Multiplex amplification for the detection of nucleic acid variations
A pre-amplification, digital amplification technology, applied in the field of digital amplification, can solve problems such as phenotype and cognitive abnormalities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0141] Example 1 - Calculation of Digital PCR Accuracy
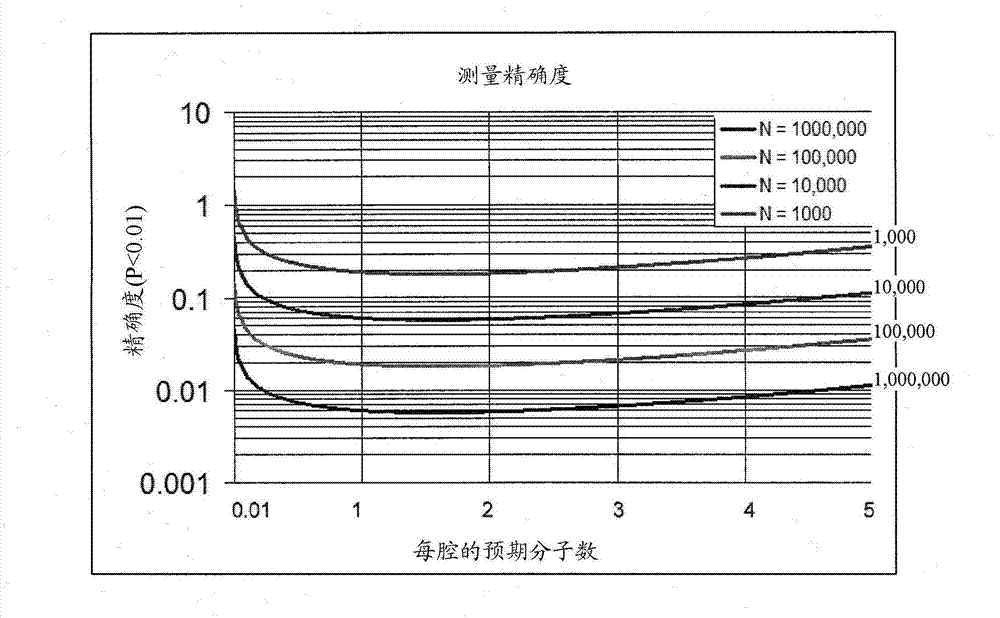
[0142] The theoretical precision of a digital PCR assay depends on the total number of chambers (N) and the expected number of molecules (λ) within each chamber. When Nλ>>1, the number of molecules present in each cavity is a random variable k, which is fully described as an independent Poisson process. The probability of detecting at least one molecule is P(k>0)=1-e -λ . The random variable x describes the number of cavities that have at least one molecule in a column of N cavities. Therefore it can be obtained by having the average N(1-e -λ ) and variable σ 2 =N(e -λ -e -2λ ) gives P(x) from the binomial distribution. For large N, this closely approximates a Gaussian distribution:
[0143] P ( x ) = 1 2 πN ( e ...
Embodiment 2
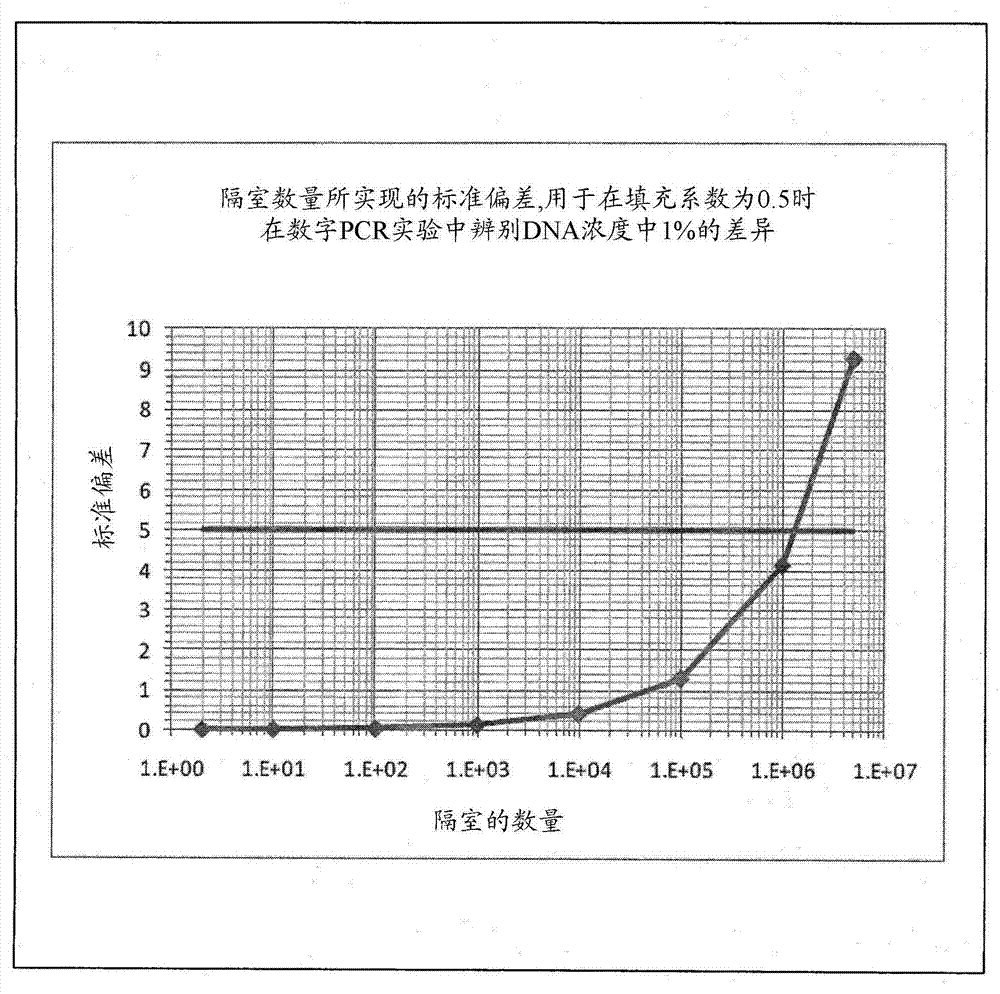
[0150] Example 2 - Calculation of the separation of the measured means of two alleles varying by 1% as a function of the number of discrete subsamples (e.g. cavities) using digital PCR
