Maximum complete subgraph-based embedded system register allocation method
A register allocation and embedded system technology, applied in memory systems, instruments, gene models, etc., can solve the problems of not considering overflow cost and reducing register allocation efficiency, so as to improve register allocation efficiency, reduce overflow cost and overflow variable individual Number, the effect of speeding up the evolution rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
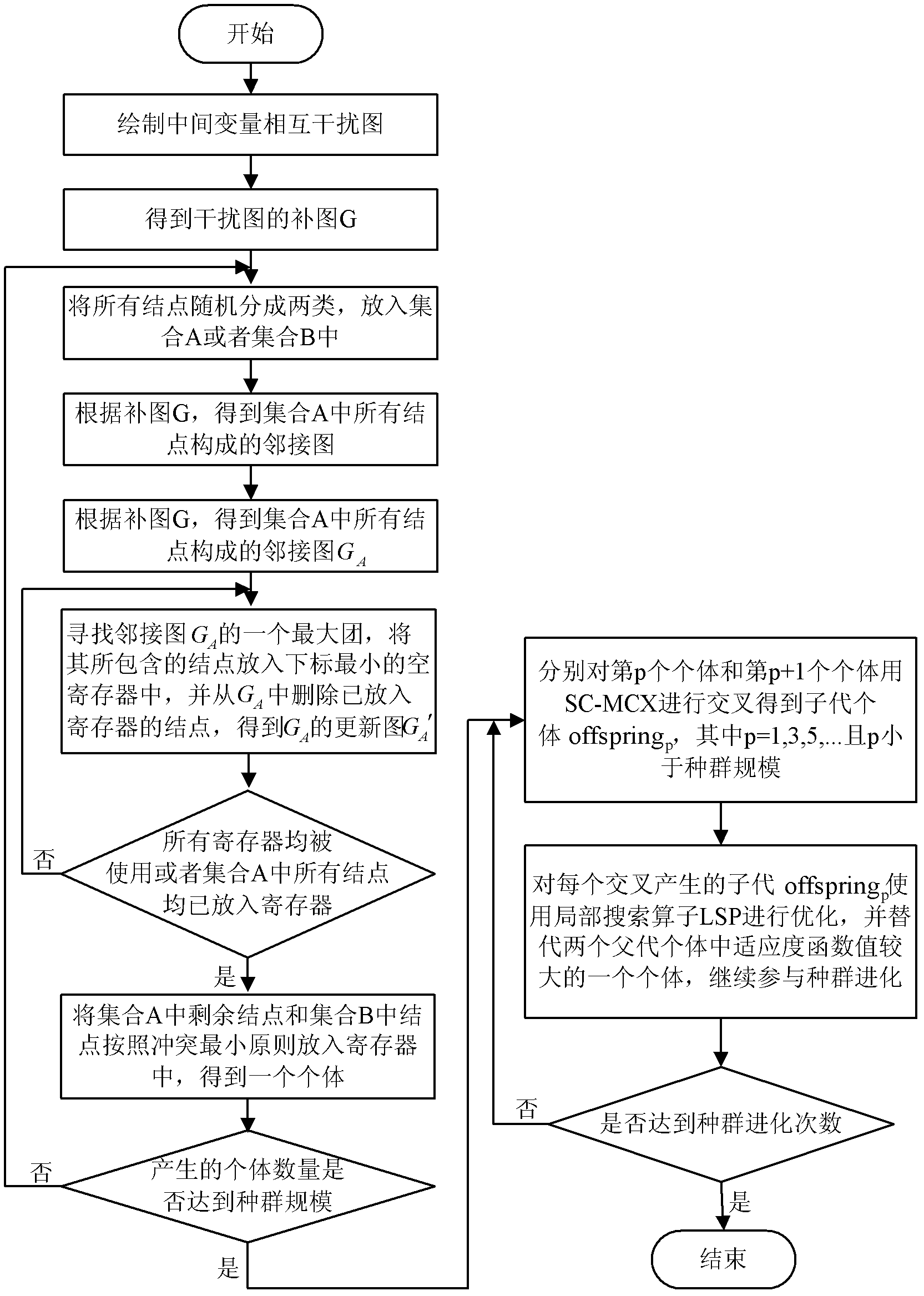
[0035] Refer to attached figure 1, the specific implementation steps of the present invention are described as follows:
[0036] Step 1. Initialize the evolutionary population.
