Marking method and initialization method for a non-volatile memory array
An initialization method and technology of a memory array, applied in the field of marking and initialization for a non-volatile memory array, can solve the problem that the memory array cannot conform to good products, normally accessible pages or bytes cannot be used, written Action failure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
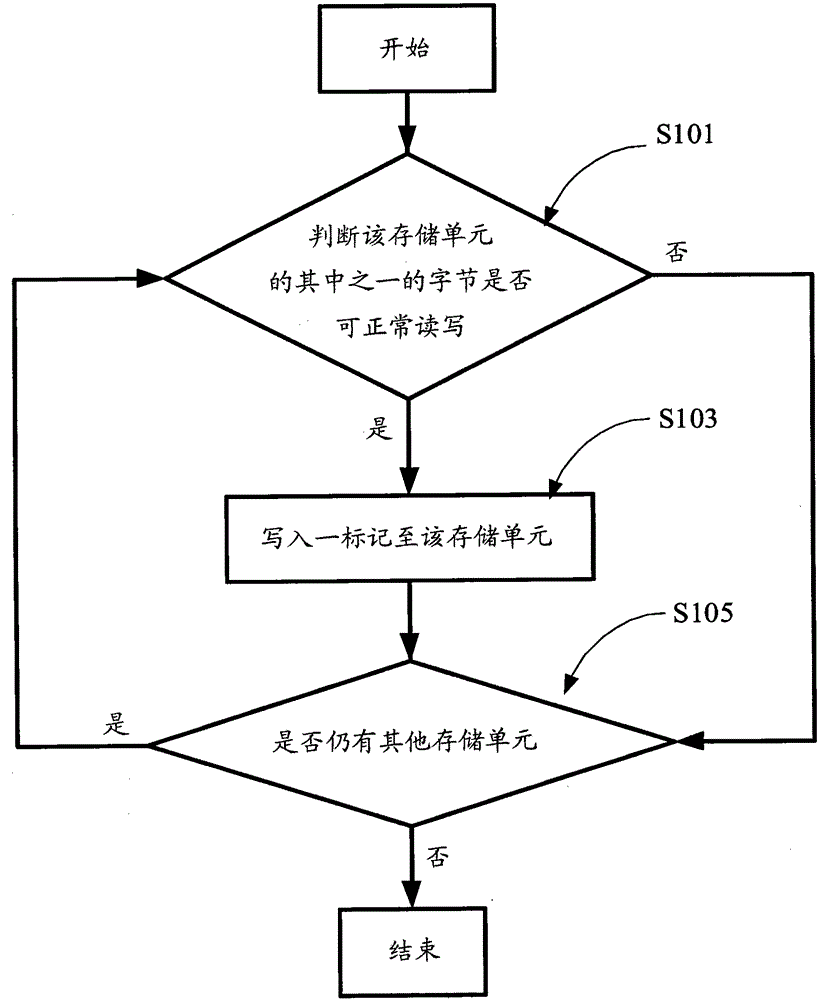
[0033] see figure 1 Shown is a preferred embodiment of the marking method for a non-volatile memory array of the present invention. Wherein, the volatile memory array to which the marking method is applied includes a plurality of storage units (or data writing units), and each storage unit includes a plurality of bytes.
