LPMSM (linear permanent magnet synchronous motor) with low-thrust fluctuation
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and low-thrust technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, propulsion systems, etc., can solve problems such as fluctuations, and achieve the effects of eliminating end positioning force, reducing unbalance, and reducing electromagnetic force fluctuations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
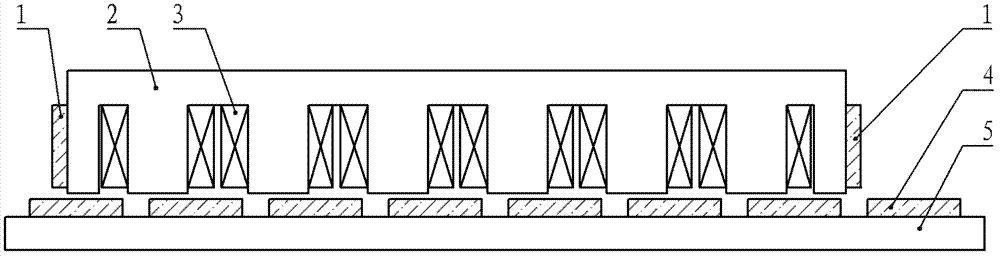
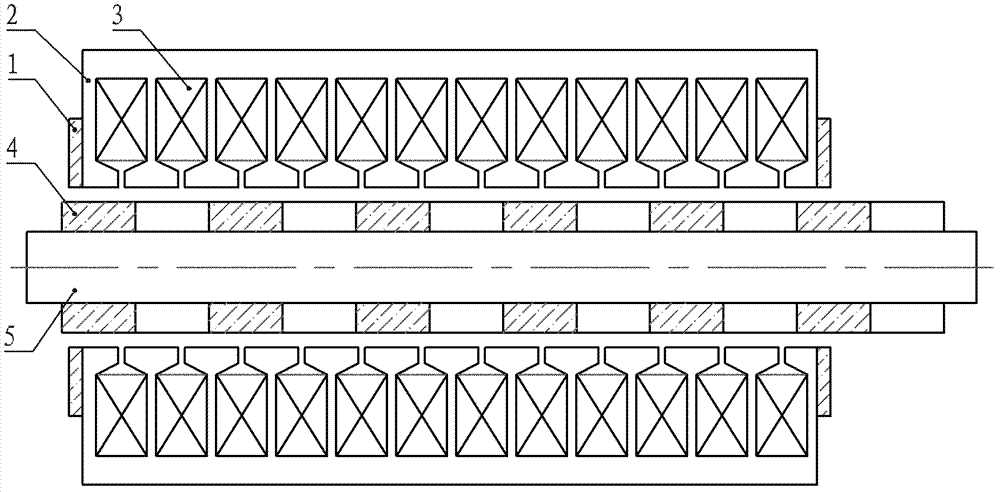
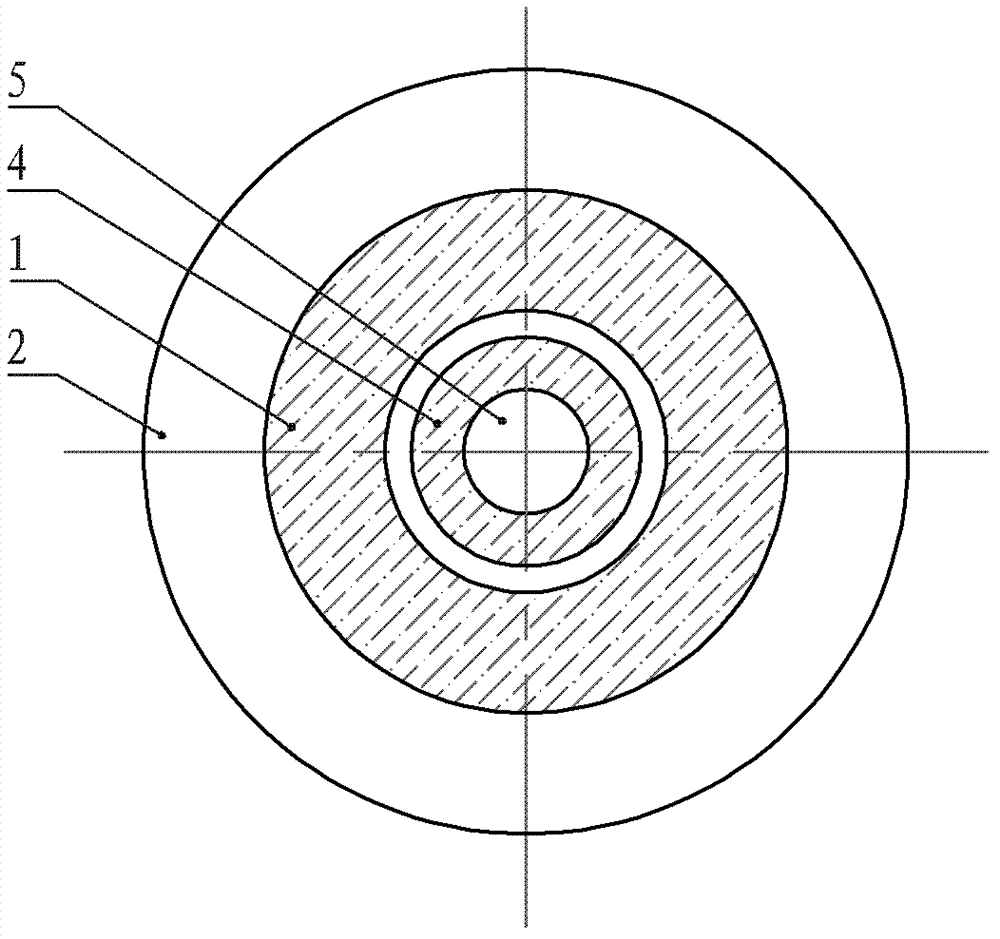
[0012] Specific Embodiments 1. The low thrust fluctuation linear permanent magnet synchronous motor described in this embodiment includes a primary, a secondary and an air gap, the secondary includes a secondary permanent magnet 4 and a yoke 5, and the primary includes an armature core 2 and an armature The winding 3 is characterized in that the primary also includes two primary permanent magnets 1; the two primary permanent magnets 1 are pasted and fixed on the front and rear ends of the armature core 2 respectively, and the magnetic field generated by each primary permanent magnet 1 The magnetic field generated by the opposite secondary permanent magnet array interacts, so that the two ends of the primary generate a force parallel to the direction of motion, and the directions of the forces generated by the two primary permanent magnets 1 located at both ends are opposite or opposite , and cancel each other out.
