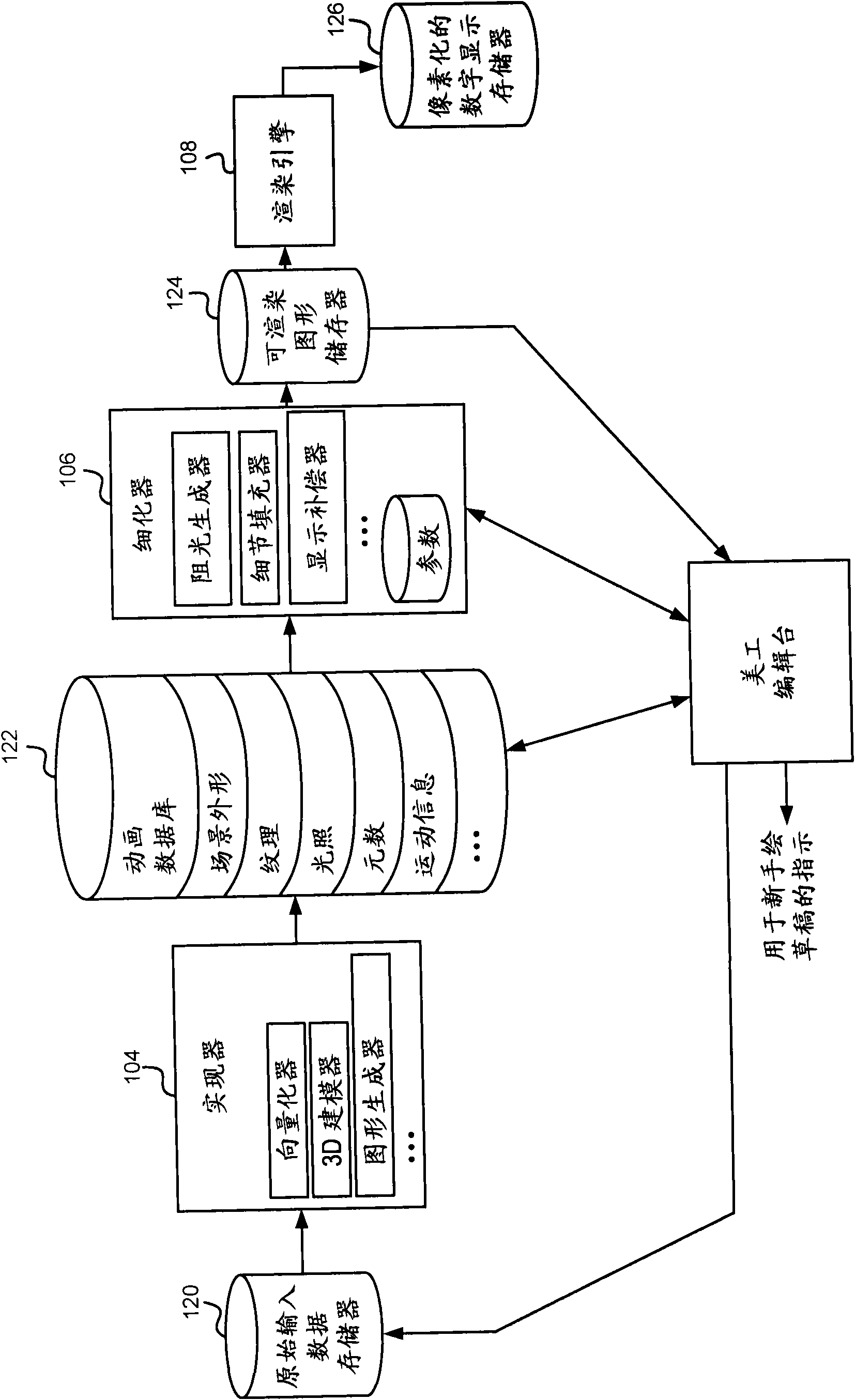
[0024] An improved image processing system is described herein that can be used to process images to reduce the perception of ghosting, and / or as part of a display system that processes images and displays them.
[0025] Since two-view stereo is only an approximation of natural depth perception, and since images are always displayed in the same plane in the depth direction, i.e., the screen, stereoscopic 3D display requires a separation between focal length and vergence, viewing stereoscopic 3D images already requires An increased perceptual burden on the Human Visual System (HVS), so ghosting should not make the situation worse. Ghosting introduces conflicting perceptual depth cues, also known as retinal competition, in which the stereoscopic process of the human visual system selectively attempts to merge intended and unintended edges for depth perception. This leads to a further increase in cognitive load. By performing perceptual deghosting, the synthesized stereoscopic 3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com