Detection method and system for MIMO system
A detection method and multi-output technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problem of complex node selection, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of node selections and simplifying node selection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
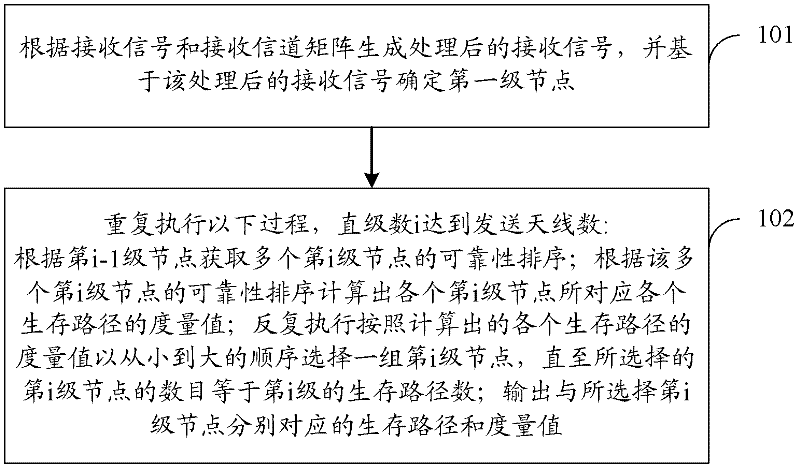
[0033] A detection method for a multiple-input multiple-output system, comprising: generating a processed received signal according to a received signal and a received channel matrix, and determining a first-level node based on the processed received signal, and repeating the following process until the number i When the number of transmitting antennas is reached, i is a positive integer greater than 1:
[0034] Obtain the reliability ranking of at least two i-th level nodes according to the i-1th level nodes; calculate the metric value of each survival path corresponding to each i-th level node according to the reliability ranking of at least two i-th level nodes;
[0035] Repeatedly select a group of i-th level nodes in ascending order according to the metric value of each survival path, until the number of selected i-th level nodes is equal to the number of survival paths of the i-th level;
[0036] Outputting survival paths and metric values for decoding sent signals cor...
Embodiment 2
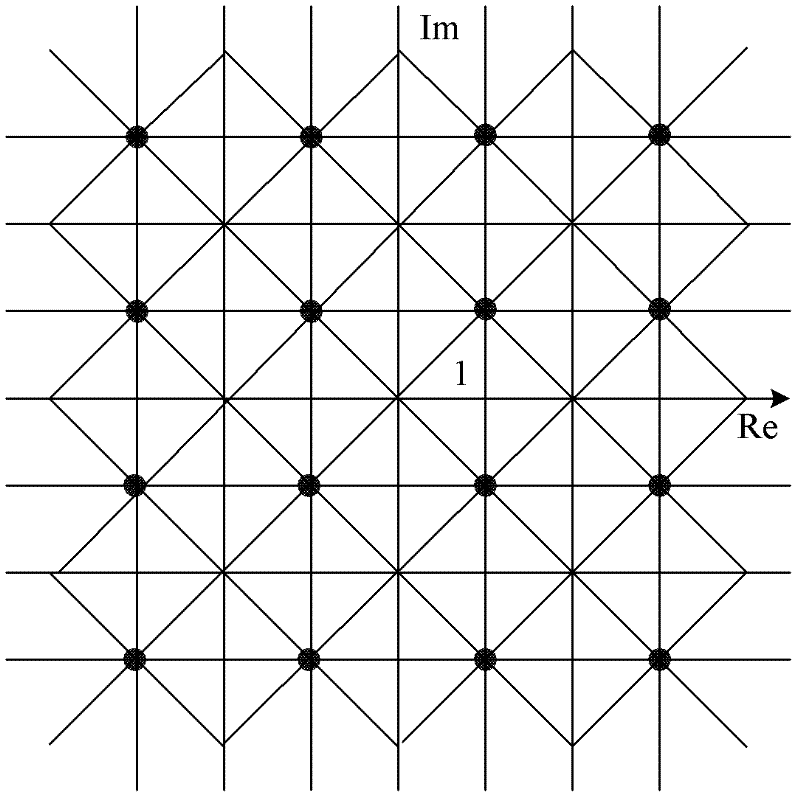
[0084] Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the preset two-dimensional space is a two-dimensional space with constellation points of 16QAM, and the two-dimensional space is divided into 128 areas, and each area is called a block, corresponding to each block, is One reliability ranking table is stored, that is, in this embodiment, 128 reliability ranking tables are stored. Each reliability ranking table correspondingly records the corresponding constellation point ranking when the node is located in the area. That is to say, as long as it is determined which block the node is located in, the constellation point ranking can be obtained by looking up the reliability ranking table of the block, thereby obtaining the reliability ranking of the node.
[0085] An example will be given below to describe in detail.
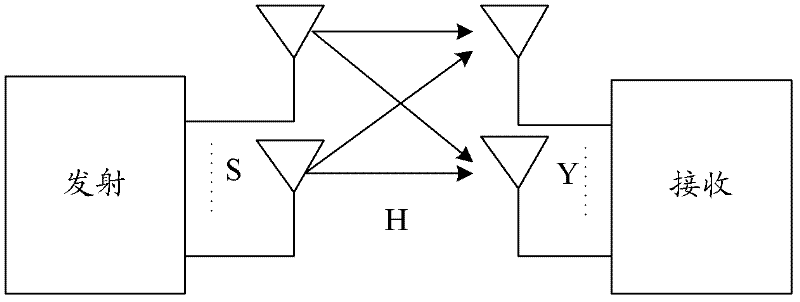
[0086] Scenario: see Figure 1a , in this MIMO system, there are T transmitting antennas at the transmitting end, and R receiving antennas at the receiving end...
Embodiment 3
[0123] In the second embodiment, the constellation point rankings of all regions are stored. The difference from the second embodiment is that in this embodiment, only the constellation point rankings of some regions are stored.
[0124] For example, it can be as follows:
[0125] Such as Figure 1c As shown, due to the symmetry of the constellation point coordinates, only the constellation point ordering of some areas can be stored. If the estimated value of the node is not in the area where the reliability ordering is stored, the estimated value of the node can be mapped to the area where the reliability ordering is stored. In the area, and look up the table to get the constellation point sorting, and then reverse the obtained sorting to get the corresponding sorting of the block where the original node estimated value is located.
[0126] The following uses an example of storing only reliability sorting tables corresponding to blocks in the first quadrant area for illustra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com