Liquid crystal display and method for manufacturing liquid crystal display
A technology of liquid crystal display and liquid crystal layer, applied in instruments, light guides, optics, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to achieve high transmittance, liquid crystal molecular orientation, etc., achieve good voltage response characteristics, prevent transmittance reduction, and high transmittance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0065] - First Example (Measurement Results of Transmittance in Case of Different Step Heights of Concave and Convex Structures)
[0066] -Second Example (Measurement Results of Transmittance in Case of Different Widths of Upper Surfaces in Modification 3)
[0067] - Third Example (Measurement Results of Transmittance in the Case of Different Step Heights in Modification 3)
Embodiment approach
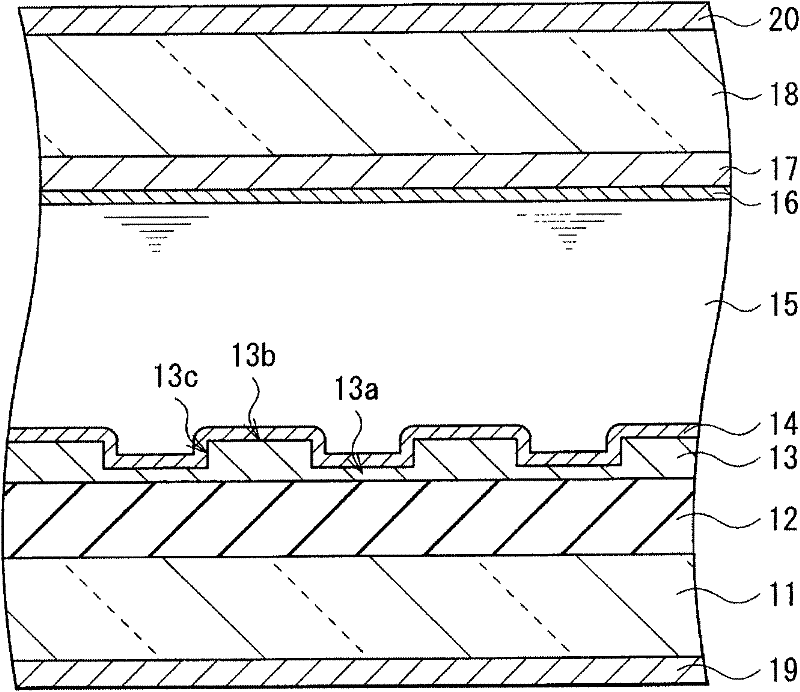
[0069] Structure of LCD 1
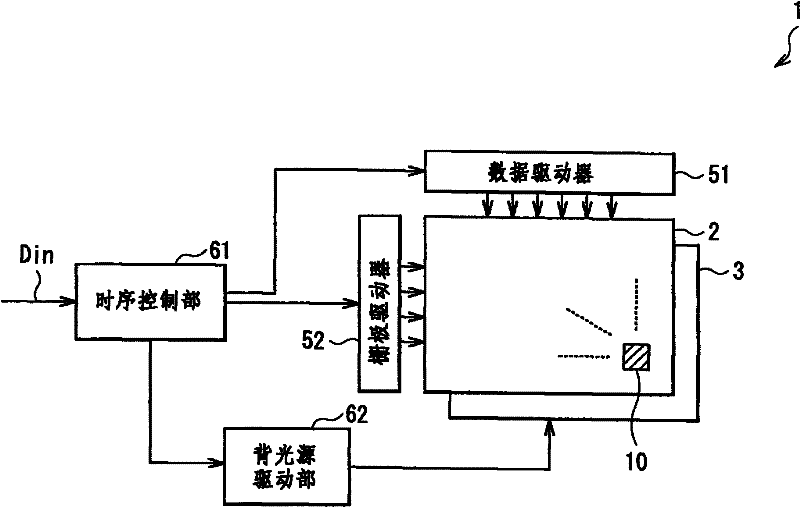
[0070] figure 1 The overall structure of a liquid crystal display (liquid crystal display 1) according to one embodiment of the present invention is shown. The liquid crystal display 1 includes, for example, a liquid crystal display panel 2 , a backlight 3 , a data driver 51 , a gate driver 52 , a timing control unit 61 and a backlight driver 62 , and displays an image based on an external input signal Din.
[0071] The backlight 3 is a light source that irradiates light to the liquid crystal display panel 2 , and is arranged on the back side of the liquid crystal display panel 2 (on the surface on the polarizing plate 19 side to be mentioned later). The backlight 3 includes, for example, LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes), CCFLs (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps), and the like. The backlight driving section 62 controls the lighting operation (light emitting operation) of the backlight 3 .
[0072] The timing control unit 61 controls the driving timing o...
no. 2 example
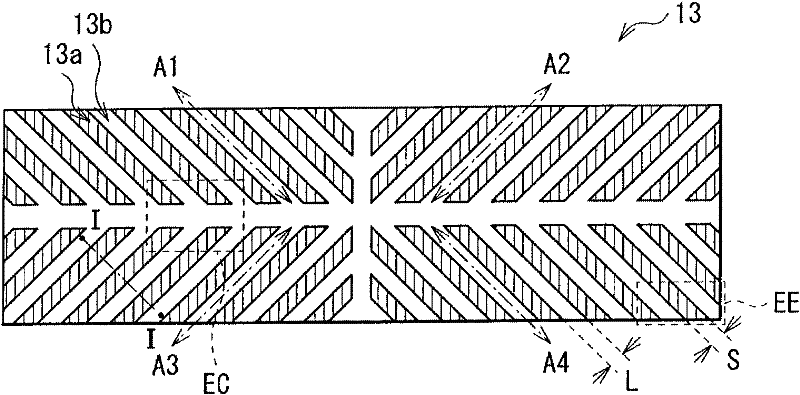
[0179] As a second example, the transmittance was measured with the slope angle θt of the slope 23 c in the pixel electrode 23 described in Modification 3 varied. Specifically, such as Figure 38 As shown, the inclination angle θt of the slope is changed under the following conditions: the width S (4 μm) of the concave surface 23a, the thickness Ta (50nm), the pitch (=the width of the bottom of the trapezoidal convex surface: 4μm), and the thickness Tb (200nm) of the convex surface 23b are constant , while the width Da of the convex surface 23b varies. At this time, the width Da changes stepwise by 0.5 μm within the range of 3.5 μm to 1 μm (both inclusive). In either case, there is no problem with liquid crystal orientation, and if Figure 39 As shown, the transmittance is very high. Also, when the width Da is 1 μm, the transmittance is highest.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com