Main-mode IKE negotiation method
A main mode, negotiating message technology, applied in the field of network communication, can solve the problem of uncertain ip address, unable to confirm the negotiation key of user identity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
[0023] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the IKE main mode negotiation method according to an embodiment of the present invention; refer to figure 1 , the method includes:
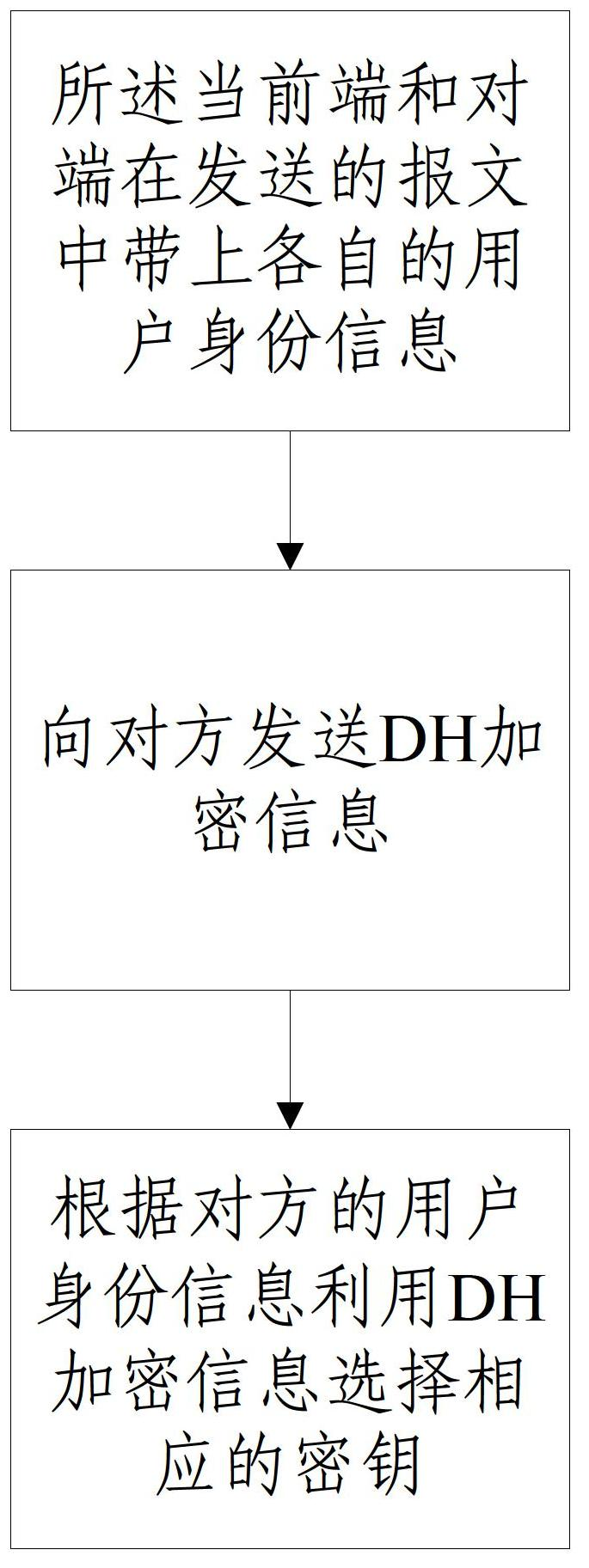
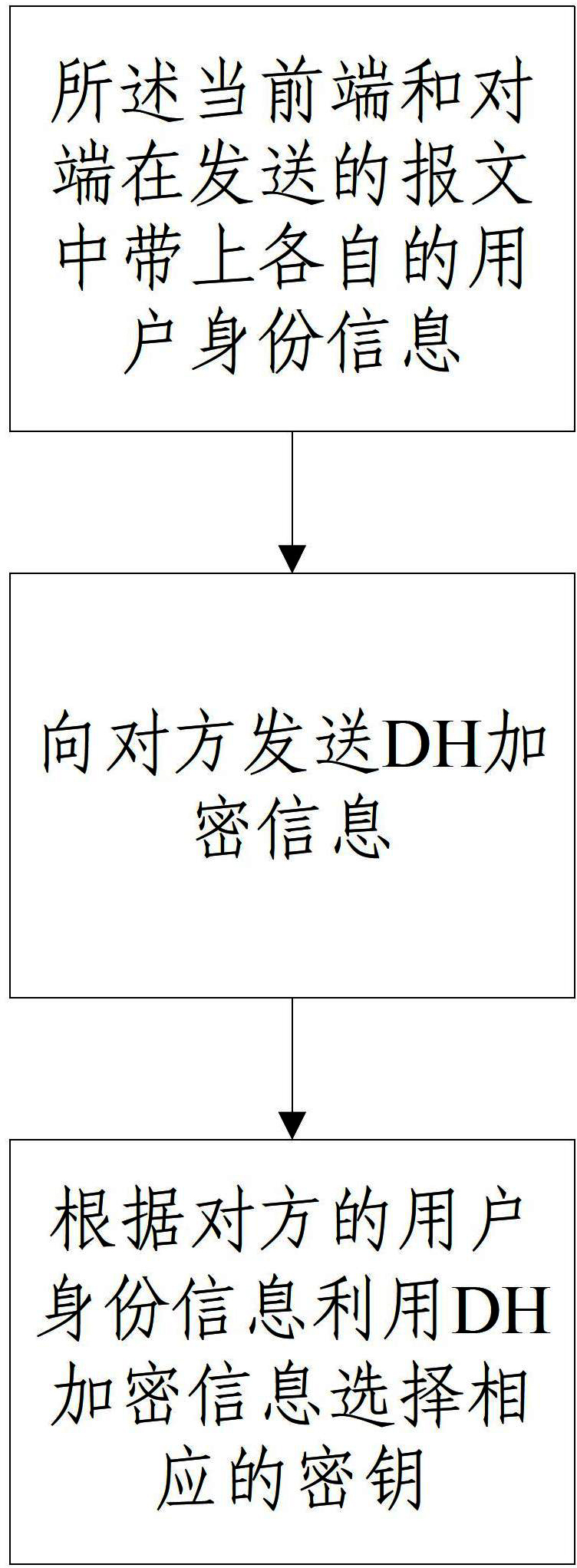
[0024] When the front end initiates the first stage of IKE main mode negotiation to the opposite end, the said current end and the opposite end carry respective user identity information in the message sent during the first interactive negotiation;
[0025] The front end and the opposite end send DH encrypted information to each other during the second interactive negotiation;
[0026] The front end and the opposite end select corresponding keys according to the user identity information of the other p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com