[0013] In this embodiment, the primary permanent magnet 1 is ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0015] Embodiment 2. This embodiment is a further limitation of the low thrust fluctuation linear permanent magnet synchronous motor described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the two primary permanent magnets 1 are pasted and fixed on the armature core 2 respectively. The end faces of the front and rear ends of the motor are perpendicular to the moving direction of the motor mover.
[0016] The installation position of the primary permanent magnet 1 described in this embodiment is suitable for the case where the plane of the end of the armature core is perpendicular to the moving direction of the mover, that is, the plane where the end surface of the armature core is located is perpendicular to the moving direction of the mover.
[0017] see figure 1 As shown, this figure shows a schematic structural diagram of a linear motor with a flat structure. In the motor shown in this figure, the primary permanent magnet 1 is a flat structure.
[0018] see figure 2 with image...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0019] Specific Embodiment 3. This embodiment is a further limitation of the low-thrust fluctuation linear permanent magnet synchronous motor described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the two primary permanent magnets 1 are pasted and fixed on the armature core 2 respectively. On the end faces of the front and rear ends of the motor, the included angle between the end faces and the moving direction of the motor mover is less than 90°.
[0020] The installation position of the primary permanent magnet 1 described in this embodiment is suitable for the case where the plane of the end of the armature core is not perpendicular to the moving direction of the mover, that is, the end face of the armature core 2 is an inclined plane or arc.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com