[0151] figure 2 Numerical calculations of the separation of measured means for two alleles varying by 1% as a function of cavity number using digital PCR are shown. Differences were normalized by the expected standard deviation (σ) determined by the combined effect of 5 random Poisson variables (curves). Calculate the template concentration corresponding to positive amplification in 50% of the wells. A 5σ separation (horizontal line) is achieved at about 1000000 cavities. Standard deviations were achieved with the number of compartments that could discern a 1% difference in DNA concentration at a fill factor of 0.5 in a digital PCR experiment.
Embodiment 3
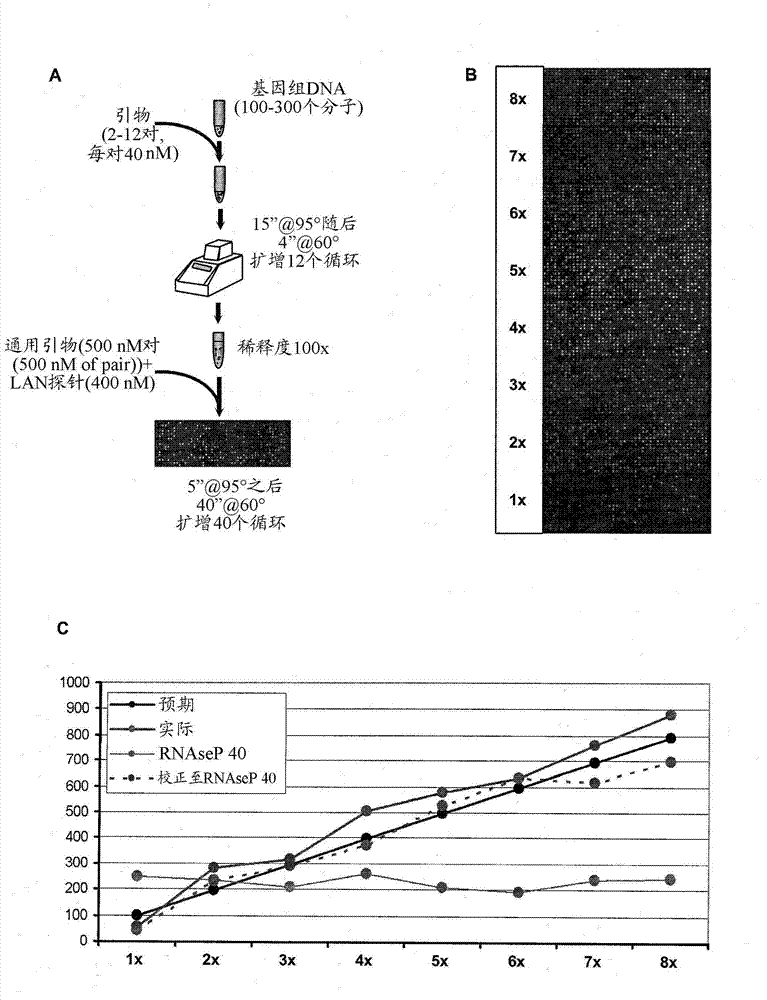
[0152] Example 3 - Theoretical Calculation of Sample Molecular Content and Blood Sample Volume
[0153] The presence of fetal DNA in maternal blood has been reported to represent approximately 2-6% of the total DNA present in cell-free serum during the first trimester (Lo et al. 1997; Lo et al. 1998; Wachtel et al. 2001; Lee et al. 2002). However, later publications showed that the fetal contribution was 9.7%, 9.0%, and 20.4% in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively (Lun et al. 2008). For example, each genome copy of the T21 segment contributes an additional copy of chromosome 21, which allows direct non-invasive maternal blood testing by measuring the ratio of chromosome copy numbers present in maternal serum. If one assumes 2% fetal DNA fraction in a maternal blood sample, the expected abundance of chromosome 21 relative to the other chromosomes in the pool is (0.02x 1) / (1x 2)=1%. Such a small difference in relative concentration is difficult to detect by t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com