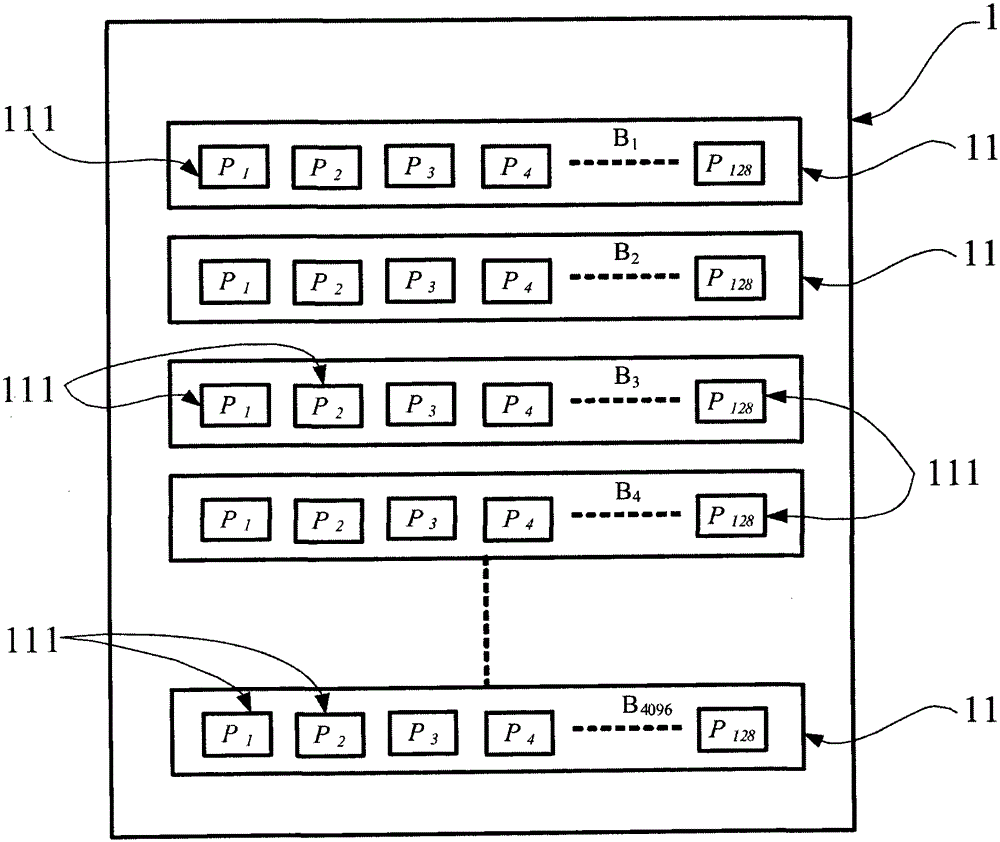
[0034] Please refer to figure 2 As shown, a non-volatile memory array 1 is taken as an example for illustration. The non-volatile memory array 1 includes a plurality of storage units 111, and each storage unit 111 includes a plurality of bytes. For example, each storage unit 111 of this embodiment can be a page (page), each page includes 4224 bytes, and 128 pages (P 1 ~P 128 ) can be combined and defined as a block (block)11, and 4096 blocks (B 1 ~B 4096 ) then further form the non-volatile memory array 1. In other words, the nonvolatile memory array 1 contains 4096×128=524288 storage units 111 (pages) in total.
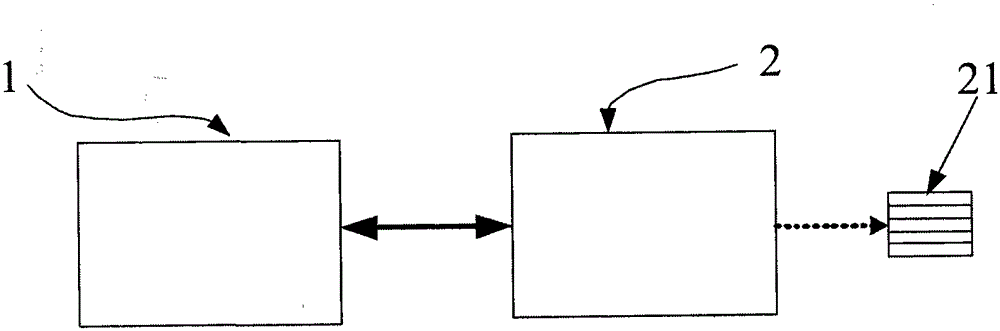
[0035] Please refer to image 3 As ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com