Apparatus and method for correcting at least one bit error within a coded bit sequence
A technique for encoding bit sequences, single-bit errors, applied in the field of devices with at least one single-bit error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
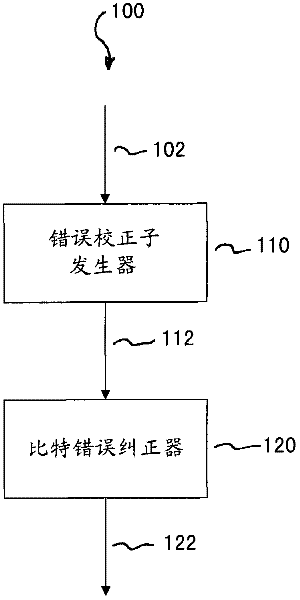
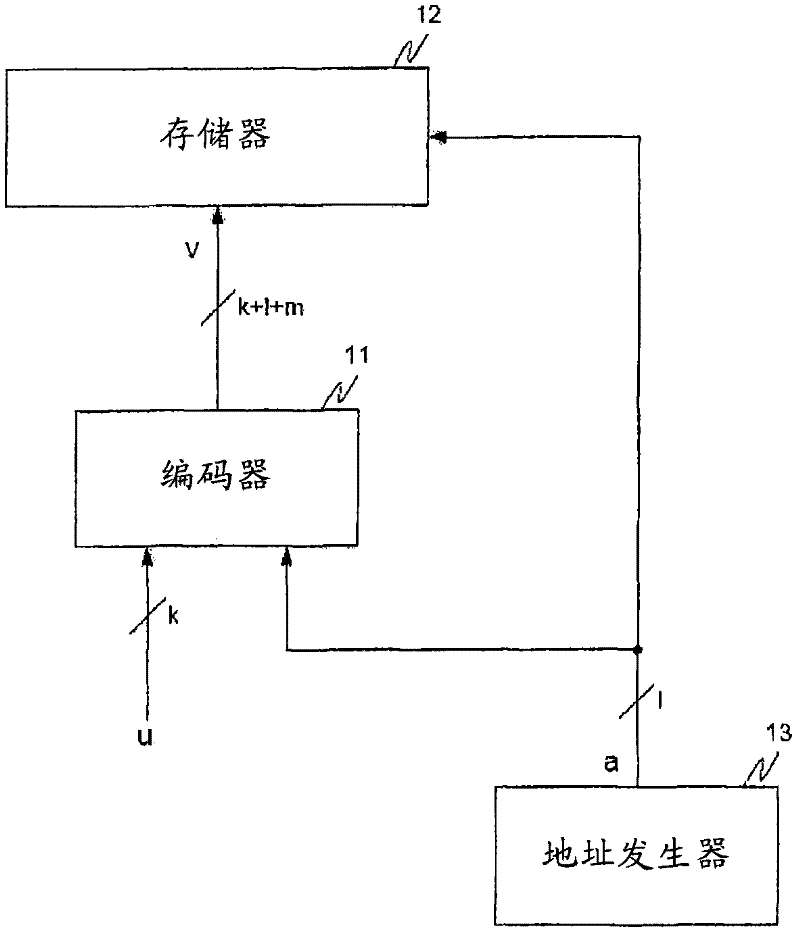
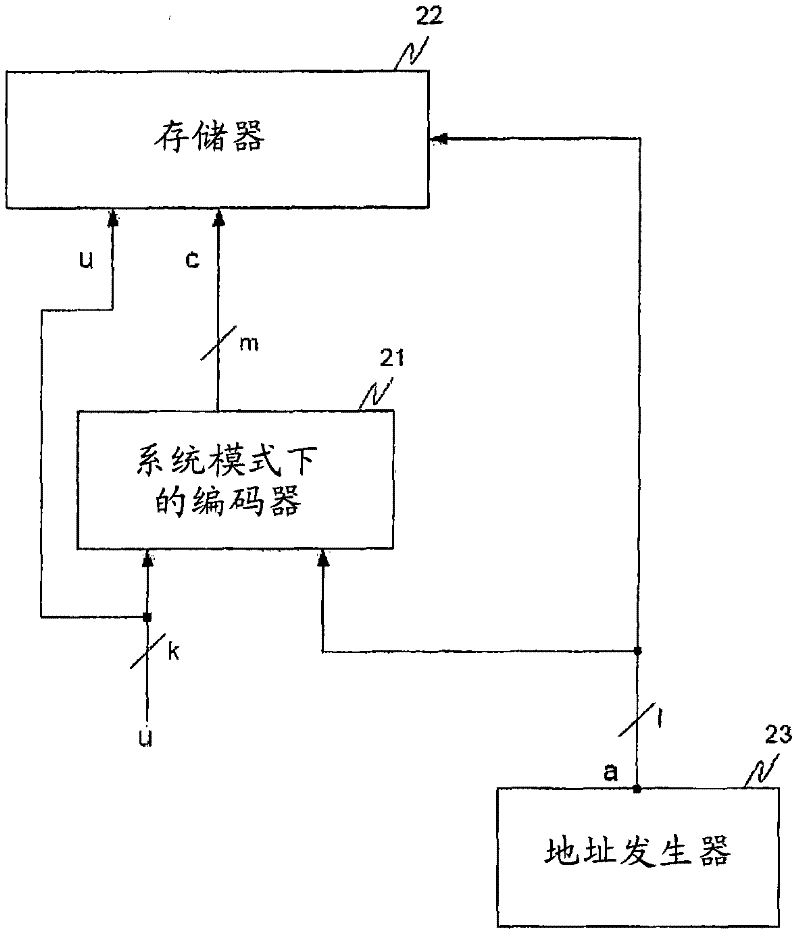
[0024] In the following, the same reference numerals are partly used for objects and functional units with the same or similar functional properties, and their descriptions with respect to the figures will also apply to the other figures in order to reduce redundancy in the description of the embodiments.
[0025] Before describing the proposed principles in more detail, some theoretical basis and basic terminology about linear block codes, especially Hamming codes, Shaw codes and BCH codes, are briefly introduced. These are also, for example, in "Fujiwara, E., Code Design for Dependable Systems, Wiley, 2006, p.49-53, p.98-101" and in "Tzschach, H. and Haflinger, G., Codes für den Datentransfer, Oldenburg Verlag, 1993, p.111-121".
[0026] A Hamming code is a linear block code with a code distance of 3. If m is the number of parity bits, its length is n=2 m -1. The number of data bits is k=2 m -1-m. As any linear code, a Hamming code can generally be described by a gener...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com