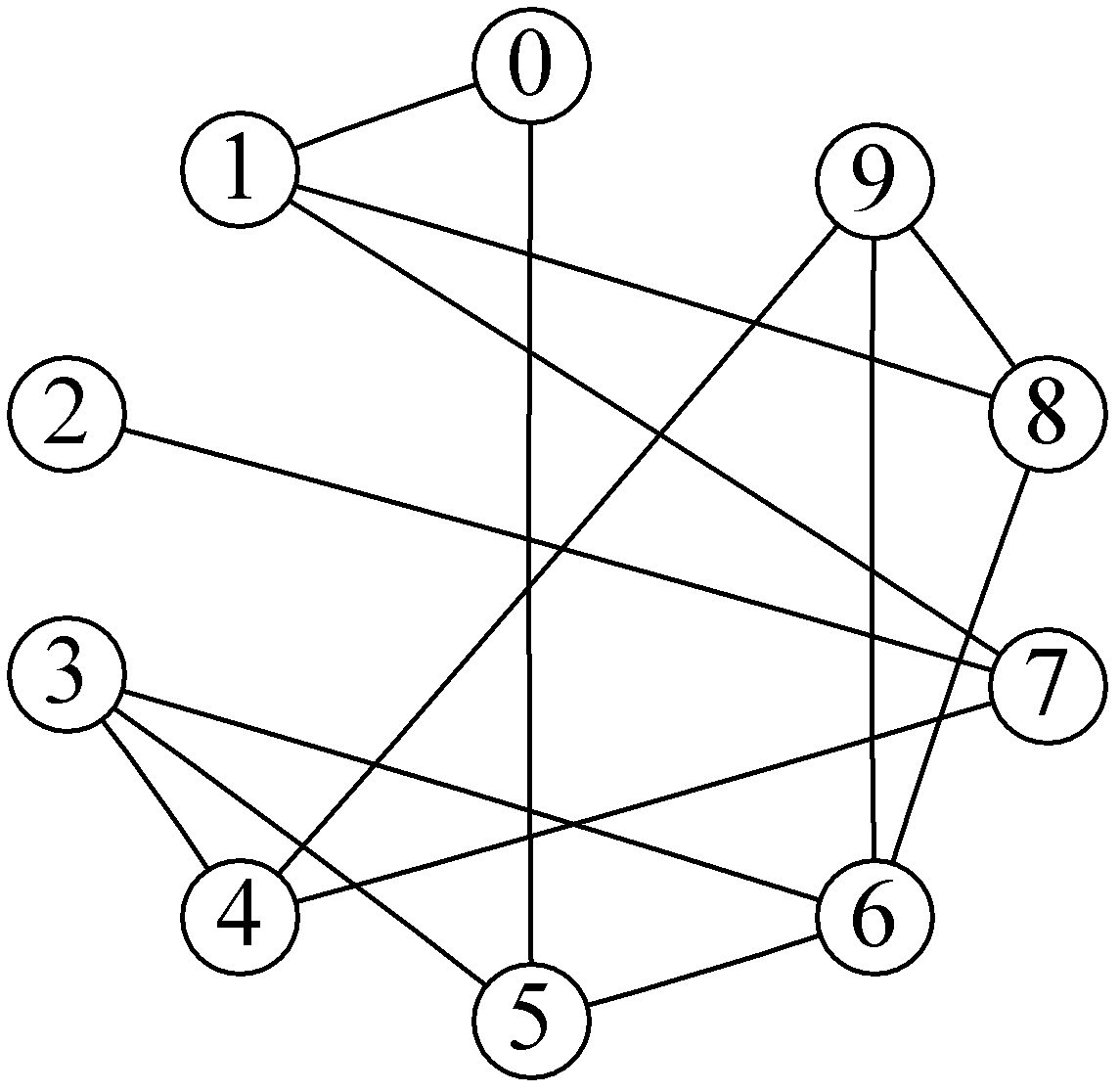
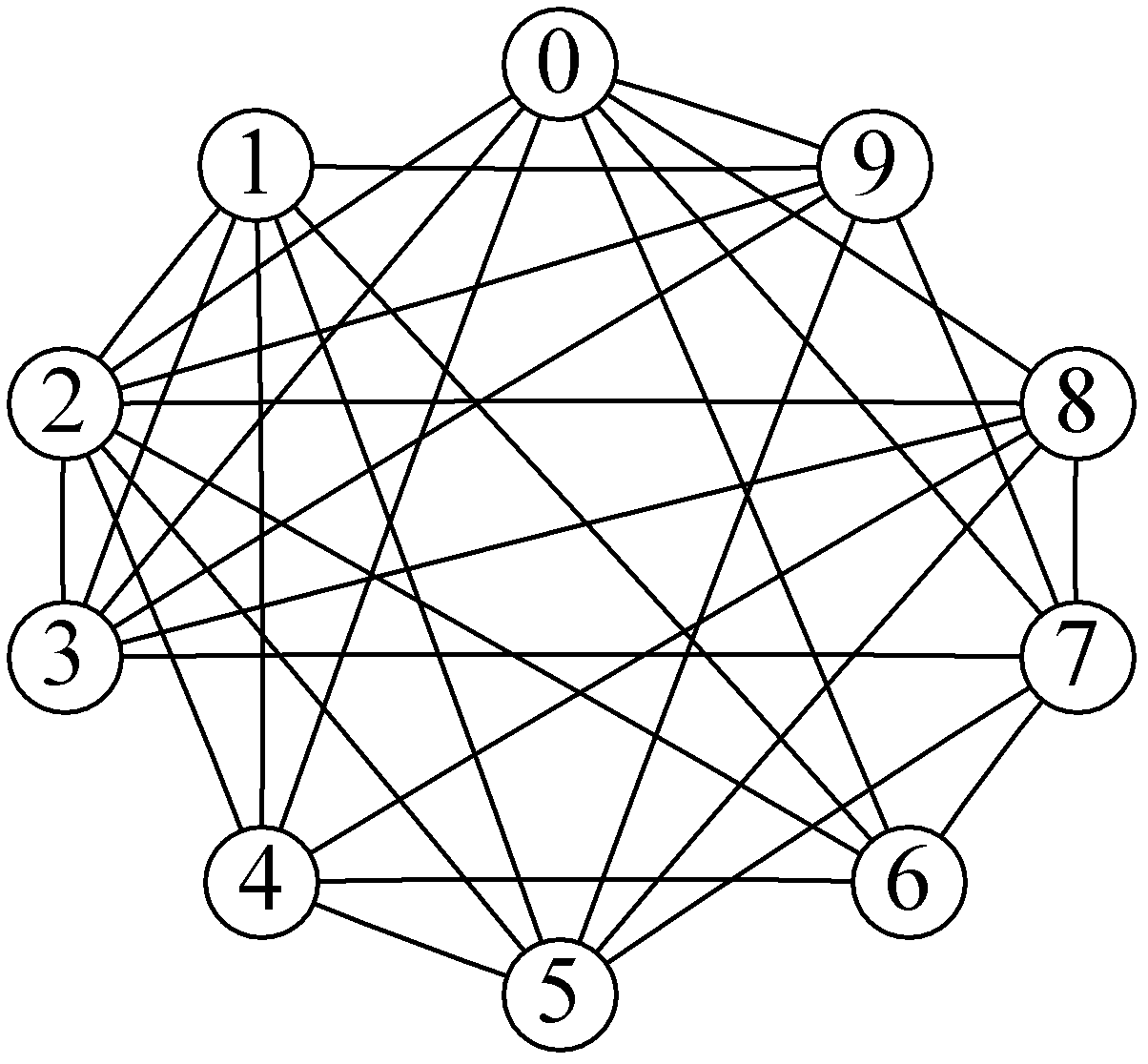
[0037] The mutual interference graph of the intermediate variables in this example is as follows figure 2 As shown, the nodes 0-9 in the figure represent ten intermediate variables, and the intermediate variables represented by the two nodes connected by each edge cannot be placed in the same register. Table 1 shows the overflow cost consumed when the intermediate variable represented by each node is overflowed to the memory. right figure 2 Take the complementary graph of the inter-interference graph of the intermediate variables shown to obtain the complementary graph G, such as image 3 shown. image 3 The intermediate variables represented by any two nodes connected by edges in G can be placed in the same register. Set the number of registers S to 4, and initialize a population individual ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com